Electric Fields & Forces Example Problems
advertisement

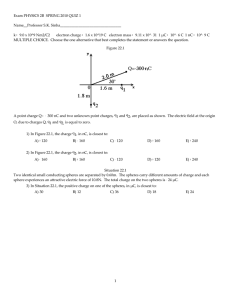
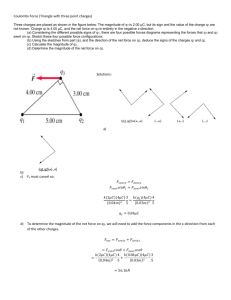
Chapter 18: Electric Fields & Forces Example Problems e 1.6 1019 C Fnet K 8.99 109 N m2 /C2 FE Kq1q2 r2 qE F F2 F2 net x y (Fx ,Fy ) 1 tan (Fy /Fx ) Example 18.1 Two identical metal spheres A and B are connected by a metal rod. Both are initially neutral. 1.0 × 1012 electrons are added to sphere A, then the connecting rod is removed. Afterward, what is the charge of A and the charge of B? Example 18.2 a. Two small plastic spheres each have a mass of 2.0 g and a charge of −50.0 nC. They are placed 2.0 cm apart. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric force between the spheres? b. A small plastic sphere with a charge of −5.0 nC is near another small plastic sphere with a charge of −12 nC. If the spheres repel one another with a force of magnitude 8.2 × 10-4N, what is the distance between the spheres? Example 18.3 The drawings show three charges that have the same magnitude but may have different signs. In all cases the distance d between the charges is the same. The magnitude of the charges is |q| = 8.6 μC, and the distance between them is d = 3.8 mm. Determine the magnitude & direction of the net force on charge 2 for each of the three drawings. Example 18.4 a. A +10 nC charge is located at the origin. (i) Draw the field diagram showing the Efield vectors at these positions (cm): (x, y) = (5.0, 0), (−5.0, 5.0) and (−5.0, −5.0). (ii) What are the strengths of the E-fields at the positions? b. A −10 nC charge is located at the origin. (i) Draw the field diagram showing the Efield vectors at these positions (cm): (x, y) = (0, 5.0), (−5.0, 5.0) and (−5.0, −5.0). (ii) What are the strengths of the E-fields at the positions?