PROBLEM SET - 3 Multiple Choice Questions
Izmir University of Economics
Department of Economics
Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics
PROBLEM SET - 3
Multiple Choice Questions
1.
A price ceiling is a. a minimum price set by government that sellers must charge for a good.B b. a maximum price set by government that sellers may charge for a good. c. the difference between the initial equilibrium price and the equilibrium price after a decrease in supply. d. the minimum price that consumers are willing to pay for a good.
2.
A price floor is a. a government set minimum price that sellers may charge for a good. b. a government set maximum price that sellers may charge for a good. c. the difference between the initial equilibrium price and the equilibrium price after a decrease in supply. d. the minimum price that buyers are able and willing to pay for a good.
3.
Assume the market equilibrium price of rice is $5.00 per pound. If the government does not allow rice farmers to charge more than $1.00 per pound of rice, a.
there will be a rice surplus. b.
there will be a rice shortage. c.
quantity demanded will equal quantity supplied. d.
the market equilibrium price will move from $5.00 to $1.00.
4.
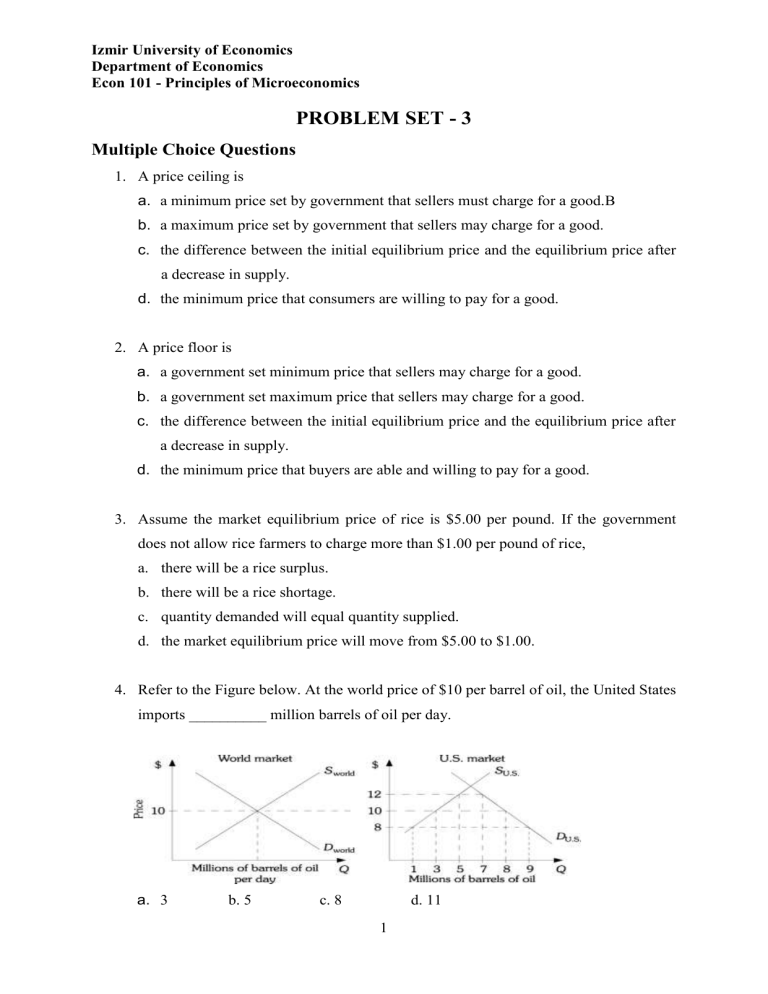
Refer to the Figure below. At the world price of $10 per barrel of oil, the United States imports __________ million barrels of oil per day. a. 3 b. 5 c. 8
1 d. 11
Izmir University of Economics
Department of Economics
Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics
5.
The difference between the maximum amount a person is willing to pay for a good and its current market price is known as a. producer surplus. b. profits. c. revealed preferences. d. consumer surplus.
6.
You would be willing to pay a maximum of $50 to attend a concert, and you can buy a ticket for $30. Your consumer surplus is a. $10 b. $20 c. $30 d. $50
7.
The difference between the minimum amount a firm is willing to accept for a good and its current market price is known as a. the paradox of value. b. profits. c. producer surplus. d. consumer surplus.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 1 below to answer the questions that follow.
Figure 1
2
Izmir University of Economics
Department of Economics
Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics
8.
Refer to Figure 4.5. Which of the following areas represents consumer surplus? a. A b. B c. C d. E
9.
Refer to Figure 4.5. Which of the following areas represents producer surplus? a. A b. B c. C d. E
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2 below to answer the questions that follow.
Figure 2
10.
Refer to Figure 2. Which areas amount to a deadweight loss? a. Areas B+E b. Areas C+D c. Areas A+B d. Areas E+F
11.
Refer to Figure 2. Which price maximizes the sum of consumer and producer surplus? a. 1.50 b. 2.50 c. 3.70 d. Any price greater than 3.75
3
Izmir University of Economics
Department of Economics
Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics
Essay Questions
1.
Explain how the price system eliminates a shortage and a surplus.
2.
List and briefly define some types of non-price rationing systems.
4






