Trinty_College_SS_3A6_Report_Group3.doc
advertisement

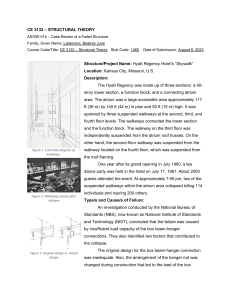
Trinity College SS 3A6 Report Hyatt Regency Walkway Collapse Date of Submission: 24th October 2008 Group 3. John Norris Simon Jones Jonathan Clarke Brían Cooney LECTURER: Dermot O’Dwyer An Introduction The Hyatt Regency walkway collapse was a major structural disaster that happened in July 17th 1981, in Kansas City, United States of America. In 1980 a new 40storey hotel with a tower and conference facilities, which were connected by a huge open concept atrium (4 storeys high) was built. The atrium featured a multistory atrium criss-crossed by suspended concrete walkways on the second, third, and fourth levels, with the fourth level walkway directly above the second level walkway. The third floor walkway was set off to the side several meters away from the other two and was not affected as you can see in the photograph below. Thousands of people had gathered in the atrium to participate in, and watch a dance contest. That night the 3 walkways were packed with visitors as they watched over the active lobby which was the dance floor. At 7:05 p.m., a loud crack was heard as the second and fourth floor walkways came crashing down to the ground level. A massive loss of life was incurred which totalled to 114 deaths and 200+ injuries. Construction Type Construction issues led to a subtle but flawed design change that doubled the load on the box-beam connection between the fourth floor walkway and the tie rods carrying the weight of the second floor walkway. The new design could barely handle the dead load weight of the structure itself; with the imposed load of all the spectators on added to that that it hadn’t a chance. The Design The original design by Jack D. Gillum and Associates called for three pairs of rods running from the second floor cross-beams directly all the way to the ceiling. Investigators eventually determined that this design could only support 60% of the minimum load required by Kansas City building codes. The contractor responsible for manufacturing the rods, Havens Steel Company, objected to the original plan, since it required the whole of the rod below the fourth floor to be threaded, and threaded through the box-beam in order to screw on the nuts to hold the fourth floor walkway in place. Havens’ new design was to tie directly the floor 2 walkway to the floor 4 walkway. This resulted in putting extra pressures on the supporting beam holding the floor 4 walkway to the ceiling. New Design Failure of the supporting washer Extent of Damage Here is a photograph of the extent of damage to the walkways which fell to the ground floor. The design failed because of the addition of an extra supporting rod. The extra rod increased the load on the fourth floor nut from 90 kN to 181 kN. The box beams were longitudinally welded as had originally proposed. Because of this they could not hold the weight of the two walkways. During the collapse, the box beam split and the support rods pulled through them. As shown in the photograph below. Conclusions The Missouri Board of Architects, Professional Engineers, and Land Surveyors convicted the engineers employed by Jack D. Gillum and Associates who had signed off on the final drawings of gross negligence, misconduct, and unprofessional conduct in the practice of engineering; all the members involved lost their engineering licenses in the states of Missouri and Texas and their membership to ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers). While Jack D. Gillum and Associates itself was cleared of criminal negligence, it was stripped of its license to be an engineering firm.Law suits followed and at least $140 million was awarded to victims and their families in both judgments and settlements. a large amount of this money came from Crown Center Corporation. An engineer has a responsibility to the public to ensure that they take all reasonable steps to ensure their design is sound. In the case of the Hyatt Regency walkway collapse the engineers did not undertake a sufficient review of the new design to the rod/box beam connection and this led to a large loss of life. As a result engineers became fully responsible for design projects in the US. The engineer must remember how important it is to review thoroughly all design modifications during the construction phase of any project. Disasters such as these are a reminder of how an error in judgement can or negligence can lead to such a large loss of life. Information gathered from: http://ethics.tamu.edu/ethics/hyatt/hyatt2.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyatt_Regency_walkway_collapse