Learning Roomba Module 5 - Localization
advertisement
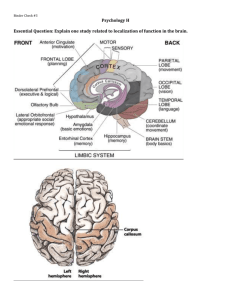
Learning Roomba Module 5 - Localization Outline What is Localization? Why is Localization important? Why is Localization hard? Some Approaches Using the Fixed-Camera Localization Exercises What is Localization? Process of determining where a robot is in its environment Absolute position in the world Position in a map Relative to the start position Relative to some landmark Relative to another robot Some other way of identifying location What is Localization? Can be done with or without a map of the environment A map contains information about the environment that the robot can use to help localize itself Why is Localization important? Robot needs to know where it is to know how to act Without knowing where you are, you can only wander around randomly Cannot navigate to a location without knowing where you are Many tasks rely on navigation Why is Localization Hard? Robot needs to know about its enviornment Sensors are not always accurate Noisy Unreliable Sensors do not tell the Robot what it needs to know Many sensors report distance to an object, not where the Robot is Some Approaches Odometry Global Positioning Systems Landmarks Trilateration Distance Sensors Others Using the Fixed-Camera Localization getLocalizedX() Returns the Localized X-position of the Roomba in Meters getLocalizedY() Returns the Localized Y-position of the Roomba in Meters Using the Fixed-Camera Localization X and Y positions are grid locations in the world Diagram taken from BBC’s website Principles of the Fixed-Camera Localization Merges 3 Concepts Odometry Readings Topological Map Image Tracking Principles of the Fixed-Camera Localization Odometry Readings Recorded from the sensors on the Roomba’s wheels Map can be built over time of where the Roomba has visited. Only as accurate as the sensors Accuracy worsens over time due to drift and skidding Principles of the Fixed-Camera Localization Topological Map Type of Graph Vertices are interesting features in the environment Edges are transitions between the features Usually able to determine when an already visited feature has been reached Principles of the Fixed-Camera Localization Image Tracking Able to find the Roomba in an image Looks for an area with an average color similar to the average color of the Roomba Tracked points in the image become points of interest (Vertices) in the Topological map Camera does not move, so the same pixel represents the same location of the Roomba Principles of the Fixed-Camera Localization As the Roomba drives in the Environment, the algorithm builds the Topological Map Vertices are tracked image coordinates Edges are odometry readings to get from one image coordinate to another The Topological Map can be used to determine the position of the Roomba Finds the current image coordinates where the Roomba is Find the shortest path between the start position and the current position through the Topological Map Exercises Report the position of a virtual wall beam. To do so, have the robot drive until it detects a virtual wall. Print the localized positions once it has reached the beam. Exercises Write a program that will have the Roomba drive in a square 10 times with each side of the square being 1 meter long. Print out the X-Position and YPosition according to Odometry and localization Questions?