Topic Aim Do Now system.
advertisement

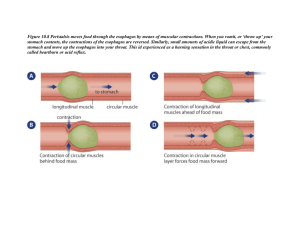
Topic: Digestive System Aim: Describe the parts and functions of the digestive system. Do Now: 1. Pass up your Food Label lab. 2. Take out your digestive system reading notes. 3. Identify the life process that requires the food we ingest and digest. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bo2Ape8JHqA HW: Read text pgs. 525-529. Complete p. 529 #’s 1 -5. Write the question and answer. Did you know.... • Americans eat about 700 million pounds of peanut butter. • Americans eat over 2 billion pounds of chocolate a year. • In your lifetime, your digestive system may handle about 50 tons of food!! • What you ate for breakfast that was not digested will come out in about 48 hoursnormally. • From intake to outlet, the digestive tract is about thirty feet long. 1. Describe the function (job) of the digestive system. • Breakdown of food into small molecules so that they can be absorbed into the blood and enter your cells 2. Identify the structure where digestion begins (or start). • Mouth • Oral cavity TEETH Incisors Canine Premolars What kind of digestion occurs in your mouth? Molars Tongue Salivary glands Opening of a salivary gland duct “Wisdom” tooth 3. How does the mouth CHEMICALLY digest food? • Saliva contains the ENZYME amylase which helps break down CARBOHYDRATES in your food. Where does the saliva come from??? Salivary glands release saliva into the mouth. Mumps is a highly contagious viral illness which causes swelling of the parotid gland. A vaccine is given to children above one year of age along with rubella and measles vaccines. IMMRV vaccine also available which gives protection against mumps, measles, rubella and chicken pox. 4. How does the mouth MECHANICALLY digest food? • Your TEETH grind your food when you CHEW, and your tongue pushes the food around your mouth. Did you know.... • We make 1 to 3 pints of saliva a day. • Your teeth started growing 3 months before you were even born. • The hardest substance in your body is the enamel on your teeth. • As you are sitting there listening, more than 100 million germs are swimming, feeding, reproducing, and making waste in the area behind your lips. In your mouth there are more living things than there are people in Australia and Canada combined. Uvula Through history, scientists have had many theories about the uvula. Among them: •That it once helped guide the flow of food and water. •That it induces the gag reflex. And therefore isn’t the best place to get a piercing. •That it contributed to “chronic cough.” A problem that 19thcentury doctors treated with a “simple” “clipping” procedure. Uvula Several such studies have concluded that the uvula is really good at releasing saliva. A lot of saliva, in a really short amount of time. Because the uvula is basically unique to humans, scientists basically agree that it primarily serves as an accessory to speech. You know what it’s like to have your throat go dry before talking to a large group? The uvula is there to provide the proper lubrication for complicated human speech. 5. What is the function of the EPIGLOTTIS? • The epiglottis is a FLAP of SKIN that COVERS the windpipe when you SWALLOW food or liquid. 6. What happens when you cough or choke? • When you cough or choke, it means the EPIGLOTTIS did not cover you WINDPIPE sufficiently. 7. Describe the function of the ESOPHAGUS? • It connects your throat to your stomach. 8. How does the esophagus push food down into the stomach? • Smooth muscles on the walls of your esophagus move in a wave motion to direct the food to the stomach. • PERISTALSIS Opening to stomach from the esophagus Topic: Digestive System Aim: Describe the parts and functions of the digestive system. Do Now: Pass up your HW. Complete the exit card using the diagram on the next slide. HW: Midterm Remediation Castle Learning due Thursday. Oral cavity A B Salivary glands C Esophagus E F D Stomach H G I J 9. Describe the function of the stomach. 9. Describe the function of the stomach. • The stomach HOLDS the food you swallow, where it is BROKEN DOWN food into a liquid mixture by GASTRIC JUICES and strong MUSCLES in stomach wall • MECHANICAL and CHEMCIAL digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o18UycWRsaA 10. Identify the chemical in the stomach that kills bacteria that may be in the food that you eat. • Hydrochloric acid http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SWMWsOXlBwE Did you know.... • An adult’s stomach can hold approximately 1.5 liters of material. • Food sloshing in the stomach can last 3-4 hours. • The stomach's wall is lined with three layers of powerful muscles. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=URHBBE3RKEs SMALL INTESTINE Length = 4-7 meters Why is it called the SMALL intestine? 11. Describe the TWO functions of the small intestine. • Food is further digested. (CHEMICAL digestion is COMPLETED) • Food (nutrients) is absorbed by your body. 12. Identify 3 structures that aid (HELP) in chemical digestion in the small intestine. • Pancreas • Liver • Gall bladder 13. Describe the pancreas, liver and gall bladder aid in chemical digestion in the SI. • Pancreas secretes juices that help digest proteins and fats. (CHEMICAL DIGESTION) 13. Describe the pancreas, liver and gall bladder aid in chemical digestion in the SI. • Liver produces bile and helps the body absorb fats. • Gall bladder stores and secretes bile. BILE Bile emulsifies fats. Liver Stomach Gall bladder Small Intestine Pancreas 14. How are nutrients absorbed in the small intestine? • Wall of SI lined with VILLI (fingerlike projections) Which blood vessels are found inside each villus? Topic: Digestive System Aim: Describe the parts and functions of the digestive system. Do Now: Take out your digestive system reading notes. HW: Midterm Remediation Castle Learning due tomorrow. Flamin’ Hot Cheetos Reading Questions If you stretched out an adult's small intestine, it would be about 22 feet long. 1. Identify the type of digestion that occurs in the SI. 2. Identify the structures that help chemically digest food in the SI. 3. Explain what occurs once digestion in completed. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JCA 9HQ795i8 VILLI 15. Describe the function of the large intestine. • The large intestine removes most of any remaining minerals or FLUIDS that the body can use from the waste. • Fluid = WATER Did you know.... • Within the colon, a typical person harbors more than 400 distinct species of bacteria. 16. Once water is absorbed in the LI, what is the waste called? • Stool • Feces 17. Identify the structure that temporarily stores stool? • Rectum 18. Identify the structure that removes stool from the body. • Anus How the bacteria in the large intestine are beneficial to humans? • Produce vitamins • Bacteria feed on undigested material (cellulose) If you squeezed out all of the bacteria that lives in your intestines, you could almost fill up a coffee mug. Anyone want a sip? Let’s Review: Identify the digestive organ described. 1. Where chemical digestion begins. Oral cavity 2. Site of water absorption. Large intestine 3. All chemical digestion is completed here.Small intestine 4. Where bile is stored. Gall bladder 5. Where feces is formed. Large intestine 6. Where mechanical digestion begins. Oral cavity 7. Releases many enzymes into the SI. Pancreas 8. Pushes food into the stomach. Esophagus 9. Produces saliva. Salivary glands 10. Where the absorption of nutrients occurs.Small intestine 1. Lining is protected by a mucus layer. Stomach 2. Lined with villi. Small intestine 3. Produces bile. Liver STARCH Oral cavity A B Salivary glands C Esophagus Liver E F Gall bladder Large G intestine PROTEINS D Stomach H Pancreas I Small intestine J Rectum Identify the organs of the digestive system that aid in digestion but food does not pass through. Gallstones occur when Bile forms solid particles (stones) in the gallbladder Stones form when the amount of cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile is high. Risk factors for the formation of cholesterol gallstones include the following: female gender being overweight, losing a lot of weight quickly on a "crash" or starvation diet taking certain medications such as birth control pills or cholesterol lowering drugs As the stones mix with liquid bile they can block the outflow of bile from the gallbladder can block the outflow of digestive enzymes from the pancreas. If blockage persists, these organs can become inflamed. Inflammation of the gallbladder is called cholecystitis. Inflammation of the pancreas is called pancreatitis. The function of the appendix is unknown. One theory is that the appendix acts as a storehouse for good bacteria, “rebooting” the digestive system after diarrheal illnesses. Other experts believe the appendix is just a useless remnant from our evolutionary past. Surgical removal of the appendix causes no observable health problems. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QYwscALNng STARCH Oral cavity A B Salivary glands C Esophagus Liver E F Gall bladder Large G intestine PROTEINS D Stomach H Pancreas I Small intestine J Rectum Salivary glands Esophagus Liver Gall baldder Small intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Large intestine http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bo2Ape8J HqA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ttQtDfv6d Co Oral cavity Gall bladder Large intestinne Stomach Pancreas Small intestine Rectum Let’s review… 1.Describe the FUNCTION of the digestive system. 2.Identify the type of digestion that occurs in the mouth. 3.Identify the tube and the process that pushed food into the stomach. 4.Identify the flap of tissue that prevents you from choking when swallowing food or liquid. 5.Identify the type of digestion that occurs in the mouth. 6.How is the stomach lining protected from the hydrochloric acid? Oral cavity A B Salivary glands C Esophagus E F D Stomach H G I J The main function of the human digestive system is to 1) rid the body of cellular waste materials 2) break down large molecules so they can enter cells 3) break down glucose in order to release energy 4) change amino acids into proteins and carbohydrates Food is ingested through the 1) salivary glands 2) small intestine 3) mouth 4) rectum Mechanical digestion in the oral cavity is primarily the result of 1) peristalsis 2) chewing food 3) absorption 4) egestion Chemical digestion in the mouth is the result of 1) enzymes 2) hydrochloric acid 3) bile 4) pancreatic juice Food that is swallowed enters the 1) stomach 2) small intestine 3) esophagus 4) large intestine The esophagus pushed food down into the stomach by the involuntary process of 1. digestion 2. peristalsis 3. absorption 4. excretion Identify the type of digestion that takes place in the stomach. 1) mechanical digestion 2) chemical digestion 3) both mechanical and chemical digestion How does mechanical digestion in the stomach occur? 1) enzymes 2) hydrochloric acid 3) peristalsis 4) mucus How does chemical digestion in the stomach occur? 1) peristalsis 2) enzymes 3) mucus 4) ulcers Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? 1. intestinal glands 2. villi 3. pseudopodia 4. cilia Identify how the stomach lining is protected from hydrochloric acid. 1) peristalsis 2) mucus 3) enzymes 4) bacteria Identify the type of digestion that occurs in the small intestine. 1) mechanical digestion 2) chemical digestion 3) both mechanical and chemical digestion Which statement regarding the small intestine is incorrect? 1. Villi on the lining of the small intestine absorb nutrients into the blood. 2. Chemical digestion is completed in the small intestine. 3. Mechanical digestion is completed in the small intestine. 4. The small intestine is where most digestion occurs. Which structures in the small intestine absorb nutrients into the blood? 1. intestinal glands 2. villi 3. pseudopods 4. cilia Which substances are released into the small intestine of a human and aid in the digestion of food? 1) bile, pancreatic juice, and intestinal juice 2) hydrochloric acid, pancreatic juice, and intestinal juice 3) salivary amylase, intestinal juice, and pancreatic juice 4) bile, hydrochloric acid, and salivary amylase https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QYwscALNng Which statement regarding the large intestine is correct? 1. The large intestine absorbs nutrients. 2. Chemical digestion is completed in the large intestine. 3. Mechanical digestion is completed in the small intestine. 4. The large intestine absorbs excess water.