Data
advertisement

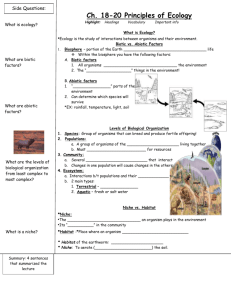
Data Qualitative • Written observations using words • Record qualitative data about the students in this class. Write your example next to the definition. Quantitative • Written observations using numbers • Next to the definition find some quantitative data in this class. Organisms in an Ecosystem Habitat: the place where an organism lives out its life. 1. it can change 2. or disappear 3. it is the location of food, shelter, and other essential resources. Niche The role and position a species has in its environment-how it meets its needs for food and shelter, how it survives, and how it reproduces. The ecological niche of an organism depends not only on where it lives but also on what it does. By analogy, it may be said that the habitat is the organisms “address”, and the niche is its “profession”, biologically speaking. For Example: Oak trees live in oak woodlands, so the oak woodland would be the habitat. Now, what do oak trees do? Oak trees: Absorb sunlight be photosynthesis Absorb water and minerals from the soil Provide shelter for animals Serve as a source of food for animals Examples Polar bears in the polar regions-fur coat. What other jobs do the polar bears have? It’s an advantage for a species to occupy a niche different from those of other species. Always try to reduce competition. Living Relationships: either beneficial or harmful Predator-Prey Such as the lion and wildebeests. The predator KILLS and eats the animals, and the PREY is being eaten. This relationship causes fights for survival. Symbiosis (3 types) Means living together; a close and permanent association among organisms of different species. Commensalisms 1 species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefited. Ex. Dog-Human Ex. Falcon-Geese Mutualism When two species benefit from living in a close association. Ex. Rhino-birds Ex. Ants-trees Parasitism One organism benefits at the expense of the other. Ex. Ticks, tape worm, round worm