Heart
advertisement
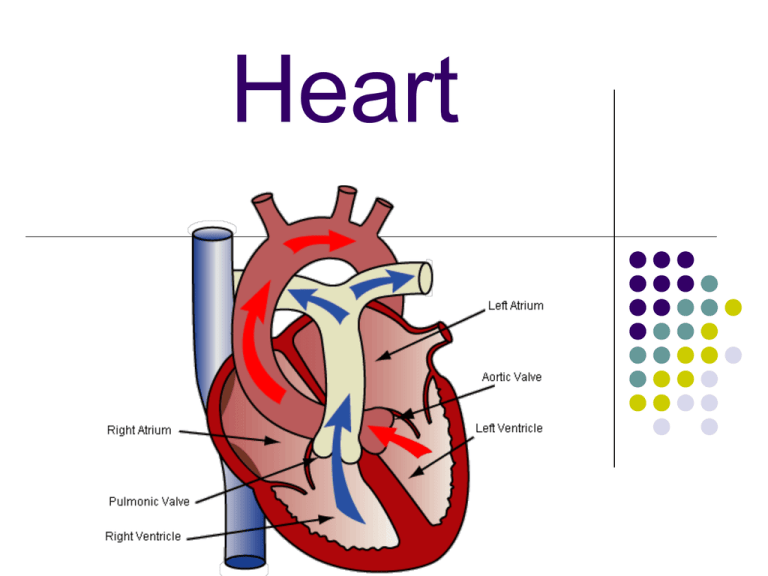
Heart Heart A large muscle which pumps blood throughout the body 1. Chambers- 4 A. Upper: right and left atria Right-receives de-oxygenated blood from body Left- receives oxygenated blood from lungs B. Lower: Right and Left Ventricle Right-pumps blood into lungs Left- pumps blood to the body 2. Valves- 4 A. Diastole: Relaxes 1. tricuspid valve-regulates blood flow between Right Atrium (RA) and Right Ventricle (RV) 2. Mitral Valve- lets Oxygen rich blood from your lungs pass from LA to LV B. Systole: Contraction 1. Pulmonary valve - Controls blood flow from rv into pulmonary arteries go to lungs for O2 2. Aortic valve - Opens the way for rich blood to pass from LV into aorta. 3. Double Pump- pumps oxygenated & deoxygenated blood (2) A. B. Right side – receives and sends blood low in O2 to get more O2. Left side – receives O2 rich blood and pumps to whole body. Path of Blood 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Low oxygenated blood enters RA Tricuspid valve RV Contraction (tricuspid-closes, pulmonary-opens) Pulmonary artery Branches into R & L lung 7. Gas exchange CO2-O2 8. Oxygenated blood enters LA 9. Mitral valve 10. LV 11. Contracts (Mitral-closes, aortic opens) 12. aorta 13. Fills capillaries 6. Path of Blood- 13 steps Label the following structures: pg. 327 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. superior vena cava inferior vena cava RA tricuspid valve RV pulmonary valve pulmonary arteries pulmonary veins LA 10. mitral valve 11. chordea tendineae 12. LV 13. aortic valve 14. aorta 15. papillary mus. 16. septum 17. apex Heart pumping HEART BEAT vital sign calculated in “bpm” males 70 bpm females 75 bpm newborn-130 3 months-150 1 year- 125 3 years- 100 12 years- 85 adult- 60-101 A. Heart Rate Abnormalities 1. 2. Tachycardia: rapid beating of the heart Bradycardia: slow beating of the heart – heart rate under 60 bpm B. Target Heart Rate: Desired range of heart rate reached during aerobic exercise. Age Target HR Zone 50–85 % Average Maximum Heart Rate 100 % 20 years 100–170 beats per minute 200 beats per minute 25 years 98–166 beats per minute 195 beats per minute 30 years 95–162 beats per minute 190 beats per minute 35 years 93–157 beats per minute 185 beats per minute 40 years 90–153 beats per minute 180 beats per minute 45 years 88–149 beats per minute 175 beats per minute 50 years 85–145 beats per minute 170 beats per minute 55 years 83–140 beats per minute 165 beats per minute 60 years 80–136 beats per minute 160 beats per minute 65 years 78–132 beats per minute 155 beats per minute 70 years 75–128 beats per minute 150 beats per minute Heart Sounds LUB-S1: Block reverse blood flow due to closure of atroventricular valves (mitral, tricuspid) DUPP-S2: sudden block of reversing blood flow due to closure of aortic and pulmonary valves. Heart Sounds heartbeat Heart Mumurs Abnormal sounds due to a turbulent flow of blood Causes: blood flowing faster increase in blood illnesses (fever, anemia) B. AV (atrioventricular) node: picks up impulse from SA and flows down the septum to carry the impulse over each of the ventricles. EKG (electrocardiogram) the tracing of the hearts electrical activity. Help diagnose arrhythmias. 3 types of waves 1. P wave: records electrical activity of atria 2. QRS wave: records electrical activity of ventricles 3. T wave: records the hearts return to rest Pulse: “heart rate”-rate at which your heart beats. Pulse is what you feel over an artery as the pressure inside increases following each heart beat. Blood Pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels Measurement: Can be measured invasively (by penetrating the skin and measuring inside the blood vessels) or non-invasively 1. 2. Systolic Pressure: maximum pressure in an artery-beating and pumping Diastolic Pressure: is the lowest pressure in an artery-resting Why might a solider standing at attention for a long period of time faint? If the leg muscles are not used, blood is not pumped back to the heart. As a result, blood pools in the leg veins, and blood pressure falls