Homeostasis: NERVOUS
advertisement
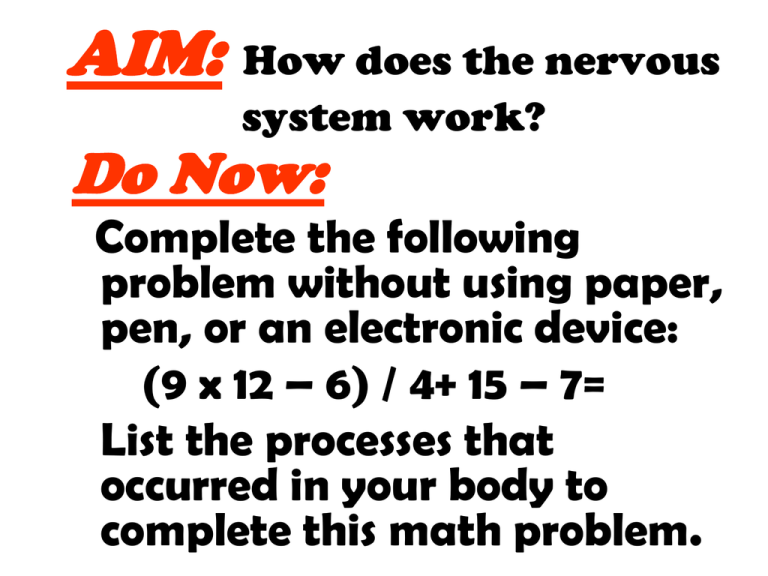
AIM: How does the nervous system work? Do Now: Complete the following problem without using paper, pen, or an electronic device: (9 x 12 – 6) / 4+ 15 – 7= List the processes that occurred in your body to complete this math problem. How is the nervous system used to maintain homeostasis in the human body? Regulates the homeostasis of many body systems. The stable internal balance of an organism that ensures survival The process in which an organism controls and coordinates all its activities THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I. Nerve Cells II. Brain III. Central NS IV. Peripheral NS Consists of Consists of: (connected to the spinal cord) (connected to the brain) •The control center •Protected by the skull •Made up of approx. 1 trillion neurons •Divided into two hemispheres Right Left Each hemisphere controls the opposite part of the body. The brain is Ex. The Left hemisphere controls that right side of divided into two equal hemispheres the body A look inside!!!! The brain consists of three major parts: The largest part of the brain Located on both the right and left hemisphere The center for thought, memory, learning, senses and voluntary movements. Located below and behind the cerebrum Coordinates all motor activities Maintains the body’s balance Located at the base of the brain and spinal cord Controls involuntary actions Such activities include Heart rate ______________ Breathing rate ______________ Peristalsis ______________ •A cluster of nerves that run along the back •Protected by the Vertebrae (backbon ______________ Imagine you’ve stepped off a curb and a car doing 70 mph, comes out of nowhere. Identify 2 human body systems at work to help you respond to this stimuli. How do they interact with one another to help you maintain homeostasis??? Specialized structures that are sensitive to stimuli physical or chemical changes within or outside an organism Specialized structure that responds to commands of the nervous system Ex. Muscles, Glands, Organs How do we relay the messages throughout our bodies to produce an action? Bundles of related nerve cells, called neurons that are contained in nerve fibers Structural unit of the brain and nervous system which conduct information and carry messages throughout an organism. 3 Types of Neurons 1. Sensory Neurons: • Found in receptors (sense organs) • Receive stimulus • Send impulses from receptors to the spinal cord and brain. 2. Inter-Neurons: •Found in the spinal cord & brain. •Receive impulses from sensory neurons •Interpret “process” stimulus •Send impulses to the motor neurons 3. Motor Neurons: •Receives the impulses from the inter-neuron, •Sends response impulse to the effectors. Which type of nerve carries a pain stimulus to the brain? Sensory nerve Sequence of events starting from the stimulus until there is a response. tester R E E L E X A R C transmit electrochemical messages called impulses throughout the nerve body. PARTS OF A NEURON cell body (c y t o n) containing the nucleus Dendrites: Branched structures that RECEIVE THE IMPULSE from the neighboring neuron A x o n/ (nerve fiber) : An elongated extension of the cell body that carries impulses away from the cell body. Myelin Sheath •Myelin Sheaths are made of fat. •MYELIN SHEATHS insulate the NERVE IMPULSES!!!!! Axon terminals The end of the axon is divided into fingerlike projections, which enable Connection to the dendrites of an adjacent neuron. How do nerve impulses reach an adjacent nerve cell? There is a GAP or SPACE between the terminal branch (axon terminal) of a neuron and the dendrites of another neuron which is called a SYNAPSE Transmission Across a Synapse Impulses are carrie d across a synapse by chemical messengers a r e called NEUROTRANSMITTERS How do neurotransmitters affect Nervous System Function???? Do Now: Handout HW: Handout 1. Watch the animation….using the following list of words create a sentence that describes what your are seeing. Axon terminal, dendrite, synapse, neurotransmitters, and impulse. 2. Explain the significance of the varying shapes. After transmission o f a n i m p u l s e ……. neurotransmitters are destroyed b y e n z y m e s OR they are returned to the axon and recycled. Why must the body inhibit the function of neurotransmitters? If they were not destroyed, they would continue to stimulate t h e n e r v e c e l l with the same impulse over and over Ex. Aspirin inhibits neurotransmitters Name three body systems that rely on the nervous system for proper functioning and explain why you chose each. How can the Nervous system malfunction? The nervous system is vulnerable to various disorders. It can be damaged by the following: •trauma •infections •degeneration •structural defects •tumors •blood flow disruption How do certain drugs or alcoholic beverages make you feel “high”? Varying concentrations of the release of neurotransmitters Ex. Dopamine or other chemicals DRUGS AND EFFECTS Stimulants like caffeine ( COLA, TEA, COFFEE, CHOCOLATE), Nicotine (CIGARETTES) and Cocaine increase breathing rate, heart rate and blood pressure. They also increase the release of neurotransmitters at some synapses in the brain. You start to feel GREAT and then neurotransmitters deplete and you become fatigued and even depressed. * Abnormal levels of neurotransmitters could cause...... 1.Twitching: Results from an over/under stimulation of the nerve cells – Short-term malfunction 2. Tourette’s Syndrome: Results from over stimulation of the nerve cell leading to limited control of the particular effectors regulated by these nerve cells.- No cure as of today! Abnormal levels of neurotransmitters could cause...... 3. Depression: Caused by abnormal levels of neurotransmitters crossing the synapse – Usually lower levels of serotonin and/or norepinephrine 4. Schizophrenia: Caused by higher than normal levels of dopamine Missing Neurotransmitters could cause….. PARKINSON’S DISEASE ALZEIHMER’S DISEASE DRUGS, BOTH LEGAL AND ILLEGAL, HINDER or OVEREXCITE THE NEUROTRANSMITTERS Decrease of oxygen and nutrients to the brain, due to break of neural/carotid blood vessels. Interference or disruption between groups of neurons (mainly interneuron dysfunction) usually due to brain trauma/injury. Symptoms show involuntary movement and poor balance. Inflammation of tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord due to infection. Lou Gerhigs’ Disease: Dysfunction of motor neurons and brain. A viral infection affects gray matter (of the brain) Leads to paralysis: Pres. Franklin D. Roosevelt Decrease of levels of neurotransmitters (dopamine and acetylcholine) which affects muscle contractions. Causes body tremors Michael J. Fox & Mohammed Ali Faulty gene, causes hardening of the neurons- decreased motor dysfunction/ coordination. Woody Guthrie plaque on neurons which blocks impulse transmission Pres. Reagan. Adrenoleukodystrophy Deterioration of myelin sheath. Lorenzo Odone








