s04qz1an.doc
advertisement
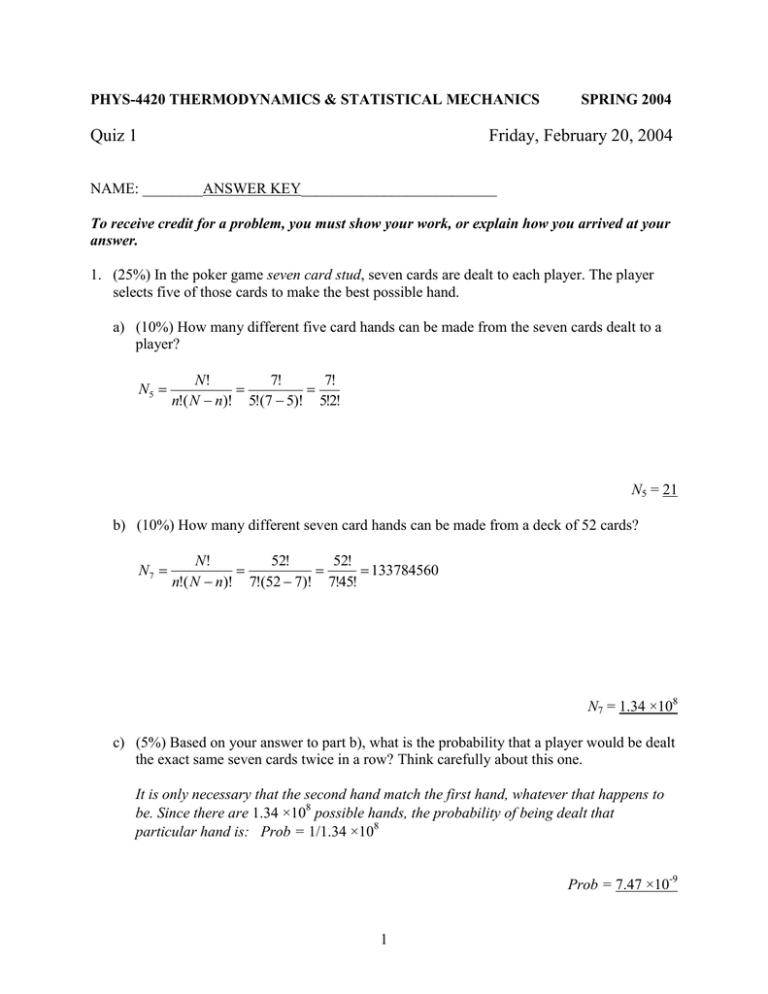
PHYS-4420 THERMODYNAMICS & STATISTICAL MECHANICS Quiz 1 SPRING 2004 Friday, February 20, 2004 NAME: ________ANSWER KEY__________________________ To receive credit for a problem, you must show your work, or explain how you arrived at your answer. 1. (25%) In the poker game seven card stud, seven cards are dealt to each player. The player selects five of those cards to make the best possible hand. a) (10%) How many different five card hands can be made from the seven cards dealt to a player? N5 N! 7! 7! n!( N n)! 5!(7 5)! 5!2! N5 = 21 b) (10%) How many different seven card hands can be made from a deck of 52 cards? N7 N! 52! 52! 133784560 n!( N n)! 7!(52 7)! 7!45! N7 = 1.34 ×108 c) (5%) Based on your answer to part b), what is the probability that a player would be dealt the exact same seven cards twice in a row? Think carefully about this one. It is only necessary that the second hand match the first hand, whatever that happens to be. Since there are 1.34 ×108 possible hands, the probability of being dealt that particular hand is: Prob = 1/1.34 ×108 Prob = 7.47 ×10-9 1 2. (10%) Consider the expression, aeax cos( y 2 )dx 2 yeax sin( y 2 )dy . Is it an exact differential? Circle the correct answer, and show why you made your selection. It IS an exact differential It IS NOT an exact differential [ae ax cos( y 2 )] must equal [2 ye ax sin( y 2 )] y x [2 ye ax sin( y 2 )] 2 yae ax sin( y 2 ) [ae ax cos( y 2 )] 2 yae ax sin( y 2 ) x y For an exact differential, These are not equal. 3. (35%) Electromagnetic radiation in an evacuated vessel of volume V, at thermal equilibrium with the walls at temperature T, behaves like a gas of photons. The internal energy and the pressure of the gas are given by the relations: E aV T 4 , and p 13 aT 4 , where a is Stephan’s constant. Initially the system is at pressure p0, volume V0 , and temperature T0. Express all your answers in terms of p0, V0, T0, and a. a) (10%) How much heat is added to the system if it expands isothermally from V0 to 2V0? Q = W + E Since T is constant, p is constant, so W = p0V. Also, E = aT0 4V. p 13 aT 4 , so aT 4 = 3p, and E = 3p0V. Then, Q = p0V + 3p0V = 4p0 (2V0 – V0) Q = 4p0V0 = 43 aT04V0 b) (5%) What is the change in entropy as the gas expands isothermally from V0 to 2V0? S Q 4 p0V0 T T0 S = 2 4 p0V0 4 3 3 aT0 V0 T0 c) (10%) How much heat must be added to the gas if the pressure is to increase from p0 to 2 p0 at a constant volume of V0? Q = W + E Since V is constant, W = 0, and Q = E. E aV T 4 3 pV , and E = 3V0 p = 3V0(2p0 – p0) Q = 3p0V0 = aT04V0 d) (10%) How much heat must be added to the gas if the temperature is to increase from T0 to 2 T0 at a constant volume of V0? Again, V is constant, so W = 0, and Q = E = a V0[(2T0) 4 – T04)] = a V0T04[16 – 1] Q = 15 a V0T04 = 45 p0V0 3 4. (30%) Consider two systems, A and B. System A contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas at a temperature of 480 K. System B contains two moles of the same monatomic ideal gas at a temperature of 240 K. a) (10%) Find the internal energies of the two systems. EA 32 N AkTA 32 RTA 32 (8.31 J/mole)( 480 K) EB 32 2 N AkTB 3RTA 3(8.31 J/mole)( 240 K) EA = 5980 J EB = 5980 J b) (10%) The two systems are placed in thermal contact, and heat flows between them. As a result, one third (1/3) of the energy in system A is transferred to system B. Show that this transfer results in an increase in the combined entropy of the two systems. 3NA 3NA S S A S B S A, f S A,i S B, f S B,i k ln( EA,2f ) k ln( EA,2i ) k ln( EB3 N, f ) k ln( EB3 N,i ) A 3NA 3NA E 2 E 3N Ak E A, f S k ln A, f k ln B , f ln 2 E A, i EB , i E A, i 3R 32 S ln 0 (S = 0.255R = 2.12 J/K) 2 27 EB , f E B,i A 2 2 3N Ak ln 2 4 2 3 3 c) (10%) Show that the total entropy of the two systems is a maximum after the transfer of energy from system A to system B. Mathematical solution: S 0 For a maximum, E A 3NA 2 A 3N Ak [ln( E A ) 2 ln( EB )] 2 3R [ln( E A ) 2 ln( E E A )] EA + EB = E, so EB = E – EA. Then, S 2 3R 2 3R 1 0 [ln( E A ) 2 ln( E E A )] E A 2 2 EA E EA S S A S B k ln( E 2EA E EA , or E A ) k ln( EB3 N ) A E 2E , and E B ; i.e. EB = 2EA which is the state of the system. 3 3 4 Or: S ( S A S B ) S A S B S A S B 0 E A E A E A E A E A EB 3N 2 S ln( E ) ln( EB3 N A k E E A EB A A A 3 N ln( E A ) ) ln( EB ) k A 3N A 2 E A EB 1 1 3N Ak 0 2 E A EB EB = 2EA which is the state of the system. Physical solution: When the system comes to equilibrium, the entropy will be a maximum, and the temperatures of A and B will be the same. Calculate the temperatures of A and B. 2 5980 J 4 5980 J 2 2EA EA 3 3 = 320 K = 320 K TA TB 3R 3(8.31 J/K) 3R 3(8.31 J/K) Entropy is a maximum. 5






