Updated C4E Matching Chart - SHM 3 (DOC, 171 KB)
advertisement
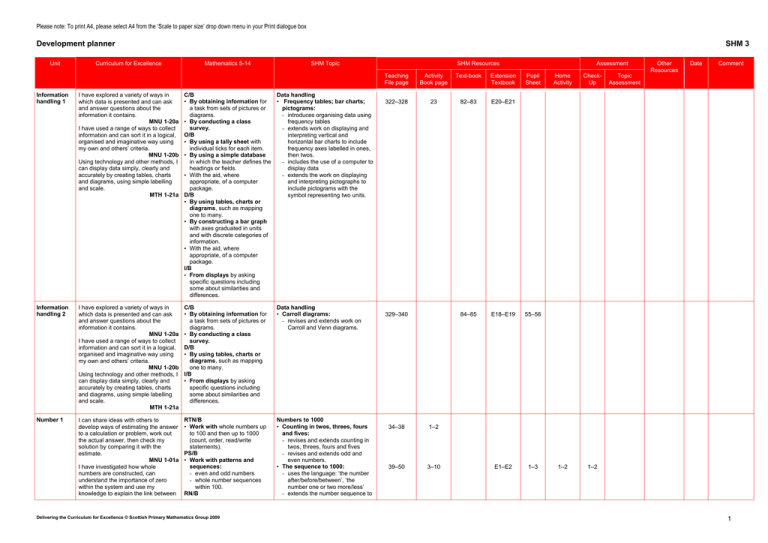
Please note: To print A4, please select A4 from the ‘Scale to paper size’ drop down menu in your Print dialogue box Development planner Unit Curriculum for Excellence SHM 3 Mathematics 5-14 SHM Topic Information handling 1 I have explored a variety of ways in which data is presented and can ask and answer questions about the information it contains. MNU 1-20a I have used a range of ways to collect information and can sort it in a logical, organised and imaginative way using my own and others’ criteria. MNU 1-20b Using technology and other methods, I can display data simply, clearly and accurately by creating tables, charts and diagrams, using simple labelling and scale. MTH 1-21a C/B Data handling • By obtaining information for • Frequency tables; bar charts; pictograms: a task from sets of pictures or diagrams. - introduces organising data using • By conducting a class frequency tables survey. - extends work on displaying and O/B interpreting vertical and • By using a tally sheet with horizontal bar charts to include individual ticks for each item. frequency axes labelled in ones, • By using a simple database then twos. in which the teacher defines the - includes the use of a computer to headings or fields. display data • With the aid, where - extends the work on displaying appropriate, of a computer and interpreting pictographs to package. include pictograms with the D/B symbol representing two units. • By using tables, charts or diagrams, such as mapping one to many. • By constructing a bar graph with axes graduated in units and with discrete categories of information. • With the aid, where appropriate, of a computer package. I/B • From displays by asking specific questions including some about similarities and differences. Information handling 2 I have explored a variety of ways in which data is presented and can ask and answer questions about the information it contains. MNU 1-20a I have used a range of ways to collect information and can sort it in a logical, organised and imaginative way using my own and others’ criteria. MNU 1-20b Using technology and other methods, I can display data simply, clearly and accurately by creating tables, charts and diagrams, using simple labelling and scale. MTH 1-21a C/B • By obtaining information for a task from sets of pictures or diagrams. • By conducting a class survey. D/B • By using tables, charts or diagrams, such as mapping one to many. I/B • From displays by asking specific questions including some about similarities and differences. Data handling • Carroll diagrams: - revises and extends work on Carroll and Venn diagrams. Number 1 I can share ideas with others to develop ways of estimating the answer to a calculation or problem, work out the actual answer, then check my solution by comparing it with the estimate. MNU 1-01a I have investigated how whole numbers are constructed, can understand the importance of zero within the system and use my knowledge to explain the link between RTN/B • Work with whole numbers up to 100 and then up to 1000 (count, order, read/write statements). PS/B • Work with patterns and sequences: - even and odd numbers - whole number sequences within 100. RN/B Numbers to 1000 • Counting in twos, threes, fours and fives: - revises and extends counting in twos, threes, fours and fives - revises and extends odd and even numbers. • The sequence to 1000: - uses the language: ‘the number after/before/between’, ‘the number one or two more/less’ - extends the number sequence to Delivering the Curriculum for Excellence © Scottish Primary Mathematics Group 2009 SHM Resources Assessment Teaching File page Activity Book page Text-book Extension Textbook 322–328 23 82–83 E20–E21 84–85 E18–E19 55–56 E1–E2 1–3 329–340 34–38 1–2 39–50 3–10 Pupil Sheet Home Activity CheckUp 1–2 1–2 Other Resources Date Comment Topic Assessment 1 Please note: To print A4, please select A4 from the ‘Scale to paper size’ drop down menu in your Print dialogue box Unit Number 1 (cont.) Curriculum for Excellence Mathematics 5-14 SHM Topic • Round 2-digit whole numbers a digit, its place and its value. 1000 MNU 1-02a to the nearest 10. - introduces finding numbers 10 or I can use addition, subtraction, 100 more/less multiplication and division when - introduces adding/subtracting 10, solving problems, making best use of 100, multiples of 10, multiples of the mental strategies and written skills 100 • Counting in hundreds, tens and I have developed. MNU 1-03a ones: I can continue and devise more - deals with counting in hundreds, involved repeating patterns or designs, then in tens, then in ones to using a variety of media. 1000. MTH 1-13a • Place value, comparing and ordering: Through exploring number patterns, I can recognise and continue simple - introduces place value in 3-digit number sequences and can explain numbers the rule I have applied. - deals with recognising: MTH 1-13b - the larger or smaller number in I can compare, describe and show a pair number relationships, using - the largest or smallest number appropriate vocabulary and the in sets of up to six symbols for equals, not equal to, less - includes ordering up to six nonthan and greater than. consecutive numbers, starting MTH 1-15a with the smallest/largest. • Numbers halfway between, estimating and rounding: - deals with numbers between and halfway between the two given numbers - develops ideas about estimation of a number from its position on a number line - consolidates rounding to the nearest ten. • Number names, ordinal numbers: - introduces number names for multiples of ten and multiples of one hundred - consolidates first, second…. tenth and the notation 1st, 2nd, … 10th - introduces, eleventh, twelfth…. twentieth and the notation 11th, 12th, … 20th ASSESSMENT Delivering the Curriculum for Excellence © Scottish Primary Mathematics Group 2009 SHM Resources Teaching File page Activity Book page 51–53 11–13 54–60 14–17 61–66 18–20 67–74 21–23 Text-book Extension Textbook Assessment Pupil Sheet Home Activity CheckUp 3 3 Other Resources Date Comment Topic Assessment 4–5 1a, 1b 2 Please note: To print A4, please select A4 from the ‘Scale to paper size’ drop down menu in your Print dialogue box Development planner Unit SHM 3 Curriculum for Excellence Mathematics 5-14 SHM Topic SHM Resources Teaching File page Number I can share ideas with others to develop ways of 2 estimating the answer to a calculation or problem, work out the actual answer, then check my solution by comparing it with the estimate. MNU 1-01a I have investigated how whole numbers are constructed, can understand the importance of zero within the system and use my knowledge to explain the link between a digit, its place and its value. MNU 1-02a I can use addition, subtraction, multiplication and division when solving problems, making best use of the mental strategies and written skills I have developed. MNU 1-03a Through exploring number patterns, I can recognise and continue simple number sequences and can explain the rule I have applied. MTH 1-13b I can compare, describe and show number relationships, using appropriate vocabulary and the symbols for equals, not equal to, less than and greater than. MTH 1-15a When a picture or symbol is used to replace a number in a number statement, I can find its value using my knowledge of number facts and explain my thinking to others. MTH 1-15b AS/B • Mentally for numbers 0 to 20; in some cases beyond 20 • Without a calculator for 2 digit numbers • With a calculator for numbers to two digits added to three digits. • In applications in number, measurement and money, including payments and change up to £1. FE/B • Find the missing numbers in statements where symbols are used for unknown numbers or operators. Addition to 100 • Addition facts to 20: - revises and consolidates addition facts to 20, for example, 6 + 8, 10 + 7 - systematises addition of a single digit and a teens number not bridging 20, for example, 15 + 3, 7 + 12 • Addition of a 2-digit number and a single digit, 10, and a multiple of 10: - introduces mental addition of a 2-digit number and a single digit (non-bridging examples only) for example, 35 + 4, 6 + 52 - revises addition of 10 and multiples of 10 to 2-digit numbers, for example, 53 + 10, 20 + 60, 28 + 40 • Addition of 2-digit numbers: - Revises adding mentally 9 or 11, based on adding 10 and adjusting, and extends this strategy to adding 19, 29, 39… and 21, 31, 41 - Deals with adding a teens number to a 2-digit number without bridging a multiple of 10, for example, 54 + 13, 45 + 7 - Introduces mental addition of 2-digit numbers, for example, 32 + 55, 71 + 27, including pairs of multiples of 5 which total 100. • Addition of 2-digit numbers and single digit/teens number, with bridging: - introduces addition of a 2-digit number and a single digit, with bridging, for example, 38 + 5, 45 + 7 - introduces addition of a 2-digit number and a teens number, with bridging, for example, 54 + 18, 14 + 67 • Addition of 2-digit numbers, with bridging: - introduces addition of 2-digit numbers, with bridging, for example, 63 + 28, 35 + 47 - continues to develop informal ‘jotting’ methods to support mental calculation strategies - introduces a vertical recording with tens and units aligned, for example, - 58 + 24 50 + 8 20 + 4 70 + 12 82 - develops mental strategies for the addition of several small numbers, for example, looking for doubles, pairs which total 10 - provides opportunities for using and applying the above methods. Activity Book page Textbook Assessment Extension Pupil Textbook Sheet Home Activity CheckUp 78–83 1–4 84–88 5–6 6 5 4 89–95 7–10 7–8 6–7 5 96–99 11–12 9 8 6 100–116 24–25 13–16 AS/B • Mentally for number 0 to 20, in some cases beyond 20. • Without a calculator for 2-digit numbers. • With a calculator for numbers to two digits subtracted from three digits. • In application in number, measurement Delivering the Curriculum for Excellence © Scottish Primary Mathematics Group 2009 Subtraction to 100 • Consolidation of facts to 20: - consolidates subtraction facts to 20. • Subtracting a single digit, a multiple of 10: - introduces subtracting a single digit from a 2-digit number using patterns of similar calculations, without bridging, for example, 39 – 7 - introduces subtracting a multiple of 10 from a 2-digit number, for example 84 – 40 - introduces subtracting mentally 11, 21 and 9, 19 and extends this to subtracting mentally 31, 41, … and 29, 30, … Topic Assessment 4 E3–E8 10– 11 2a, b ASSESSMENT Number I can share ideas with others to develop ways of 3 estimating the answer to a calculation or problem, work out the actual answer, then check my solution by comparing it with the estimate. MNU 1-01a I have investigated how whole numbers are constructed, can understand the importance of zero within the system and use my knowledge to explain the link between a digit, its place and its value. MNU 1-02a I can use addition, subtraction, multiplication and division when solving problems, making best use of the mental Other Date Comment Resources 120–125 17–20 126–132 21–23 12– 13 9 7 8 3, 14– 16 3 Please note: To print A4, please select A4 from the ‘Scale to paper size’ drop down menu in your Print dialogue box Unit Curriculum for Excellence Mathematics 5-14 SHM Topic SHM Resources Teaching File page Number strategies and written skills I have developed. and money, including 3 MNU 1-03a payment and change u (cont.) Through exploring number patterns, I can recognise and to £1. continue simple number sequences and can explain the FE/B rule I have applied. MTH 1-13b • Finding the missing numbers in statements I can compare, describe and show number relationships, using appropriate vocabulary and the symbols for equals, where symbols are not equal to, less than and greater than. used for known MTH 1-15a numbers or operators. When a picture or symbol is used to replace a number in a number statement, I can find its value using my knowledge of number facts and explain my thinking to others. MTH 1-15b • Subtracting a 2-digit number: - introduces subtracting a teens number from a 2-digit number, for example, 76 – 14 - introduces subtracting a 2-digit number from a 2-digit number, for example, 88 – 23 - applies mental strategies to the subtraction of 2-digit numbers. • Subtracting a single digit, bridging multiples of 10: - introduces mental subtraction of single-digit numbers ‘bridging’ 20, for example, 24 – 8, 25 – 7 - introduces mental subtraction of single-digit numbers ‘bridging’ other multiples of 10, for example, 45 – 6, 73 – 7 • Subtracting a 2-digit number, bridging multiples of 10: - introduces subtraction of 2-digit numbers, bridging multiples of 10, using: - number lines and ‘jottings’ - mental calculation, for example, 54 – 16, 63 – 47 - prepares for the introduction of a standard written method of subtracting 2-digit numbers: - not bridging a multiple of 10, for example, 78 – 35 - bridging a multiple of 10, for example, 65 – 37 - applies mental strategies to the subtraction of 2-digit numbers. • Linking addition and subtraction, problem solving and enquiry: - links addition and subtraction of 2-digit numbers - uses and applies addition and subtraction of 2-digit numbers - introduces addition and subtraction of 3-digit numbers using a calculator. Activity Book page Textbook 133–138 24–26 139–142 27–28 143–151 29–32 152–160 26 33–36 Assessment Extension Pupil Textbook Sheet 17 Home Activity CheckUp 10 9 MD/B • Mentally by 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, within the confines of these tables. • Without a calculator for 2-digit numbers multiplied by 2, 3, 4, 5, 10. • With a calculator for 2digit numbers multiplied by any digit. • In applications in number, measurement and money to £1. FE/B • Find the missing numbers in statements where symbols are used for unknown numbers or operators. Delivering the Curriculum for Excellence © Scottish Primary Mathematics Group 2009 Multiplication • The 2, 10 and 5 times table: - revises the 2 times table - introduces the 10 and 5 times table. • The 3 and 4 times tables: - introduces the 3 and 4 times tables - consolidates the 2, 3, 4, 5 and 10 times table. • Multiplication of a 2-digit number: - deals with multiples of 2 - introduces multiplication of multiples of 10 up to 50 by 2, 3, 4, 5, and 10 - introduces doubling to double 15 and extends this to doubling 16 to 20 - introduces multiplication of a 2-digit number by 2, 3 and 4 without bridging, for example, 2 × 41, 4 × 22 - uses and applies multiplication facts. ASSESSMENT Topic Assessment 11 18– 23 10 12 E9 ASSESSMENT Number I can share ideas with others to develop ways of 4 estimating the answer to a calculation or problem, work out the actual answer, then check my solution by comparing it with the estimate. MNU 1-01a I have investigated how whole numbers are constructed, can understand the importance of zero within the system and use my knowledge to explain the link between a digit, its place and its value. MNU 1-02a I can use addition, subtraction, multiplication and division when solving problems, making best use of the mental strategies and written skills I have developed. MNU 1-03a Through exploring number patterns, I can recognise and continue simple number sequences and can explain the rule I have applied. MTH 1-13b I can compare, describe and show number relationships, using appropriate vocabulary and the symbols for equals, not equal to, less than and greater than. MTH 1-15a When a picture or symbol is used to replace a number in a number statement, I can find its value using my knowledge of number facts and explain my thinking to others. MTH 1-15b Other Date Comment Resources 3a, b 164–172 27–30 37–39 173–181 31–32 40–43 182–190 44–46 E10 13–15 11–12 3 16–18 13 24 19 14 4a, b 4 Please note: To print A4, please select A4 from the ‘Scale to paper size’ drop down menu in your Print dialogue box Development planner Unit Number 5 Number 6 Curriculum for Excellence I can share ideas with others to develop ways of estimating the answer to a calculation or problem, work out the actual answer, then check my solution by comparing it with the estimate. MNU 1-01a I have investigated how whole numbers are constructed, can understand the importance of zero within the system and use my knowledge to explain the link between a digit, its place and its value. MNU 1-02a I can use addition, subtraction, multiplication and division when solving problems, making best use of the mental strategies and written skills I have developed. MNU 1-03a Through exploring number patterns, I can recognise and continue simple number sequences and can explain the rule I have applied. MTH 1-13b I can compare, describe and show number relationships, using appropriate vocabulary and the symbols for equals, not equal to, less than and greater than. MTH 1-15a When a picture or symbol is used to replace a number in a number statement, I can find its value using my knowledge of number facts and explain my thinking to others. MTH 1-15b SHM 3 Mathematics 5-14 MD/B • Mentally by 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, within the confines of these tables. • With a calculator for 2-digit numbers multiplied by any digit. • In application in number, measurement and money to £1. FE/B • Find the missing numbers in statements where symbols are used for unknown numbers or operators. M/B I can share ideas with others to develop • Use coins up to £1 including ways of estimating the answer to a calculation or problem, work out the actual exchange (50p = 5 × 10p). answer, then check my solution by comparing it with the estimate. MNU 1-01a I have investigated how whole numbers are constructed, can understand the importance of zero within the system and use my knowledge to explain the link between a digit, its place and its value. MNU 1-02a I can use addition, subtraction, multiplication and division when solving problems, making best use of the mental strategies and written skills I have developed. MNU 1-03a I can use money to pay for items and can work out how much change I should receive. MNU 1-09a I have investigated how different combinations of coins and notes can be used to pay for goods or be given in change. MNU 1-09b Delivering the Curriculum for Excellence © Scottish Primary Mathematics Group 2009 SHM Topic Division • Dividing by 2 and by 10; halving: - revises mental division by 2 and by 10 - revises linking division by 2 with halving an even number to 20. • Dividing by 5: - introduces mental link between division by 5 - reinforces the link between division and multiplication • Dividing by 3: - introduces mental division by 3 - reinforces the link between division and multiplication • Dividing by 4; consolidation: - introduces mental division by 4 - consolidates mental division by 2, 3, 4, 5 and 10 - reinforces the link between division and multiplication. • Problem solving and enquiry, remainders: - introduces remainders through grouping and sharing - deals with rounding answers in context. SHM Resources Teaching File page Activity Book page Text-book 194–200 33–37 47–48 Extension Textbook Assessment Pupil Sheet Home Activity CheckUp 49–50 3, 25 23 15–16 205–208 51–52 3 24 17 209–217 53–58 3 25–26 18–19 38–39 59–60 Comment Topic Assessment E12–E13 ASSESSMENT Money • Using the £1 coin: - revises counting coin collections and laying out amounts to 99p - introduces the £1 coin - deals with counting and laying out amounts beyond £1 - includes finding change from £1 - involves finding the difference between two amounts. Date 20–22 201–20 218–226 Other Resources 5a, b 228–232 61–66 E11 26–27 27 20–21 5 Please note: To print A4, please select A4 from the ‘Scale to paper size’ drop down menu in your Print dialogue box Development planner Unit Curriculum for Excellence SHM 3 Mathematics 5-14 SHM Topic SHM Resources Teaching File page Number 7 Measure 1 Measure 2 Having explored fractions by taking part in practical activities, I can show my understanding of: - how a single item can be shared equally - the notation and vocabulary associated with fractions - where simple fractions lie on the number line. - MNU 1-07a Through exploring how groups of items can be shared equally, I can found a fraction of an amount by applying my knowledge of division. MNU 1-07b Through taking part in practical activities including use of pictorial representations, I can demonstrate my understanding of simple fractions which are equivalent. MTH 1-07c RTN/B • Work with quarters (practical applications only). FPR/B • Find halves and quarters of quantities involving 1 or 2 digit numbers, for example by sharing. Factions • Halves and quarters: - revises and consolidates halves and quarters of shapes - revises finding half of a number - introduces finding one quarter of a number and uses this to find three quarters of a number - provides extension activities which introduce finding one tenth of a shape and number. I can estimate how long or heavy an object is, or what amount it holds, using everyday things as a guide, then measure or weigh it using appropriate instruments and units. MNU 1-11a I can use the common units of measure, convert between related units of the metric system and carry out calculations when solving problems. MNU 2-11b ME/B • Measure in easily handled standard units and fractions of them: 1 1 Length: m, 2 m, 4 m, cm. Measure • Length: metres and centimetres: - introduces estimation of length in metres and in centimetres - introduces measurement of lengths in metres and in centimetres using metre sticks and rulers. I have experimented with everyday items as units of measure to investigate and compare sizes and amounts in my environment, sharing my findings with others. MNU 0-11a I can estimate how long or heavy an object is, or what amount it holds, using everyday things as a guide, then measure or weigh it using appropriate instruments and units. MNU 1-11a ME/B • Measure in easily handled standard units and fractions of them: 1 Weight: kg, 2 kg. • Place sets of objects in order of length. • Use the abbreviations m, cm. • Realise that length can be conserved when shape changes. • Read scales on measuring devices to the nearest graduation, where each graduation is labelled. • Place sets of objects in order of weight. • Read scales on measuring devices to the nearest graduation, where each graduation is labelled. Delivering the Curriculum for Excellence © Scottish Primary Mathematics Group 2009 Measure • Weight: - revises comparing weights using non-standard units - introduces the kilogram and half kilogram - deals with weighing in kilograms, using scales. Activity Book page 234–240 242–250 1–4 252–256 5–7 Assessment Text-book Extension Textbook Pupil Sheet Home Activity CheckUp 67–68 E14–E15 28–33 28 22 Other Resources Date Comment Topic Assessment 69–70 6 Please note: To print A4, please select A4 from the ‘Scale to paper size’ drop down menu in your Print dialogue box Development planner Unit Measure 3 Time 1 Time 2 Shape 1 Curriculum for Excellence SHM 3 Mathematics 5-14 I have experimented with everyday items as ME/B • Measure in easily handled units of measure to investigate and standard units and factions of compare sizes and amounts in my environment, sharing my findings with them • Read scales on measuring others. MNU 0-11a devices to the nearest I can estimate how long or heavy an object graduation, where each is, or what amount it holds, using everyday graduation is labelled. things as a guide, then measure or weigh it using appropriate instruments and units. MNU 1-11a SHM Topic Measure • Capacity: the litre: - revises comparison of capacities for non-standard units - introduces the litre as a standard unit - introduces calculations involving litres. I am aware of how routines and events in my world link with times and seasons, and have explored ways to record and display these using clocks, calendars and other methods. MNU 0-10a I can tell the time using 12 hour clocks, realising there is a link with 24 hour notation, explain how it impacts on my daily routine and ensure that I am organised and ready for events throughout my day. MNU 1-10a T/B • Place events in time sequences • Tell time using analogue displays, and the terms ‘quarter past/to, half past’ • Read time in hours and minutes using digital displays. Time • Telling the time: - revises and consolidates ‘o’clock’ and ‘half past’ times on analogue and digital clocks - introduces ‘quarter past’ and ‘quarter to’ times on analogue and digital clocks - involves writing these times as, for example, quarter to 7 - introduces a ‘new’ notation for these times, for example, 9.00, 9.15, 9.30, 9.45 - deals with ordering ‘o’clock’, ‘quarter past’, ‘half past’ and ‘quarter to’ times given as analogue or digital displays and in the 12-hour notation. I am aware of how routines and events in my world link with times and seasons, and have explored ways to record and display these using clocks, calendars and other methods. MNU 0-10a I can tell the time using 12 hour clocks, realising there is a link with 24 hour notation, explain how it impacts on my daily routine and ensure that I am organised and ready for events throughout my day. MNU 1-10a T/B • Place events in time sequence • Tell time using analogue displays, and the terms ‘quarter past/to, half past’ • Read time in hours and minutes using digital displays. Time • Durations: - introduces finding the time 15 or 30 minutes after or before given digital or analogue times - introduces finding durations of 15 minutes, 30 minutes or whole hours between given digital or analogue times. I enjoy investigating objects and shapes and can sort, describe and be creative with them. MTH 0-16a I have explored simple 3D objects and 2D shapes and can identify, name and describe their features using appropriate vocabulary. MTH 1-16a RS/B • Collect, discuss, make and use 3D shapes. • Respond to written or oral descriptions which refer to features of shapes such as faces, edges, corners, sides and angles. • Identify and name triangular prism, square pyramid. • Make 3D shapes from diagrams or pictures. SHM Resources Teaching File page Activity Book page 258–260 8–9 262–272 10–12 273–280 13 Text-book 71–72 Extension Textbook Assessment Pupil Sheet Home Activity CheckUp 34–36 29 23 37–39 30 24 ASSESSMENT Delivering the Curriculum for Excellence © Scottish Primary Mathematics Group 2009 Shape • 3D shape: - revises recognising and naming spheres, cubes, cuboids, cones and cylinders - introduces pyramids - introduces prisms - builds models with these shapes - deals with properties associated with 3D shapes – faces, corners and edges. Other Resources Date Comment Topic Assessment 6a, b 282–290 14–16 73–75 40–42 7 Please note: To print A4, please select A4 from the ‘Scale to paper size’ drop down menu in your Print dialogue box Development planner Unit Shape 2 Shape 3 Shape 4 Curriculum for Excellence I have spotted and explored patterns in my own and the wider environment and can copy and continue these and create my own patterns. MTH 0-13a I enjoy investigating objects and shapes and can sort, describe and be creative with them. MTH 0-16a I can continue and devise more involved repeating patterns or designs, using a variety of media. MTH 1-13a I have explored simple 3D objects and 2D shapes and can identify, name and describe their features using appropriate vocabulary. MTH 1-16a SHM 3 Mathematics 5-14 RS/B Shape • Collect, discuss, make and • 2D shape: recognising and use 2D shapes. describing shapes: • Respond to written or oral - revises the circle, square, descriptions which refer to rectangle, triangle, hexagon and features of shapes such as simple properties of their sides corners, sides, angles. and corners • Find shapes that will tile and - introduces the pentagon and continue tilings using grids or octagon and simple properties tiles. of their sides and corners PS/B - uses shape to copy, continue Work with patterns and and create patterns. sequences: - more complex sequences with shapes. S/B I have had fun creating a range of symmetrical pictures and patterns using a • Recognise symmetrical shapes range of media. by folding or using a mirror. MTH 0-19a I have explored symmetry in my own and the wider environment and can create and recognise symmetrical pictures, patterns and shapes. MTH 1-19a I can illustrate the lines of symmetry for a range of 2D shapes and apply my understanding to create and complete symmetrical pictures and patterns. MTH 2-19a I can describe, follow and record routes and journeys using signs, words and angles associated with direction and turning. MTH 1-17a I have developed an awareness of where grid reference systems are used in everyday contexts and can use them to locate and describe position. MTH 1-18a I have investigated angles in the environment, and can discuss, describe and classify angles using appropriate mathematical vocabulary. MTH 2-17a Through practical activities, which include the use of technology, I have developed my understanding of the link between compass points and angles and can describe, follow and record directions, routes and journeys using appropriate vocabulary. MTH 2-17c SHM Topic PM/B • Discuss position and movement. • Give and understand instructions for turning through right angles. • Recognise and name the four compass points. • Use grid references to read or plot location on grid. • Give and follow directions to create a square or rectangle. A/B • Use a template to draw or check for a right angle. Delivering the Curriculum for Excellence © Scottish Primary Mathematics Group 2009 Shape • 2D shape: symmetry: - revises folding paper shapes to find a line of symmetry - introduces finding and sketching a line of symmetry with the aid of a mirror - introduces completing a symmetrical pattern. Shape • 2D shape: position, movement and angle: - introduces turning clockwise and anti-clockwise through whole, half and quarter turns - introduces right angles - introduces grid references - introduces the four compass directions North, South, East and West - revises moving forwards and turning left and right on a squared grid and introduces the abbreviations F, R and L for these movements SHM Resources Assessment Teaching File page Activity Book page Text-book Extension Textbook Pupil Sheet 292–300 17–18 76–78 E16 43–48 301–306 19 79 E17 49–50 308–318 20–22 80–81 E22 51–54 Home Activity CheckUp Other Resources Date Comment Topic Assessment 8