consolidated EOC Review
advertisement

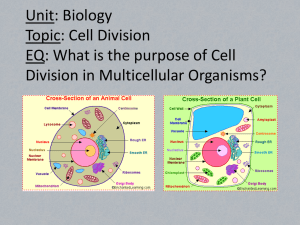
CATEGORY 1- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Cell- smallest unit of living things Prokaryotic- simple cells ex: bacteria Eukaryotic- complex cells with defined nucleus and membrane bound organelles Characteristic Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Cell membrane Yes Yes Cytoplasm Yes Yes Nucleus No Yes organelles No yes EUKARYOTES Plant Cell Animal Cell Prokaryote Cell Part/ Organelle Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi body/ complex Lysosome Vacuole Cell wall Chloroplast Description Surrounds cell; maintains homeostasis by controlling what leaves and enters cell Enclosed within cell membrane; contains the organelles Control center of cell; contains DNA Makes energy Moves substances within cell (transport system for cell) Protein factories; found freely floating in cytoplasm or attached to rough E.R. Changes and packages cell products Contains enzymes Stores materials like water; larger in plant cells Supports and protects plant cell Contains chlorophyll used in photosynthesis Virus: tiny NON-LIVING structure -no metabolism -causes disease (Chicken Pox, HIV, flu) -cannot treat with anti-biotics -requires host cell for life cycle -Lytic cycle- Plant Parts Leaf- contains chloroplast for photosynthesis; stomas are present here to allow for gas exchange Stem- xylem moves water and minerals while phloem moves nutrients like glucose Root- absorbs water and nutrients Cell Cycle- series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide INTERPHASEG1: rapid cell growth S: chromosomes are replicated G2: organelles reproduced and preparation for cell division MITOSIS- Nuclear division ; results in identical daughter cells Prophase- chromatin condenses and nuclear envelope breaks down Metaphase- chromosomes line up in center of cell Anaphase- sister chromatids separate Telophase- chromosomes at opposite ends of cell and two nuclear envelopes form CYTOKINESIS- division of cytoplasm DNA molecule- contains genetic info DNA replication- copying process by which cell duplicates its DNA; new strand contains one old and one new strand Disruption of Cell Cycle- if there is problem within cell cycle, cell reproduction will go unchecked and cancers can develop Cell differentiation- cells become specialized and different from each other by turning on and off genes Biomolecules Biomolecule Carbohydrate (sugar, starch) Monomer (building block) monosaccharide Lipid (steroid, wax, oil, fatty acid) Fatty acids & glycerol Protein (enzyme, hormone) Nucleic acids Amino acids Sugar SUg Protein Nucleotides Structure Functions Contains carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms Contains carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms Source of energy Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen Sugar group, phosphate group, and nitrogen base Source of long-term energy; cell membrane component; chemical messenger Enzymes, hormones Carries genetic info Lipid Nucleic acids *Small organic molecules (monomers) link together to make longer and more complex molecules (polymers) CATERGORY 2- MECHANISMS OF GENETICS Nucleotide- contains sugar (ex: ribose or deoxyribose), phosphate group, and nitrogen base (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- contains genetic Info; double stranded in form of double helix RNA (ribonucleic acid)- uses genetic info from DNA to produce proteins; single stranded Nucleic Acid Sugar Complementary Base Pairing DNA Deoxyribose A-T; G-C RNA Ribose A-U; G-C Transcription and Translation Codon- sequence of three nucleotides (AUG, GCC) Protein- molecule made of amino acids that performs a specific function Transcription- copies DNA’s genetic info to mRNA (occurs in nucleus) 1. DNA unwinds 2. Complementary RNA nucleotides pair up with one strand of DNA nucleotides Translation- protein is made from mRNA (occurs on ribosome in cytoplasm) 1. mRNA enters cytoplasm and attaches to ribosome 2. Translation begins at start codon (AUG) and anticodon on tRNA binds to codon 3. Amino acid chain begins to assemble DNA Fingerprinting Genetic modification Karyotyping Mutation- change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic info; may be harmful or beneficial Point mutations- includes insertions, deletions, and substitutions; these cause frameshift mutations because they cause problems in the “reading frame” of the genetic message Ex: original DNA: TAC GGC GTT AUC DNA: TAC CGG CGT TAU C *Mutations that change codon AAA to AAG will have no effect because they both code for Lysine since there is a redundancy in the code Genes Gene- segment of DNA; controls specific hereditary characteristics Gene expression- regulated process by which gene transcription and translation are controlled by various factors, such as hormones Genome- set of all genes that specify an organisms’ traits Fragment of an organism’s DNA separated using electrophoresis and compared to a sample Genes are changed for specific purpose (making plants resistant to insects Cells examined for missing, extra, or abnormal chromosomes to identify disorders Genetic Combinations Trait- organism’s characteristics Heredity- passing of traits from one generation to the next Chromosome- structure in cell’s nucleus that contains DNA; humans have 46 total (26 pairs) Sex chromosome- determines sex (Male XY; Female XX) Allele- form of a gene that controls a characteristic (dominant- R; recessive- r) Homozygous- has two identical alleles Heterozygous- has two different alleles Dominant trait- trait appears when at least one dominant allele is present Recessive trait- appears when two recessive alleles are present Genotype- inherited combination of alleles that is represented by two letters (RR, Rr, rr) Phenotype- organism’s appearance due to genotype Mendelian Genetics- laws regarding inheritance of traits 1. Alleles segregate and recombine (one allele inherited per parent) 2. One trait may dominate the effect of another 3. Alleles for a trait segregate and recombine independently (eye color and hair color do not influence each other) Monohybrid cross (one trait) R- right handed Mother Rr x Father rr r- left handed R r Genotype Probability Phenotype Rr rr r RR 0 of 4 Right handed Rr 2 of 4 Right handed rr 2 of 4 Right handed Rr rr r Dihybrid Cross (two traits) T and B –tall, brown-eyed T and b- short, green-eyed (TtBb) tB tb TB Tb TB TTBB TTBb TtBB TtBb Tb TTBb TTB TTbb TtBb Ttbb tB TtBB TtBb ttBB ttBb tb TtBb Ttbb ttBb ttbb Father TtBb Mother Possible outcomes: 9- tall and brown-eyed 3- tall and green-eyed 3- short and brown-eyed 1 short and green-eyed Non-Mendelian Genetics Incomplete dominance- situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another Codominance- situation in which both alleles of a gene contribute to the phenotype of the organism Meiosis Asexual reproduction- offspring’s genes come from one parent (not from meiosis) Sexual reproduction- genes from two parents; results in greater genetic variation Gamete- sex cells; eggs in females and sperm in males Meiosis- two-staged cell division that produces gametes 1. Parent cell’s chromosomes are replicated 2. Chromosomes “crossover” (Prophase I) 3. Chromosomes are pulled apart and cell divides in two 4. Cells divide again forming four haploid daughter cells (gametes) CATEGORY 3- BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION AND CLASSIFICATION Common ancestry Evidence Description Fossil record Information about past life, including the structure of organisms, what they ate, what ate them, in what environment they lived, and order in which they lived Biogeographical Geographic distribution of organisms Anatomical homology Structural similarities Molecular homology Molecular similarities among organisms Developmental homology Embryonic similarities among certain organisms show how some organisms develop in common ways Natural Selection- process proposed by Charles Darwin by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully Reproductive Success can be influence by several factors Factor Description Inherited variations Genes for a triat that help an organism obtain food, avoid prey or disease, or attract a mate become more common in subsequent populations Environmental resources Competition for limited resources or a change exerts selective pressure on certain traits Potential to produce offspring Species with higher reproduction rates can exhibit increased reproductive success Evolutionary mechanisms Genetic drift- random change in allele frequencies that occurs in small populations Gene flow- change in gene pool caused by movement of organisms into or out of the population Mutation- change in genetic pool caused by insertion, deletion, or substitution in DNA sequence of gamete cell; tends to increase genetic variation Recombination- sexually reproducing species have increased genetic variation b/c of gene crossover Taxonomy Taxonomy- discipline of classifying organisms and assigning each organism a universally accepted name Autotroph- organisms that can capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce its own food; a producer Heterotroph- organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes Domains Archae Bacteria Eukarya Description Primitive unicellular prokaryotes; some live in harsh conditions Prokaryotes; some autotrophs but most heterotrophs Unicellular and multicellular eukaryotes Examples halophiles Staphylococcus bacteria; Fungus, trees, animals Eukarya domain can be divided into four kingdoms Kingdom Description Protist Typically unicellular; some autotrophs and some heterotrophs; can be found in water Fungi Typically multicellular eukaryotes; heterotrophs Plant Multicellular eukaryotes; autotrophs Animal Multicellular eukaryotes; heterotrophs Examples Amoeba, algae Mushrooms, mold, yeast Tree, grass, moss Dog, fish, human Kingdom-> Phylum-> Class-> Order-> Family-> Genus-> Species *Remember- King Phillip cam over for great spaghetti Binomial nomenclature- system of naming an organism using its genus and species (Ex: Homo sapiens) Phylogeny- study of evolutionary relationships among organisms CATEGORY 4- BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS Photosynthesis- process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches Interactions Among Systems in Plants Function Transport Reproduction Response Aerobic cellular respiration- process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen; occurs in mitochondria Enzymes- protein that acts as a biological catalyst; speeds up specific chemical reaction and lowers activation energy; often named by affected substrate (ex: Lactase speeds of breakdown of lactose) Levels of Organization Atom-> molecule-> cell-> tissue-> organ-> organ system-> organism-> population-> community Interactions Among Systems in Animals Function Regulation Nutrient absorption Reproduction Example of Interaction(s) Endocrine system makes certain hormones and is carried through circulatory system Food broken down mechanically by muscular system and absorbed through digestive system Hormones produced in endocrine system control ovulation in female’s reproductive system Example of Interaction(s) The root system uptakes water; xylem vessels transport water to leaves in the shoot system. Phloem vessels transport sugars and nutrients throughout the plant Reproductive organs like the pistil (female) and the stamen (male) are regulated by hormones in the plant’s root system When one side of a plant does not receive enough light, a hormone that causes growth is produced in the shoot system’s leaves. It is then transported to the dark side and as the dark side grow, the plant bend toward the light (phototropism) Homeostasis and Internal Feedback Mechanisms Homeostasis- regulation of conditions within an organism or system which allows for stable, “normal” internal equilibrium (balance) Internal feedback mechanism- self-regulating process, like a chemical reaction, that can help maintain homeostasis Negative feedback- decreases effect (Ex: When you exercise, your body creates sweat to cool you down) Positive feedback- increases effect (Ex: When fruits ripen, they release a chemical called ethylene which will cause more apples to ripen; “one bad apple spoils the bunch”) CATEGORY 5- INTERDEPENDENCE WITHIN ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS Organisms, populations, and communities must respond to external factors (like changes in the environment or other organisms). If an entire species is unable to respond to changes, it could face extinction Role of microorganisms Microorganism- tiny organism (like a bacteria or protest) that can be seen only with a microscope; microorganisms play critical roles in the maintenance and disruption of the health of both individual organisms and entire ecosystems. BENEFICIAL ROLES OF BACTERIA HARMFUL ROLES OF BACTERIA Decompose organic material Spoil food Change nitrogen from one form to another in Produce harmful or damaging toxins the nitrogen cycle Have role in making drugs, foods, and Cause shortage of oxygen in lakes when vitamins “blooms” occur Help absorb nutrients in digestive system Causes disease Ecological Succession- gradual change in living communities that follows a disturbance; diversity of populations and species changes during process Primary succession- occurs in surfaces where no soil exists Secondary succession- succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil Variations and Adaptations Ecosystem- collection of all organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving environment Organism- living thing Species- group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring Population- group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area Variation- differences among organisms Adaptation- inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival Matter and Energy Flow ORGANISM Producer Consumer Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Decomposer SOURCE OF FOOD (ENERGY) Makes its own food Gets food from other organisms Gets food from plants Gets food from animals Gets food from plants and animals Gets food from dead organisms or the waste of organisms Food chain- series of steps in an ecosystem in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten Food web- network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem Trophic level- step in a food chain or food web Ecological pyramid- shows biomass, energy flow, and relative number of organisms within an ecosystem Pioneer organisms (Ex: lichens) Species begin to diversify Relationships Among Organisms RELATIONSHIP Predation Competition Parasitism Commensalism Mutualism DESCRIPTION One population (predator) captures and feeds upon another population (prey) Two populations struggle for same resource Symbiotic relationship in which one organism lives in or on another organisms (host) and consequently harms it Symbiotic relationship in which one member benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed Symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit *only 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level Survival of Species Extinct species- refers to species that have died out Endangered species- species whose population size is rapidly declining and will become extinct if the trend continues Limiting factors- factor that causes the growth of a population to decrease (ex: food, water, disease, etc) Carrying capacity- largest number of individuals of a population that a given environment can support Carbon cycle- constant movement of carbon throughout environment Cycles Nitrogen cycle- movement of nitrogen though the environment Scientific Process Skills Laboratory Safety Rules and Equipment 1. Read and understand all safety instructions before you begin 2. Follow directions and use the equipment only as instructed 3. Locate the emergency exit and safety equipment (eye wash, fire extinguisher, fire blanket, alarm) 4. Wear all required safety equipment; tie back long hair and secure loose clothes 5. Pour acid into water, not water into acid (Do what you oughta, add acid to water) 6. Do not dissect while holding specimen in your hand 7. Avoid contamination 8. Report all accidents, spills, and broken glass 9. Avoid eating, drinking and only waft chemicals to detect odor 10. Keep metals and water away from electrical equipment 11. Point test tubes away from you and others 12. Clean up your area 13. Turn off equipment Scientific Investigation INVESTIGATION Descriptive Comparative Experimental Scientific Method 1. Begin with well-defined question 2. Research and collect data 3. Make hypothesis 4. Design and conduct experiment Variable Independent Dependent EXAMPLE Measure growth of plant Observe similarities and differences between viruses and bacteria Applying different amounts of fertilizer to plants to find which works best Description Variable that is manipulated during the experiment (x-axis) Variable that responds to changes; measured result (y-axis) Variable that is held constant Controlled 5. Collect and organize observation 6. Looks for patterns in data 7. Make a conclusion Data Evaluation Inference- logical interpretation based on prior knowledge and experience Hypothesis- possible explanation for a set of observations or possible answer to a scientific question Theory- well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations Average/Mean Sum of values divided by number of items Precision Closeness of values to each other Accuracy Closeness to “true” or “correct” value Probability Likelihood of an event Laboratory Equipment Beaker- measures liquid volume Burette- dispenses precise liquid amounts Erlenmeyer flask- holds liquids Graduated cylinder- measures liquid volume Hot plate- heats chemicals on a hot, flat surface Mortar and pestle- crushes and grinds materials into powder Petri dish- allows for growth and observation of organisms PROPERTY Time Temperature Length Mass Volume UNIT Second (s) °Celsius (°C) Meter (m) Gram (g) Liter(L) MEASUREMENT TOOL Stopwatch Thermometer Metric ruler Electronic balance Graduated cylinder