NUCLEIC ACID NOTES 2012 with Video

Biomolecules
A short video review.
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
NUCLEIC ACID NOTES
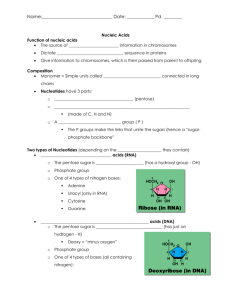
Nucleic Acids
Molecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon & phosphorus
Function in the body
Store & transmit hereditary or genetic information
Building Blocks
Nucleotides – the building blocks of nucleic acids
Nucleotides have 3 parts:
5-carbon sugar
A phosphate group
Sugar and phosphate are held together by strong covalent bonds
A nitrogenous (nitrogen-containing) base
(adenine, thymine, cytocine, guanine)
Bases are held together by weak hydrogen bonds.
Check for Understanding #1
The diagram below represents a portion of a nucleic acid molecule. The part indicated by arrow X could be
1 adenine
2 ribose
3 deoxyribose
4 phosphate
Nucleic Acids Video
Check for Understanding #2
The weakest bonds in a double-stranded molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid exist between the
(1) deoxyribose sugars
(2) phosphate groups
(3) nitrogenous bases
(4) 5-carbon sugars
Examples
Ribonucleic Acid
(RNA)
Deoxyribonucleic
Acid (DNA)
Check for Understanding #3
One similarity between DNA and RNA molecules is that they both contain
1 the same sugar
2 genetic codes based on sequences of bases
3 a nitrogenous base known as uracil
4 double-stranded polymers