Introduction to Genetics
advertisement

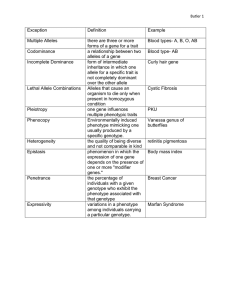
Topic: Genetics Aim: Explain the basic principles of genetics, Directions: Read the text below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1 - 20. Gregor Mendel is known as the founder of genetics. He performed studies on pea plants to study genetic inheritance, or how genes are inherited, or passed on. In Mendel’s experiments he crossed pea plants with different colored seeds (green and yellow) and observed the differences in plants that were produced. The probability or chance of inheriting a trait can be predicted using a Punnett square. Genes are (5) inherited when two living organisms create offspring. What is passed on by the parents are genes. Genes are made up of alleles or different forms of the same gene and can be expressed or shown as either dominant or recessive. Two terms used when describing genetic inheritance are genotype and phenotype. Genotype is the (10) genetic makeup of an individual. Phenotype is the observed characteristics of an organism including, color, shape, size, and behavior. Phenotype depends on genotype. The genes of an organism for a trait are represented by TWO letters or alleles. The capital letter is the dominant gene and the lower case letter is the recessive gene. A homozygous pair of alleles is made up of two alleles (or genes) that are the same (YY or yy). When both alleles are dominant (YY), it is called (15) homozygous dominant. When both alleles are recessive (yy), it is called homozygous recessive. A heterozygous (hybrid) pair of alleles is made up of genes that are different (Yy). The dominant gene (YY or Yy) will always be expressed UNLESS there are two recessive genes (yy) paired in the genotype, in which the recessive phenotype will then be expressed. Questions: 1. Who is the founder of genetics? (l)_________________________________________________________ 2. Which organism did Mendel study? (1)___________________________________________ 3. What did Mendel investigated or study? (1-2) __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is a Punnett square used for? (5) __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is a gene made up of? (5 - 6) ______________________________________________________________ 6. What are the two ways alleles, or genes, are expressed? (6 – 7) _________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What is genotype? (9 - 10) __________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is phenotype? (10) ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What are some examples of phenotype? (10 – 11) __________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. What does the phenotype depend on? (11) ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 11. How many letters or alleles represent the genes for a trait? (12)__________________________ 12. What kind of letter represents a dominant gene? (12 - 13) ___________________________________________ 13. What kind of letter represents a recessive gene? (13) _______________________________________________ 14. What is a homozygous pair of alleles made up of? (14) _____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. What is the pair of alleles called when there are two dominant genes (YY)? (14-15)_______________________ 16. What is the pair of alleles called when there are two recessive genes (yy)? (15)___________________________ 17. What is a heterozygous pair of alleles made up of? (15)_____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 18. What is another word for heterozygous? (15) ______________________________ 19. When will a dominant gene be expressed? (16 – 17) _________________________________________________________________________________________ 20. When will the recessive gene be expressed? (17 – 18) _________________________________________________________________________________________ CLASS DISCUSSION Use the information from the reading to help answer the questions regarding gene combinations. 1. The trait for height in pea plants can be represented by using the letter “T.” T represents the allele for tall and t represents the allele for short. a. What do we call the genotype for TT? __________________________________________________________________ b. What is the phenotype for TT? __________________________________________________________________________ c. What do we call the genotype for tt? ___________________________________________________________________ d. What is the phenotype for tt? ___________________________________________________________________________ e. What do we call the genotype for Tt? __________________________________________________________________ f. What is the phenotype for Tt? ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. The trait for seed color in pea plants can be represented by using the letter “G.” G represents the allele for green seeds and g represents the allele for yellow seeds. a. What do we call the genotype for gg? ___________________________________________________________________ b. What is the phenotype for gg? ___________________________________________________________________________ c. What do we call the genotype for Gg? ___________________________________________________________________ d. What is the phenotype for Gg? ___________________________________________________________________________ e. What do we call the genotype for GG? ___________________________________________________________________ f. What is the phenotype for GG? ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. The trait for seed shape in pea plants can be represented by using the letter “R.” R represents the allele for round seeds and r represents the allele for wrinkled seeds. a. What do we call the genotype for rr? ___________________________________________________________________ b. What is the phenotype for rr? ___________________________________________________________________________ c. What do we call the genotype for Rr? ___________________________________________________________________ d. What is the phenotype for Rr? ___________________________________________________________________________ e. What do we call the genotype for RR? ___________________________________________________________________ f. What is the phenotype for RR? ____________________________________________________________________________ 4. The trait for flower color in pea plants can be represented by using the letter “P.” P represents the allele for purple flowers and p represents the allele for white flowers. a. What do we call the genotype for pp? ___________________________________________________________________ b. What is the phenotype for pp? ___________________________________________________________________________ c. What do we call the genotype for Pp? ___________________________________________________________________ d. What is the phenotype for Pp? ___________________________________________________________________________ e. What do we call the genotype for PP? ___________________________________________________________________ f. What is the phenotype for PP? ____________________________________________________________________________ Conclusion Questions: 1. What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? 2. What is the difference between a homozygous pair of alleles and a heterozygous pair of alleles? 3. Write the THREE possible genotype combinations (WRITE THE NAMES, NOT THE LETTERS).