Infectious and Non-Infectious Diseases
advertisement

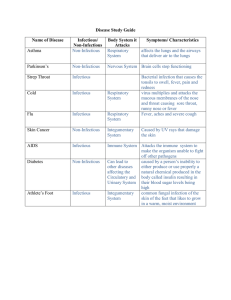
Infectious vs. Non-infectious Diseases ISA (B) Directions: Read the passage below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1- 6 on the loose-leaf below. Some diseases can be transmitted, or passed on, from one person to another. These are called infectious diseases. They are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi. These diseases can be spread, directly or indirectly, from one person to another. One common form of transmission is known as the respiratory route. If an infected person coughs or sneezes on another person the pathogens, suspended in warm, moist droplets, may enter the body through the nose, mouth or eye surfaces. Diseases that are commonly spread by coughing or sneezing include bacterial meningitis, chickenpox, the common cold, influenza and strep throat. Sexually transmitted diseases, or STD’s, refer to any disease that can be caught during sexual activity with another person. Transmission is either directly between surfaces in contact during intercourse or from body secretions such as semen. Examples of STD’s include HIV/AIDS and herpes. Contagious diseases can be transmitted by direct contact. For example, these diseases can be transmitted by sharing a towel (where the towel is rubbed vigorously on both bodies) or items of clothing in close contact with the body (socks, for example) if they are not washed thoroughly between uses. For this reason, contagious diseases often break out in schools, where towels are shared and personal items of clothing accidentally swapped in the changing rooms. Some diseases that are transmissible by direct contact include athlete's foot and warts. Non-infectious diseases are those diseases that are not caused by a pathogen and cannot be transmitted from one person to another. They are caused by how people live, by conditions they are born with (genetically inherited), or by hazards around them. Heart disease, asthma, diabetes and certain types of cancer are examples of non-infectious diseases. In order to reduce the risk of getting these diseases, they must try to change how they live or decrease the hazards around them. For example, heart disease which is the number-one killer in the U.S., can be prevented by eating a healthy diet and staying at a healthy weight. The most common type of cancer, nonmelanoma skin cancer, can be prevented by wearing sunblock when you are outside .Lung cancer can be prevented by not smoking. Other common cancers include bladder, breast, leukemia, pancreatic, prostate, thyroid, colorectal, endometrial and kidney cancer. Questions: 1. Describe the difference between infectious and noninfectious disease. 2. How can infectious disease be spread? 3. Identify TWO examples of infectious diseases. 4. Identify TWO examples of non-infectious diseases. 5. Identify an example of a non-infectious disease that can be prevented. 6. Identify an example of a non-infectious disease that cannot be prevented. Infectious vs. Non-infectious Diseases ISA (B) Directions: Read the passage below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1- 6 on the loose-leaf below. Some diseases can be transmitted, or passed on, from one person to another. These are called infectious diseases. They are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi. These diseases can be spread, directly or indirectly, from one person to another. One common form of transmission is known as the respiratory route. If an infected person coughs or sneezes on another person the pathogens, suspended in warm, moist droplets, may enter the body through the nose, mouth or eye surfaces. Diseases that are commonly spread by coughing or sneezing include bacterial meningitis, chickenpox, the common cold, influenza and strep throat. Sexually transmitted diseases, or STD’s, refer to any disease that can be caught during sexual activity with another person. Transmission is either directly between surfaces in contact during intercourse or from body secretions such as semen. Examples of STD’s include HIV/AIDS and herpes. Contagious diseases can be transmitted by direct contact. For example, these diseases can be transmitted by sharing a towel (where the towel is rubbed vigorously on both bodies) or items of clothing in close contact with the body (socks, for example) if they are not washed thoroughly between uses. For this reason, contagious diseases often break out in schools, where towels are shared and personal items of clothing accidentally swapped in the changing rooms. Some diseases that are transmissible by direct contact include athlete's foot and warts. Non-infectious diseases are those diseases that are not caused by a pathogen and cannot be transmitted from one person to another. They are caused by how people live, by conditions they are born with (genetically inherited), or by hazards around them. Heart disease, asthma, diabetes and certain types of cancer are examples of non-infectious diseases. In order to reduce the risk of getting these diseases, they must try to change how they live or decrease the hazards around them. For example, heart disease which is the number-one killer in the U.S., can be prevented by eating a healthy diet and staying at a healthy weight. The most common type of cancer, nonmelanoma skin cancer, can be prevented by wearing sunblock when you are outside .Lung cancer can be prevented by not smoking. Other common cancers include bladder, breast, leukemia, pancreatic, prostate, thyroid, colorectal, endometrial and kidney cancer. Questions: 1. Describe the difference between infectious and noninfectious disease. 2. How can infectious disease be spread? 3. Identify TWO examples of infectious diseases. 4. Identify TWO examples of non-infectious diseases, 5. Identify an example of a non-infectious disease that can be prevented. 6. Identify an example of a non-infectious disease that cannot be prevented Infectious vs. Non-infectious Diseases ISA (C) Directions: Read the passage below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1- 5 on the loose-leaf below. Some diseases can be transmitted, or passed on, from one person to another. These are called infectious diseases. They are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi. These diseases can be transmitted directly or indirectly, from one person to another. One typical mode of transmission is known as the respiratory route. If an infected person coughs or sneezes on another person the pathogens, suspended in warm, moist droplets, may enter the body through the nose, mouth or eye surfaces. Diseases that are commonly spread by coughing or sneezing include bacterial meningitis, chickenpox, the common cold, influenza and strep throat. Sexually transmitted diseases, or STD’s, refer to any disease that can be caught during sexual activity with another person. Transmission is either directly between surfaces in contact during intercourse or from body secretions such as semen. Examples of STD’s include HIV/AIDS and herpes. Contagious diseases can be transmitted by direct contact. For example, these diseases can be transmitted by sharing a towel (where it is rubbed vigorously on both bodies) or items of clothing in close contact with the body such as socks, if they are not washed thoroughly between uses. For this reason, contagious diseases often break out in schools, where towels are shared and personal items of clothing accidentally swapped in the changing rooms. Some diseases that are transmissible by direct contact include athlete's foot and warts. Non-infectious diseases are those diseases that are not caused by a pathogen and cannot be transmitted from one person to another. They are caused by how people live, by hazards around them or are genetically inherited. Heart disease, asthma, diabetes and certain types of cancer are examples of non-infectious diseases. In order to reduce the risk of getting these diseases, they must try to change how they live or decrease the hazards around them. For example, people can reduce their risk of lung cancer by not smoking. Mayo Clinic reports heart disease, a non-infectious disease, as the number-one killer in the United States. Heart disease can be prevented by eating a healthy diet and staying at a healthy weight. Cancer is a non-infectious disease that affects millions of people. The National Cancer Institute reports the most common cancer type as nonmelanoma skin cancer, with about one million cases a year. Lung cancer is the second-most common, with about 219,440 new cases and 159,390 deaths. Other common cancers include bladder, breast, leukemia, pancreatic, prostate, thyroid, colorectal, endometrial and kidney cancer. Questions: 1. Contrast infectious and noninfectious disease. 2. Identify the different ways infectious disease can be transmitted. 3. Identify three examples of infectious diseases and three examples of non-infectious diseases. 4. Identify two examples of non-infectious diseases that can be prevented. 5. Identify two examples of non-infectious diseases that cannot be prevented. Infectious vs. Non-infectious Diseases ISA (C) Directions: Read the passage below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1- 5 on the loose-leaf below. Some diseases can be transmitted, or passed on, from one person to another. These are called infectious diseases. They are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi. These diseases can be transmitted directly or indirectly, from one person to another. One typical mode of transmission is known as the respiratory route. If an infected person coughs or sneezes on another person the pathogens, suspended in warm, moist droplets, may enter the body through the nose, mouth or eye surfaces. Diseases that are commonly spread by coughing or sneezing include bacterial meningitis, chickenpox, the common cold, influenza and strep throat. Sexually transmitted diseases, or STD’s, refer to any disease that can be caught during sexual activity with another person. Transmission is either directly between surfaces in contact during intercourse or from body secretions such as semen. Examples of STD’s include HIV/AIDS and herpes. Contagious diseases can be transmitted by direct contact. For example, these diseases can be transmitted by sharing a towel (where it is rubbed vigorously on both bodies) or items of clothing in close contact with the body such as socks, if they are not washed thoroughly between uses. For this reason, contagious diseases often break out in schools, where towels are shared and personal items of clothing accidentally swapped in the changing rooms. Some diseases that are transmissible by direct contact include athlete's foot and warts. Non-infectious diseases are those diseases that are not caused by a pathogen and cannot be transmitted from one person to another. They are caused by how people live, by hazards around them or are genetically inherited. Heart disease, asthma, diabetes and certain types of cancer are examples of non-infectious diseases. In order to reduce the risk of getting these diseases, they must try to change how they live or decrease the hazards around them. For example, people can reduce their risk of lung cancer by not smoking. Mayo Clinic reports heart disease, a non-infectious disease, as the number-one killer in the United States. Heart disease can be prevented by eating a healthy diet and staying at a healthy weight. Cancer is a non-infectious disease that affects millions of people. The National Cancer Institute reports the most common cancer type as nonmelanoma skin cancer, with about one million cases a year. Lung cancer is the second-most common, with about 219,440 new cases and 159,390 deaths. Other common cancers include bladder, breast, leukemia, pancreatic, prostate, thyroid, colorectal, endometrial and kidney cancer. Questions: 1. Contrast infectious and noninfectious disease. 2. Identify the different ways infectious disease can be transmitted. 3. Identify three examples of infectious diseases and three examples of non-infectious diseases. 4. Identify two examples of non-infectious diseases that can be prevented. 5. Identify two examples of non-infectious diseases that cannot be prevented. Infectious vs. Non-infectious Diseases ISA (A) Directions: Read the passage below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1- 6 on the loose-leaf below. Infectious diseases can be transmitted, or passed on, from one person to another. They are caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi. These diseases can be spread from one person to another. One way infectious diseases can be spread is by your respiratory system. If a sick person coughs or sneezes on another person, the pathogens that enter the air can enter the nose, mouth or eyes. Diseases that are usually spread by coughing or sneezing include bacterial meningitis, chickenpox, the common cold, influenza and strep throat. Sexually transmitted diseases, or STD’s, refer to any disease that can be caught during sexual activity with another person such as during intercourse (sex) or from direct contact with body secretions such as semen. Examples of STD’s include HIV/AIDS and herpes. Contagious diseases can be transmitted by direct contact, or touch. For example, these diseases can be transmitted by sharing a towel (where the towel is rubbed vigorously on both bodies) or items of clothing in close contact with the body (socks, for example) if they are not washed thoroughly between uses. This is why contagious diseases often break out in schools, where towels are shared and personal items of clothing accidentally swapped in the changing rooms. Some diseases that are transmissible by direct contact include athlete's foot and warts. Non-infectious diseases are those diseases that are not caused by a pathogen and cannot be transmitted from one person to another. They are caused by how people live, by conditions they are born with, or by hazards around them. Heart disease, asthma, diabetes and certain types of cancer are examples of non-infectious diseases. In order to reduce the risk of getting these diseases, they must try to change how they live or decrease the hazards around them. For example, heart disease which is the number-one killer in the U.S., can be prevented by eating a healthy diet and staying at a healthy weight. The most common type of cancer, nonmelanoma skin cancer, can be prevented by wearing sunblock when you are outside .Lung cancer can be prevented by not smoking. Other common cancers include bladder, breast, leukemia, pancreatic, prostate, thyroid, colorectal, endometrial and kidney cancer. Questions: 1. What is the difference between infectious and non-infectious disease? 2. How can infectious disease be spread to another person? 3. What is ONE example of an infectious disease? 4. What is ONE example of a non-infectious disease? 5. What is ONE example of a non-infectious disease that CAN BE PREVENTED? 6. What is ONE example of a non-infectious disease that CANNOT BE PREVENTED? Infectious vs. Non-infectious Diseases ISA (A) Directions: Read the passage below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1- 6 on the loose-leaf below. Infectious diseases can be transmitted, or passed on, from one person to another. They are caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi. These diseases can be spread from one person to another. One way infectious diseases can be spread is by your respiratory system. If a sick person coughs or sneezes on another person, the pathogens that enter the air can enter the nose, mouth or eyes. Examples are bacterial meningitis, chickenpox, the common cold, influenza and strep throat. Sexually transmitted diseases, or STD’s, are any disease that can be caught during sexual activity with another person such as during intercourse (sex) or from direct contact with body secretions such as semen. Examples of STD’s include HIV/AIDS and herpes. Contagious diseases can be transmitted by direct contact, or touch. These diseases can be spread by sharing a towel (where the towel is rubbed vigorously on both bodies) or items of clothing in close contact with the body (socks, for example) if they are not washed thoroughly between uses. This is why contagious diseases often break out in schools, where towels are shared and personal items of clothing accidentally swapped in the changing rooms. Some diseases that are transmissible by direct contact include athlete's foot and warts. Non-infectious diseases are those diseases that are not caused by a pathogen and cannot be transmitted from one person to another. They are caused by how people live, by conditions they are born with, or by hazards around them. Heart disease, asthma, diabetes and certain types of cancer are examples of non-infectious diseases. In order to reduce the risk of getting these diseases, they must try to change how they live or decrease the hazards around them. For example, heart disease which is the number-one killer in the U.S., can be prevented by eating a healthy diet and staying at a healthy weight. The most common type of cancer, nonmelanoma skin cancer, can be prevented by wearing sunblock when you are outside .Lung cancer can be prevented by not smoking. Other common cancers include bladder, breast, leukemia, pancreatic, prostate, thyroid, colorectal, endometrial and kidney cancer. Questions: 1. What is the difference between infectious and non-infectious disease? 2. How can infectious disease be spread to another person? 3. What is ONE example of an infectious disease? 4. What is ONE example of a non-infectious disease? 5. What is ONE example of a non-infectious disease that CAN BE PREVENTED? 6. What is ONE example of a non-infectious disease that CANNOT BE PREVENTED?