Algebra II Description and Outline
advertisement

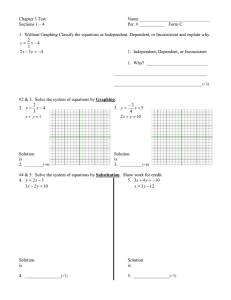
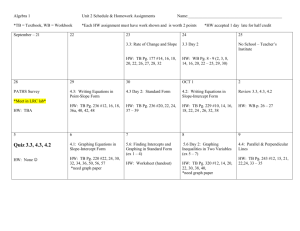
Algebra II Description and Outline Course Overview: This course will review and extend the students understanding of basic algebra. The students will analyze in depth linear, quadratic, and circular relations and will investigate logarithms, complex numbers, sequences and probability. Text: Glencoe, copyright 2010 Teacher Expectations: 1. Students will be expected to attend class on a regular basis. 2. Homework must be completed and turned in on time. No late work will be accepted except in cases of excused absences. In such cases of excused absences the student will be given two days to complete work missing as a result of the absence. Time extensions will be given on a case by case basis. 3. Students must furnish their own paper, pencil. Calculators are optional but recommended. 4. Students will exhibit respect for others at all times. 5. Students will be encouraged to participate in class discussions and communicate with the teacher any difficulties with comprehension of the material covered. Grading: Homework: 30% per quarter Tests/Quizzes: 70% per quarter Each quarter: 40% of the semester grade Semester test: 20% of the semester grade Course Outline: 1. Analyzing Equations and Inequalities. a. Expressions and formulas b. Properties of real numbers c. Solving equations d. Solving absolute value e. Solving inequalities f. Solving absolute inequalities 2. Graphing Linear Relations and Functions a. Relations and functions b. Linear equations c. Slope d. Writing linear equatons e. Scatter plots— Statistics f. Special functions g. Linear inequalities and absolute value 3. Solving Systems of Linear equations and Inequalities a. Graphing systems of equations b. Solving systems of equations algebraically c. Graphing systems of inequalities d. Linear programming e Solving systems of equation--three variables 4. Using Matrices a. Introducing matrices b. Operations with matrices c. Multiplying matrices d. Matrices and determinants, Cramer’s Rule e. Identify and inverse matrices 5. Quadratic Functions and Relations a. Graphing Quadratics b. Solving Quadratics by Graphing c. Solving Quadratics by Factoring d. Complete the Square e. Quadratic Formula and Discriminant f. Transformations g. Quadratic Inequalities 6. Polynomials and Polynomial Functions a. Operations with Polynomials b. Dividing Polynomials c. Polynomial Functions d. Graphs of Polynomials e. Solving Polynomial Equations f. Remainder and Factor Theorems g. Roots and Zeros h. Rational Root Theorem 7. Inverses and Radical Functions and Relations a. Operations b. Inverse Functions and Relations c. Square Root Functions and Inequalities d. nth Root e. Operations with Radical Expressions f. Solving Radical Equations and Inequalities 8. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions and Relations a. Graphing Exponential Functions b. Solving Exponential Equations and Inequalities c. Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions d.Solving Logarithmic Equations e. Properties of Logarithms f. Base e and Natural Logarithms g. Using Exponential Functions 9. Rational Functions and Relations a. Graphing rational functions b. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions c. Adding and subtracting rational expressions d. Solving rational equation 10. Conics a. Midpoint and Distance Formulas b. Parabolas c. Circles d. Ellipses e. Hyperbolas f. Identifying Conic Sections g. Solving Linear-Nonlinear Systems 11. Sequences and Series a. Sequences as Functions b. Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences and Series c. Infinite Geometric Series d. Recursion and Iterations e. The Binomial Theorem f. Proof by Mathematical Induction 12. Probability and Statistics a. Experiments, Surveys, and Observational Studies b. Statistical Analysis c. Probability and Distributions d. The Normal Distribution e. Hypothesis Testing f. Binomial Distributions 13. Trigonometric Functions a. Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles b. Angles and Angle Measure c. Trig Functions of General Angles d. Law of Sines e. Law of Cosines f. Circular Functions g. Graphing Trig Functions h. Translations of Trig Graphs i. Inverse Trig Functions 14. Trigonometric Identities and Equations a. Trig Identities b. Verifying Trig Identities c. Sum and Difference of Angle Identities d. Double and and Half Angle e. Solving Trig Equations Pacing: Units 1-3: first nine weeks Units 4-7: second nine weeks Units 8-10: third nine weeks Units 10-12: fourth nine weeks pacing is dependent upon the progress of the students