Introduction to Genetics
advertisement

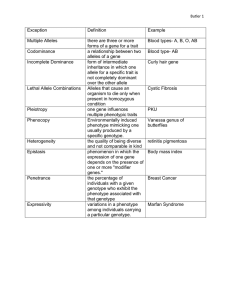
Topic: Genetics Aim: Explain the basic principles of genetics. Do Now: Take out your metamorphosis ISA. HW: Genetics Reading notes due tomorrow. 1. Identify structure X. Support your answer. Pollen tube 2. Describe the function of the structure X. •Enables POLLEN (sperm nuclei) to travel into the ovary. 3. Why do the sperm nuclei travel into the ovules?•For fertilization. 4. Describe what occurs to the flower once all eggs in the ovary are fertilized. •Ovules turn into seeds. •Ovaries turn into fruit. 1.Identify all structures labeled in the diagram. 2.Describe the function of structure C. seed coat B embryoA C cotyledon Stores food for embryo An adaptation for reproduction in most terrestrial organisms is (1) regeneration (2) internal fertilization (3) mitosis (4) external fertilization External fertilization occurs most often in 1. mammals and birds 2. reptiles and birds 3. amphibians and reptiles 4. fish and amphibians Which represents binary fission? Support your answer. 1. Identify • Gregor Mendel the founder of genetics. 2. Identify the organism Mendel investigated. • Pea plants 3. Identify • Genetic inheritance what Mendel investigated? Identify the traits Mendel observed when working with pea plants. A B F C D G E 4. Explain • To predict the probability and what a outcome of genetic inheritance Punnett Square is used for. 5. Identify what genes consist of. • Alleles or alternate forms of the same gene Gene B A Replicated chromosome C DNA 1. Identify the two alleles for eye color in fruit flies. 2. How many alleles are necessary for this trait? 6. How are alleles expressed? • As dominant OR recessive 7. Describe • The genetic makeup of an genotype. organism. 8. Describe • The observed phenotype. characteristics of an organism. 9. Identify • Color some • Shape examples of phenotype. • Size • Behavior 10. Describe • Phenotype depends on the genotype. relationship between phenotype and genotype. (What does phenotype depend on?) Bb Brown Explain the meaning of this statement. 11. How many alleles represent the genes for a trait? • TWO Gene from dad Gene from mom 12. Identify the letter representing a dominant gene. • Capital letter •B 13. Identify the letter representing a recessive gene. • Lower case letter •b 14. Describe • 2 alleles or genes that are what a the same homozygous • Ex: BB or bb pair of alleles consists of. 15. Identify the pair of alleles that consist of two dominant genes. • Homozygous dominant • Ex: BB 16. Identify the pair of alleles that consist of two recessive genes. • Homozygous recessive • Ex: bb 17. Identify • One dominant and one what a recessive gene heterozygous • Ex: Bb pair of alleles consists of. 18. Identify another term with the same meaning as heterozygous. • Hybrid 19. When will • It is always expressed a dominant unless there are two gene be recessive genes. expressed? • Ex: – BB – Bb 20. When will • When there are two a recessive recessive genes. gene be • Ex: bb expressed? The allele for brown eyes is dominant. The allele for blue eyes is recessive. Why does Bb combination result in brown eyes and not blue? 1. The trait for height in pea plants can be represented by using the letter “T.” T represents the allele for tall and t represents the allele for short. a. What do we call the genotype for TT? Homozygous dominant b. What is the phenotype for TT? Tall c. What do we call the genotype for tt? Homozygous recessive d. What is the phenotype for tt ?short e. What do we call the genotype for Tt ? Heterozygous f. What is the phenotype for Tt ? tall 2. The trait for seed color in pea plants can be represented by using the letter “G.” G represents the allele for green seeds and g represents the allele for yellow seeds. a. What do we call the genotype for gg? Homozygous recessive b. What is the phenotype for gg? yellow c. What do we call the genotype for Gg? Heterozygous d. What is the phenotype for Gg? green e. What do we call the genotype for GG? Homozygous dominant f. What is the phenotype for GG? green 3. The trait for seed shape in pea plants can be represented by using the letter “R.” R represents the allele for round seeds and r represents the allele for wrinkled seeds. a. What do we call the genotype for rr? Homozygous recessive b. What is the phenotype for rr? wrinkled c. What do we call the genotype for Rr? Heterozygous d. What is the phenotype for Rr? Round e. What do we call the genotype for RR? Homozygous dominant f. What is the phenotype for RR? Round 4. The trait for flower color in pea plants can be represented by using the letter “P.” P represents the allele for purple flowers and p represents the allele for white flowers. a. What do we call the genotype for pp? Homozygous recessive b. What is the phenotype for pp? White flowers c. What do we call the genotype for Pp? Heterozygous d. What is the phenotype for Pp? Purple e. What do we call the genotype for PP? Homozygous dominant f. What is the phenotype for PP? Purple Conclusion Questions: 1. Contrast genotype and phenotype. Genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism, phenotype is the observed characteristics. 2. Contrast a homozygous pair of alleles and heterozygous pair of alleles. Homoszygous is two of the SAME alleles. Heterozygous are two different alleles. 3. Identify the 3 possible genotype combinations (NAMES, NOT LETTERS) Homozygous recessive Homozygous dominant Heterozygous DOMINANT F RECESSIVE f DOMINANT H RECESSIVE h W = widow’s peak w = straight hairline P = bent pinkie p = straight pinkie (cannot bend inwards) E = attached earlobes e = unattached earlobes R = Rolling of the tongue r = cannot roll tongue C = Cleft chin c = smooth chin D = Dimples d = Without dimples Let’s summarize… 1. Explain what is studied in genetics. 2. Who is the father of genetics? What did he use in his experiments? 3. How many alleles are needed for every trait? 4. Explain the difference between a dominant and recessive gene. 5. Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype. 6. Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous. Sometimes tens, or even hundreds of genes can play a role in just one trait! Melanin, a brown pigment, is controlled by the following genes: • brown-blue gene on chromosome 15 • green-blue gene on chromosome 19 Another brown-type gene was also discovered on chromosome 15. Recently, a gene for a brownish yellow pigment, lipofuscin, that appears in amber, green and violet irises was discovered. And there's likely at least one other gene, not yet located, that plays a role in iris color. Goldfish have 96 chromosomes in each cell while humans only have 46. Dogs have 78 chromosomes. And here’s the real shocker, a fern has 512 chromosomes. You can easily see that the skin on your fingertips is folded into patterns called dermal ridges. They form whorls, arches and loops. The # of dermal ridges in a fingerprint pattern is determined by genetics, but the pattern can also be changed early in pregnancy. During weeks 6-13, the fetus touches the finger and toe pads to the wall of the amniotic sac which sometimes can alter the ridge pattern. This is why the fingerprints of identical twins are not exactly alike, even though they have identical genes.