Dichotomous Keys
advertisement

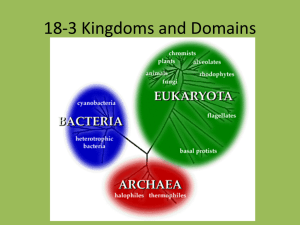
Topic: Classification Aim: Describe how to use dichotomous keys. Do Now: HW: Classification Castle Learning due Tuesday, January 12th. 1. Identify the kingdoms that contain Archaea, Eubacteria, unicellular organisms. Protists, Fungi 2. Identify the kingdoms that consist of multicellular organisms. Fungi, Plants, Animals 3. Identify the kingdoms that contain prokaryotic cells. Archaea and Eubacteria 4. Identify the kingdoms that consist of eukaryotic cells. Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals 5. Identify the kingdoms that consist of autotrophic organisms. Protists and Plants 6. Identify the kingdoms that consist of heterotrophic organisms. Protists, Fungi, Animals 7. Identify the kingdom that consists of organisms that live in EXTREME environments. Archaea bacteria 8. Identify the kingdom that contains PROTOZOA. Are they autotrophic or heterotrophic? Protists Protozoa are heterotrophic. Which kingdom does this picture represent? Support your answer. Archaea bacteria live in extreme environments. Which kingdom does this picture represent? Support your answer. Eubacteria are very common and can be found in a lot of places. Which kingdom does this picture represent? Support your answer. Ameba are PROTISTS. They are heterotrophic protozoa. Which kingdom does this picture represent? Support your answer. Algae are PROTISTS. They are autotrophic. Which kingdom does this picture represent? Support your answer. FUNGI are heterotrophic. They are decomposers. PLANTS are autotrophic. They are multicellular. Which kingdom does this picture represent? Support your answer. ANIMALS are heterotrophic. They are multicellular. 1.What do scientists use dichotomous keys for? • To classify organisms into classification categories or taxa 2. Describe the meaning of the term “dichotomous.” • Divided in two parts 3. How many choices does each step consist of? • TWO choices • Example: 1. A. Has a backbone. B. Does not have a backbone 4. When using a dichotomous key, which number (or pair) must you always begin with? • Always start with #1. 5. In each pair, which statement do you read first? • Begin with statement A. • Example: 1. A. Has a backbone. B. Does not have a backbone 6. Explain what to do when statement A is correct. • Follow the directions located to the right. 7. Explain what to do if statement A is incorrect. • Read statement B and follow the directions located to the right. BANANA APPLE PEACH Topic: Classification Aim: Describe how to use dichotomous keys. Do Now: Work on the Alien Dichotomous Key on the back of the reading notes. HW: Classification Castle Learning due Tuesday, January 12th. Let’s go over the DK rules. 1. Identify the number you must always start with when your identifying an organism. 2. Identify the letter you must always start with. 3. Explain what must be done if statement A is correct. 4. Explain what must be done if statement A is incorrect. 5. Explain what must be done if statement B is correct. How to Use a Dichotomous Key backbone 1 2 backbone 3 backbone No 4 backbone 1 a. Backbone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . go to 2 b. No backbone . . . . . . . . . . . . . go to 5 2 a. Wings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . bat b. No wings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . go to 3 3 a. Legs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . go to 4 b. No legs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . snake 4 a. Shell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . tor toise b. No shell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . lizar d 5 a. Antenna . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ant b. No antenna . . . . . . . . . . . . . . spider No 5 backbone 1. SNAKE 2. LIZARD 3. TORTOISE 4. SPIDER 5. ANT 6. BAT 6 backbone 1 a. Mout h open . . . . . . . . . . . . . . go t o 2 b. Mout h not open . . . . . . . . . . . go t o 4 2 a. Ar ms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . go t o 3 b. No Ar ms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Alienus q uadlegicus 3 a. Hair y . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Alienus hair icus b. Not hair y . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Alienus t r it oot hicus 4 a. No hor ns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . go t o 5 b. Hor ns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Alienus st r ipicus 5 a. No legs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Alienus blobicus b. Legs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Alienus f uzzicus Wr it e your answer s below. Alienus quadlegicus Alienus biobicus ! ! Alienus fuzzicus Alienus stripicus Alienus tritoothicus Alienus hairicus Each of t hese aliens belongs t o t he same genus. What is t heir genus? Alienus Let’s review… 1. Why do scientists use dichotomous keys? To classify an organism into a certain taxa 2. When starting a dichotomous key, which step or number do you ALWAYS start with? Always start with #1. 3. How many choices are found at each number? Two choices A and B 4. Which choice do you always start with (A or B)? Always start with A. 5. What do you do if the first statement (A) is false? Read statement B. Topic: Classification Aim: Describe how to use dichotomous keys. Do Now: Numbers!!! HW: Classification Exam Review sheet due Monday, Classification Castle Learning due Tuesday, January 12th. Review: Which kingdom is made up of unicellular organisms with no nucleus and can be found in hydrothermal vents? (1.) Eubacteria (2.) Fungi (3.) Archaebacteria (4.) Protists A scientist recently discovered a pond organism that is unicellular, contains chloroplasts and other membranebound organelles, and possesses a flagellum. In which kingdom is this organism classified? (1.) Eubacteria (2.) Fungi (3.) Protists (4.) Plant Mushrooms and molds belong to the kingdom (1.) Fungi (2.) Plants (3.) Protists (4.) Animals An organism that is unicellular, contains a nucleus and is autotrophic is classified as a (1.) Plant (2.) Protist (3.) Algae (4.) Fungi Multicellular organisms that absorb digested nutrients from the environment is classified as (1.) animals (2.) fungi (3.) protists (4.) paramecia The scientific name for a lion is Panthera Leo. The word Panthera tells us the lion’s (1.) kingdom (2.) phylum (3.) genus (4.) species Members of a population of gray squirrels, Sciurus carolinensis, are classified in the same species because they (1.) obtain their food in the same manner (2.) produce enzymes by synthesis (3.) can mate and produce fertile offspring (4.) live in the same area In today’s classification system, 2 organisms would be most closely related if they were classified in the same (1.) kingdom (2.) phylum (3.)genus (4.)species Review: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6 H2O + X 1. What is the name of the process represented above? 2. Where does this process occur? 3. What molecule does X represent? C6H12O6 CO2 + alcohol + X C6H12O6 lactic acid + X 1. Identify the type of respiration these processes represent. 2. Identify the name and location of each of these processes. 3. Describe what X represents. The diagram above shows the same type of molecule in area A and area B. With the passage of time, some molecules move from area A to area B. Identify the name of this process. Support your answer. The diagram above shows the same type of molecule in area A and area B. Identify the name of this process if some molecules move from area B to area A. Support your answer. The movement of materials from lower to higher concentration requiring energy in the form of ATP is called 1. movement 2. diffusion 3. active transport 4. cell division These groups of cells represent different (1) tissues in which similar cells function together (2) organs that help to carry out a specific life activity (3) systems that are responsible for a specific life activity (4) organelles that carry out different functions.