OCR AS Biology Student Worksheet Activity 29 (DOC, 197 KB)
advertisement
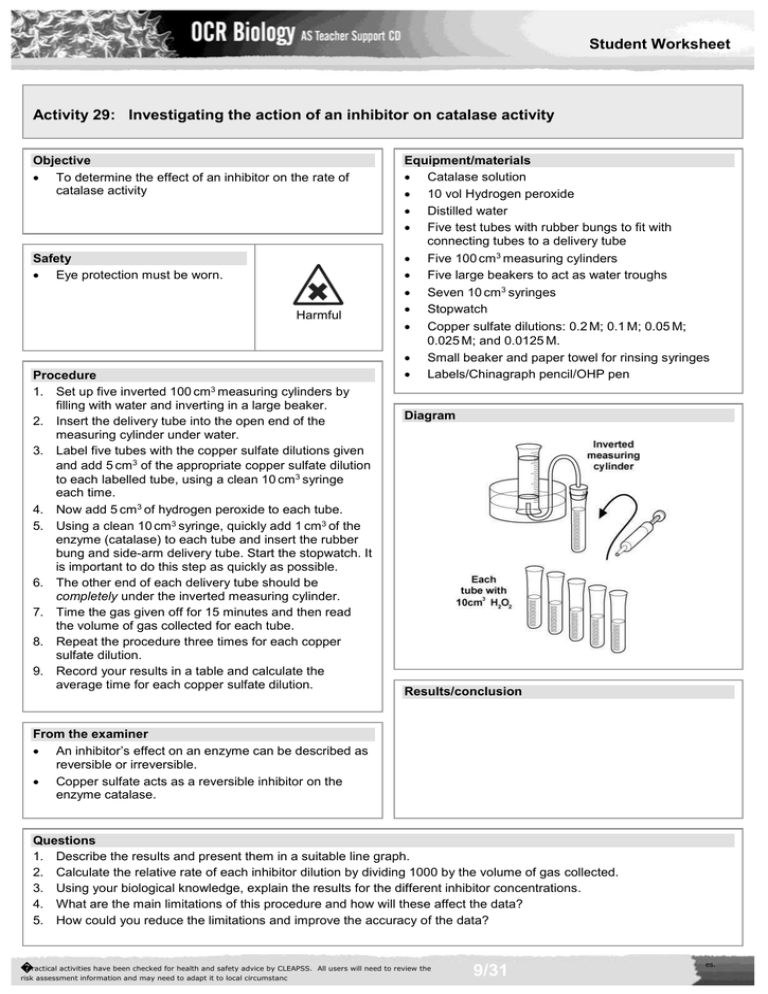
Student Worksheet Activity 29: Investigating the action of an inhibitor on catalase activity Objective To determine the effect of an inhibitor on the rate of catalase activity Safety Eye protection must be worn. Harmful Procedure 1. Set up five inverted 100 cm3 measuring cylinders by filling with water and inverting in a large beaker. 2. Insert the delivery tube into the open end of the measuring cylinder under water. 3. Label five tubes with the copper sulfate dilutions given and add 5 cm3 of the appropriate copper sulfate dilution to each labelled tube, using a clean 10 cm3 syringe each time. 4. Now add 5 cm3 of hydrogen peroxide to each tube. 5. Using a clean 10 cm3 syringe, quickly add 1 cm3 of the enzyme (catalase) to each tube and insert the rubber bung and side-arm delivery tube. Start the stopwatch. It is important to do this step as quickly as possible. 6. The other end of each delivery tube should be completely under the inverted measuring cylinder. 7. Time the gas given off for 15 minutes and then read the volume of gas collected for each tube. 8. Repeat the procedure three times for each copper sulfate dilution. 9. Record your results in a table and calculate the average time for each copper sulfate dilution. Equipment/materials Catalase solution 10 vol Hydrogen peroxide Distilled water Five test tubes with rubber bungs to fit with connecting tubes to a delivery tube Five 100 cm3 measuring cylinders Five large beakers to act as water troughs Seven 10 cm3 syringes Stopwatch Copper sulfate dilutions: 0.2 M; 0.1 M; 0.05 M; 0.025 M; and 0.0125 M. Small beaker and paper towel for rinsing syringes Labels/Chinagraph pencil/OHP pen Diagram Results/conclusion From the examiner An inhibitor’s effect on an enzyme can be described as reversible or irreversible. Copper sulfate acts as a reversible inhibitor on the enzyme catalase. Questions 1. Describe the results and present them in a suitable line graph. 2. Calculate the relative rate of each inhibitor dilution by dividing 1000 by the volume of gas collected. 3. Using your biological knowledge, explain the results for the different inhibitor concentrations. 4. What are the main limitations of this procedure and how will these affect the data? 5. How could you reduce the limitations and improve the accuracy of the data? �Practical activities have been checked for health and safety advice by CLEAPSS. risk assessment information and may need to adapt it to local circumstanc All users will need to review the 9/31 es.




