4- ECG Lectures
advertisement

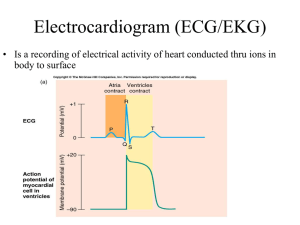
Aim: To get knowledge of the basic principles of Electrocardiography Objectives : 1.Review the principles of cardiac anatomy physiology 2.Know the main 12 leads ECG electrodes and basic waves ,intervals and complex. 3.Determin Heart rate , rhythm ,axis from the ECG 4. Diagnose certain abnormalities , IHD, chamber enlargement, dysrrhythmia Introduction During depolarization & depolarization of the cardiac tissue ,there are changes in the electrical field around the heart. ECG is the recording of these changes . This recording is by surface leads (chest and limbs). Definitions Automaticity : ability of self stimulation. Rhythmicity: forming impulses at regular intervals. Refractory period : time during which the cardiac tissue is refractory to be stimulated Conductivity All or none response. Contractility Conductive Tissue of the Heart Sino atrial node SA node Intra atrial tracts Atrio-ventricular node AV node Atrio-ventricular junction Bundle of Hiss : Left Bundle branch LBB Anterior fascicle posterior fascicle Right Bundle Branch Purkinje fibers Spontaneously firing cells are located:1. Sino-atrial node (right atrial wall near opening of superior vena cava) .2. Atrio-ventricular node (base of right atrium near septum, just above A-V junction) .3. Bundle of His, bundle branches, Purkinje fibres Pace Maker The tissue with higher rate of discharging impulses, usually the SA node(60100/min) Other pacemakers : Atrial tissue 60-80/min. A-V junction 40-60/min. Purkinje system 20-40/min The ECG paper Thermal sensitive paper Measured tow elements : Time &Voltage Horizontal plane measure the time Vertical plane measure the voltage Basic element of the ECG paper is a small square 1mm = 0.04 sec. in the horizontal plane & 1 mm = 0.1 mvolt. In the vertical plane ECG Recording The electrical activity is recorded by Leads positioned at variable points over the body. These are 12 standard leads : Bipolar Limb leads : I(Rt arm-Lt arm) ,II(Rt arm-Lt leg),III (Lt arm-Lt leg) Unipolar Limb leads: aVR(Rt arm), aVL(Lt arm), aVF(Lt leg). Unipolar Chest Leads V1: 4th Rt intercostal space V2: 4th Lt intercostal space V3: between V2 & V4 V4: 5th intercostal space mid clavicular line. V5: 5th intercostal space anterior axillary line. V6: 5th intercostal space mid axillary line Important points in the ECG Correct labeling of the ECG : name , age & exact timing. Correct connection . Correct Calibration :10 mm= 1 m volt. Correct speed (25 mm/sec.) Components of ECG Base line or isoelectrical line. Wave : positive (upward), negative (downward). Segment :length between 2 waves, named by the wave before and after. Interval: length of wave or segment. Complex: group of waves in sequence , QRS complex. How to read the ECG You showed have a system to read & report the followings: Name, Time & date, Calibration, Correct connection ,Rate, Rhythm, Axis. ECG waves , intervals, complex, segment TERMINOLOGY – labelling the waves The rules: the first wave, irrespective of its polarity, is always called a P wave the final wave is called a T wave (unless U waves (rare) are present the first positive wave after a P wave is called an R wave any negative wave after a P wave but before an R wave is called a Q wave any negative wave after an R wave is called an S wave any positive wave after an S wave is called R' Definitions P wave = Atrial depolarization. PR interval = Time for the impulse to travel from SA node to Myocardium. QRS = ventricular depolarization ST segment = Isoelectrical period before re polorazation T wave = ventricular repolarization Heart Rate In normal sinus rhythm , the Atrial rate =ventricular rate =Heart rate Exceptions : e.g In Atrial fibrillation & ventricular tachycardia Each small squire 1 mm = 0.04 ms , ECG paper speed 25mm/sec, 25 x 60=1500 mm/min. Measure P – P interval --- 1500/ P-P = Atrial rate Measure R-R interval --- 1500/R-R = ventricular rate The ECG components P wave - represent atrial contraction or depolarization Duration = 3mm (3 small sq.) Height = 2.5 mm Usually the 1st +ve deflection except in lead aVR Usually rounded Notched P wave – LT atrial enlargement (lead II) Biphasic usually in lead V1 , pecked P wave RT atrial enlargement ( lead III) The PR interval Represents the time needed for the impulse to travel from The SA node –Atria– AV node (where there is usually delay)– Bundle of His – Rt & LT bundle branches– Perkinji fibers – ventricle. The QRS duration = time needed for ventricular depolarization = 0.06-0.1 sec. = 2 ½ small sq. . QRS> 0.1 sec. indicates delay in interventricular conduction PR = 3 mm – 5 mm ( 0.12 -0.2 sec.) Measured from the begging of P to the beginning of R wave QRS voltage = variable according to age , sex ,body build .Low voltage ECG =if the sum R+S in lead I II III < 15 mm seen in advanced heart failure, obesity , emphysema, pericardia effusion High voltage ECG if R wave in I or aVL > 20 mm, S V1 + R V5 or V6 > 35 mm seen in left ventricular hypertrophy The ST segment : Iso electrical period between ventricular depolarization and repolarization ST deviation from base line is abnormal , either ST elevation in MI , pericarditis or ST depression seen in myocardial ischemia , electrolyte disturbances, Ventricular hypertrophy The T wave : ventricular repolarization Usually Up in lead I,II, V3-V6 Usually down in aVR Usually variable in lead III, aVF, aVL,V1V2 Shape : usually rounded , pecked seen in MI Height 5 mm in limb leads , 10 mm in chest leads Tall T wave in MI ,CVA, Hyperkalemia The QT interval Measured from the begging of Q to the end of T wave ( Ventricular depolarization + iso electrical + ventricular repolarization) Normal = 0.32 msec.--- 0.46 msec. Prolonged in heart failure, hypocalemia, drugs. U Wave May be seen in normal ECG usually after the T wave especially in lead V3. *Same direction of T wave . *Become prominent in hypokalemia * Becomes opposite to T wave direction in Myocardial ischemia Cardiac Axis (QRS Axis) It is the average direction of spread of ventricular depolarization. We have to chose 2 leads perpendicular on each other : Lead I X aVF Lead II X aVL Lead III X aVR Lecture 2 Objectives • Know how to diagnose IHD ( Angina , Myocardial infarction) • Know how to diagnose Chamber Hypertrophy Which of the following is True PR interval , represent the time taken for the impulse to travel from SA node to AV nose. QT interval represent Atrial depolarization and depolarization. Q waves are almost always pathological ORS complex duration should be less than 0.1 sec The next lecture will be on “Heart failure” Myocardial infarction Indicate Myocardial necrosis and death Mainly of two types : 1.ST Elevation MI STEMI , full thickness MI , transmural MI, Q MI 2.Non ST Elevation MI , NSTEMI , Sub Endocrinal MI , Non Q MI STEMI : stages Stage 1 : peaked T wave + ST segment Elevation, sub endocrinal injury , no cell death( 1st few hours) Clinical implications : Time limit for reperfusion therapy , 6 hours after the onset of symptoms to preserve myocardial mass (salvage) Stage 2 : Loss of amplitude of R wave , still ST elevation , 1st day , injury extend to epicardium Stage 3 : T inversion ,beginning of Q wave , decrease of ST elevation, 2-3 day Stage 4 : Deep T wave inversion , Marked Q wave , ST my back to base line, > 3 day . Stage 5 :after several weeks : ST back normal wave , T inversion less Age of Myocardial Infarction Acute : peaked T wave ,ST segment elevation. Recent : ST segment Elevation , T wave inversion. Old : If only Q wave . NSTEMI No ST segment elevation ST segment depression , T wave inversion. Clinical implication Since the pathophysiology differ from that of STEMI , thrombolytic therapy is not indicated Localization of MI Anterior V1V2V3V4 Inferior II III aVF Lateral aVL I V5, V6 A 55 year old male patient presents to the ER with central chest pian radiate to the jaw of 3 hours duration associated with SOB , sever exhaustion and sweating .He was heavy smoker , hypertensive on Atenolole 100mg . If you are on call in the ER , your immediate step will be : 1.Do an ECG and if the result is normal, reassure the patient ,send him back home and ask to seek medical advice if symptoms worsen. 2.Do an ECG and if the result is normal , do cardiac enzymes (troponin,CPK) and if it was normal , reassure the patient and send him home . 3.Do and ECG and cardiac enzymes observation even if both are normal. and admit the patient to the hospital for Left Atrial Enlargement P wave < 0.12 sec width , < 2.5 mm height If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I ,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1 , 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral valve stenosis is the most common cause of LA enlargement . It is called P Mitrale RT Atrial Enlargement P wave > 0.12 sec , 2.5 mm (pecked) usually in Lead II III aVF and V1. It is called P pulmonale , because chronic pulmonary disease is frequently the cause. LT Ventricular Hypertrophy Voltage criteria : 1. R Lead 1 or aVL > 20 mm 2. R V5 or V6 + S V1 > 35 mm 3. In sever LVH There will be ST segment depression and T wave inversion in Lateral leads (I aVL,V5 V6) RT Ventricular Hypertrophy Prominent R in V1 ( =or > S wave) . prominent S in V 6( = or > R wave ). Usually associated with RT axis deviation(>+110). In sever RVH ST depression & T wave inversion V1 may be V2 V3 Heart Block The impulse will be conducted from : SA node --- AV node ---- Bundle of His --- RT & LT bundle branches. Any interference with this path way leads to impulse delay or block Level of the block : SA block , AV block , Bundle branch block (BBB), Fascicular block Second degree AV Block Two types : 1- Mobitz type 1 (wenchebach phenomena): Progressive PR segment prolongation till the beat will drop out , P wave which will not followed by QRS , the cycle will recurs again . 2- Mobetiz type 2 P wave which is not followed by QRS without preceding PR segment prolongation. We see P waves> than QRS complexes, if the P waves are double the no. of QRS , called 2:1 block , if every 3 Ps one QRS complexes , called 3:1 block and so on . The more the no of P for QRS the more sever the block. Third degree AV Block Complete Heart Block The impulse generated in the SA node will not pass at all to the ventricle , the lower pace maker in the Perkinje fibers will act to stimulate the ventricle . There are P waves not related to QRS complexes, PP interval regular and different from RR interval also regular at other rate (30-40 b/min) Bundle Brach Block RT BBB : QRS > 0.12 , Broad S lead I and V6 RSR in V1 . T inversion in V1-V3 LT Bundle Brach Block QRS > 0.11 RSR in lead I aVL , V5 V6. ST segment depression , T wave inversion in the same leads. High voltage but LVH cannot be diagnosed. Fascicular Block LT anterior hemi block : unexplained LT axis deviation. LT posterior hemi block : RT axis deviation Lecture 3 Dysrythmia Look at the ECG , regular or irregular. If it is regular irregularity or irregular irregularity . Look for the P wave and its relation to QRS Look to the Shape of the P wave and QRS configuration. Sinus Bradycardia There P wave for each QRS. PP or RR < 60 beat/mint . Frequently seen in Athletes , Hypothyroidism Hypothermia, Increased intracranial pressure, inferior MI. Sinus Tachycardia Hear rate > 100 b/min. P wave for each QRS . Seen in fever , anxiety ,exercise, anemia , hyperthyrodsim. Sinus Arrhythmia P wave for each QRS but the rate is irregular The longest RR interval > the shortest RR by 0.16 sec. (4 mm) , then sinus arrhythmia is diagnosed. Normal in infants and young children . Pathological in elderly . Atrial Premature Contraction (APC) Basically the ECG is regular , some impulses are not , but there is P wave (which looks different from previous one) for each QRS (which is normal). The PR interval is changeable in these beats ( shorter or longer). Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) Different Shape P waves, different PR interval ,different PP and RR interval . Multiple area of origin of P wave . Usually seen in patient with advanced pulmonary disease. Supra Ventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Very common dysrrhythmia. Heart rate 160-220 b/m. Usually regular rhythm . Atrial Flutter Rapid atrial rate 250-350 b/m. Usually there is AV block (2:1, 3:1,4:1 etc.) Usually the PP rate is Faster than RR rate , the atrial rate is regular, ventricular rate could be regular or irregular depending on the degree of block . Because of very frequent P wave the base line in undulated , called saw teeth appearance. Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Completely irregular (irregular irregularity). No P wave but there is f wave (fibrillatory wave). Atrial rate 350-450 , ventricular rate is totally irregular. Ventricular Premature Beats (PVC) Generally the ECG is regular with some beats looks wide ,no preceding P wave , wide QRS and T wave in opposite direction to QRS . Usually followed by compensatory Pause. Could be single or multiple. Ventricula Tachycardia (VT) Runs of wide QRS complexes fast tachycardia, no preceding P wave, regular . Usually serious dysrrhytmia, may progress to more serious Ventricular fibrillation.