Fall 2015 Colonial Era Part I. 1607-1700. (1)(1).ppt
advertisement

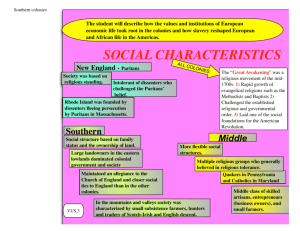
The Colonial Period: 1607-1750s Characteristics of English North America England: Prior to Expansion into North America • Key Turning Points • The Reformation divides Europe • The Reformation changes Europe • Economic changes in England The Puritans and Separatists- The Debate Christian Access to God •Catholic & conservative Protestants: Traditions of Church •Puritans: Corruption of Church for centuries Goals of the Puritans- 1630 Boston- to purify the Church •Broke with traditions •Individual congregation- began with covenant, election of ministers •Conduct represented salvation •Knowledge of redemption Goals of the Separatists (Pilgrims, 1620 Plymouth Colony) •Questioned legitimacy of Church of England •Paul: “Come out among them and be separate.” Economic Model of Colonies: Mercantilism, Corporations, Capitalism • • • • Mercantilism Merchants: relationship with King Chartered Companies: Corporations Corporate Colonies: Ventures in Capitalism By 1732: Three distinct colonial governments • Royal • Proprietary • Corporate Slow to Enter the “New World”… Early Explorations: • Queen Elizabeth • 1576 Martin Frobisher (3 ships) Beginnings: 1607- (after Spanish and French) Reasons for English Colonization • Establish markets for their goods- wool • Access to raw materials • Growing rivalry with Spain (Privateers) • Social Crisis- economic needs/population influx • Religious: Spreading Protestantism • Economic inequality- Masterless men English Explorations and the First Settlement Early Attempts •Gilbert and Raleigh- Elizabeth I/ charter – Two attempts that failed – Half-brother- named the land Virginia •Roanoke- Failure – First voyage 1585 – Second voyage in 1587 – Governor White: war in England – Empty houses and the letters “CRO” The Coming of the English English Emigrants • Lower ranks of society • 1600s- indentured servants Land and Liberty • Basis for liberty- control of land and vote The Indigenous • English wanted land • Resentment towards English • Alcohol: common and disruptive • Landscape changes: fencing, new crops, livestock, depletion of forest Settling the Chesapeake: Jamestown and Maryland Founding of Jamestown 1607 •Virginia Company •Early Troubles – The “Starving Time,” 1609-1610 •Finding new “settlers.” • Uprising of 1622 •Tobacco: Cross-breed strains • King James and the “evil weed.” Founding of Maryland 1632 •Proprietary colony of Cecilius Calvert (feudal domain) •Refuge for persecuted Catholics The New England Way The Rise of Puritanism • Shaped early New England • Congregationalists Moral Liberty • John Winthrop • Rejection of natural liberty for moral liberty The Pilgrims at Plymouth • 1620-private investors Netherlands • The Mayflower- Cape Cod • The Mayflower Compact – No women signed document The Great Migration • 1629 Massachusetts Bay Company (London Merchants) • 1642 21,000 Puritans New England Divided Dissenters in the Puritan World • Roger Williams (Rhode Island) • Puritans and the Indigenous • The Pequot War Economic and Social Inequality • The New England economy • The Merchant Elite • The Half-Way Covenant The 13 Colonies New England: Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Hampshire Southern Colonies- Virginia, Maryland, North and South Carolina, Georgia Middle Colonies- New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Delaware Distinctions of Southern Colonies Governance: Corporate, Royal, Proprietary • Plantation Elite Economy: Single crop economics • Tobacco & Rice Social Structure •Stratified. English Law •Plantations •Biracial society- Black and White •English traditions: viewpoints about politics, religion, economy Indigenous Communities •Bacon’s Rebellion- Several Causes •Scapegoat: Indigenous Religion • Anglican- minor role in politics and economy* Distinctions of the New England Colonies Governance: Early years/ under control of Crown/ Central & Local Gov. • Religious leaders through small town meetings Economy: Family-run farms and household manufacturing • Craftsmen and Merchants Social System: Clustered settlements • Indentured Servants • Cultural traditions: Diverse culture, economic, political, social Religion: •Strictly Calvinist faith- dictated political, social, economic Indigenous Societies: Europeans used concept of “divide and rule” Pequot War and Metacomet’s War •1676 Distinctions of the Middle Colonies Governance: Diverse settlement • Unchartered- Delaware • Democratic: Pennsylvania • Small town governments Economy: Dutch-strong commercial economy- Hudson River Valley Social System: Multicultural • Small towns encouraged country governments • Separatist ideologies Religion: • Religious tolerance Indigenous Societies: Iroquois League (1451) Women in the Colonial Era Western Christianity and the Proper Place of Women • Original sin of Eve= untrustworthy • Proper place for women • Paul- “Women should keep silence in the churches.” • Patriarchal hierarchical family= basic unit of English society Gendered English Law: •No vote or participate in politics •“English law made to fit”- standards of acceptable behavior in colonies •Feme Sole: single women •Feme Covert: “taking the identity of husband” John Winthrop and the “True Wife” VS. Brabbling Women •Subjection to religious and familial authority •Outspoken in public Anne Hutchinson & the charges of heresy •Questioned teachings, Claimed direct revelations •Banished 1638 Witches and Witch Hunts •Reflection of societal stresses •Salem, Massachusetts 1691-1692