Sampling, DFT, FFT
advertisement
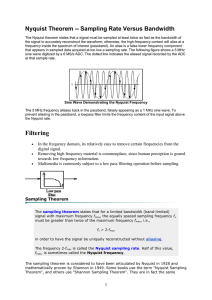
Life in the frequency domain Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier (1768-1830) Spectrogram, Northern Cardinal Sampling frequency in radians / sec f frequency in cycles / sec T period 1 / f 2 / sec/ cycle Sampling if Ts sampling interval, Ts T / 2, or fs 2 f ( Nyquist theorem ) Example: CD rate f = 44,100 Hz, so the highest frequency that can be represented is 22,050 Hz Called Nyquist frequency = ½ cycle/sample = f/2 Hz Sampling and aliasing Aliasing a sine wave: • One frequency can masquerade as another • When viewed as a strobed phasor, it’s easy to see that we need to sample at least twice each period to capture the frequency unambiguously • Nyquist’s theorem: Highest allowed signal frequency is half the sampling frequency = Nyquist frequency Aliasing strikes! • Prefiltering: avoids aliasing on A-to-D • Oversampling: can substitute cheap digital filtering for expensive analog filtering for A-to-D or D-to-A conversion The DFT and FFT Think of the n samples of the signal as n points on a circle And also think of n frequency points as n points on the circle The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) N 1 1 i k t xt X k e , N k 0 N 1 X k xt e i k t , t 0,..., N 1 k 0,..., N 1 representation transform t 0 k k 2 N , k 0,..., N 1 Frequencies on circle Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777-1855) Heideman, Johnson, Burrus (1985) The FFT Divide-and-conquer algorithm for DFT T ( N ) 2T ( N / 2) cN Yields O(N log N) algorithm FFT Butterfly A once-a-minute application: JPEG Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) Steven W. Smith's Book (1997)