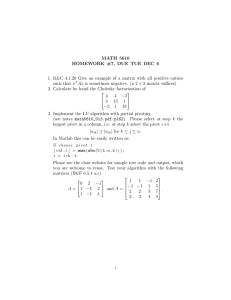
Slideshow: QuickSort
advertisement

Divide and Conquer
Reduce the problem by reducing the data set.
•
The argument being that a smaller data will easier to solve.
•
Recursion
•
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
Quicksort
Quicksort outline
First choose some key from the list for which
about half the keys will come before and half
after. Call this key the pivot.
Then partition the items so that all those with
keys less than the pivot come in one sublist, and
all those with greater keys come in another.
Then sort the two reduced lists separately, put the
sublists together, and the whole list will be in
order.
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
Quicksort
Algorithm
void QSort( int * A, int left, int right )
{
int pivotIndex = Partition(A, left, right);
if( pivotIndex > left + 1 )
QSort( A, left, pivotIndex );
if( pivotIndex < right - 2 )
QSort( A, pivotIndex + 1, right );
}
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
Quicksort
Partition
Partition determines the pivot.
Everything before pivot is less than.
Everything after pivot is greater than.
These elements are all less
than or equal to the pivot
...
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
These elements are all
greater than the pivot
Pivot
Quicksort
...
Choosing the pivot
Algorithm will work for any value we choose
for pivot.
Choose the first element (arbitrarily) as the
pivot.
Move all values less than or equal to pivot
towards the beginning of array.
Move all values greater towards the end.
Where is the dividing line?
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
Quicksort
Moving the elements
Work inwards from both ends of the array.
Start from "left" and look for first element
greater than pivot.
Start from "right" and look for first element
less than pivot.
Swap the two items. They will now be in the
correct ends of the array.
Repeat until searching "meet".
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
Quicksort
Searching
Pivot
40
20
10 80 60 50 7 30 10 90 70
0
leftIndex
[3]
40
20
rightIndex
[7]
10 30 60 50 7 80 10 90 70
0
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
Quicksort
When indexes cross each,
we stop.
Cross over
Low becomes new pivot
exchange old pivot with new pivot
Pivot
40
20
10 30 7 50 60 80 10 90 70
0
rightIndex leftIndex
[4] [5]
7
20
10 30 40 50 60 80 10 90 70
0
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
Quicksort
int Partition(int * A, int left, int right )
{
int
pivot = A[left];
int
indexLeft = left+1;
int
indexRight= right - 1;
{
while( indexLeft < indexRight )
while (indexLeft < right && A[indexLeft] <= pivot)
indexLeft++;
while (A[indexRight] > pivot)
indexRight--;
}
}
if (indexLeft < indexRight)
Swap (A, indexLeft, indexRight);
Swap(A, left, indexRight); //swap pivot & right index
return indexRight; // new location of pivot
Analysis
"
Recursively, the list is divided, resulting in O(log n)
Original
list
What about the partition function?
BIT 143 - Gerard Harrison
File: D|\data\bit143\Fall01\day1212\quicksort.sdd
Quicksort