Ch 24 Notes

Nationalist Revolutions
Sweep the West
Ch 24
1789-1900
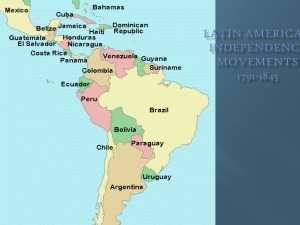
Latin America
Society 1. Peninsulares
(people born in Spain)
2. Creoles (people born in Latin
America of Spanish descent they couldn’t hold public office)
3. Mestizos (mixed Spanish +
Indian)
4. Mulattos (mixed Spanish +
African)
5. Africans
6. Indians
Revolutions in
Latin America are influenced by:
American Rev.
French Rev.
The Enlightenment
Most people in Latin
America resent colonial control
Haiti’s
Revolution
French colony known as St.
Domingue
1791, 100,000 slaves revolted led by Toussaint L’Ouverture
By 1801, he had control of the entire island + had freed the slaves
1802, French troops arrive +
Toussaint agreed to halt revolution if French would end slavery
He’s sent to the French Alps where he later dies
1804, Toussaint’s lieutenant Jean-
Jacques Dessalines declares the colony to be an independent country –became Haiti
1 st black colony to free itself from
European control
Gran
Colombia
Creoles lead indep. movement
Go to Europe to get educated, come back + spread
Enlightenment ideas
When Napoleon removed Spain’s king
+ put his brother on the throne,
Spain lost the loyalty of many Creoles
2 brilliant Creole Generals lead rev. in
South America
1. Simon Bolivar –“Libertador”
“George Washington of Latin
America”
Helped free Colombia +
Venezuela
2. Jose de San Martin
Helped Chile gain its indep.
Bolivar + San Martin meet + combined armies under
Bolivar
1824, Bolivar defeats Spanish at the Battle of Ayacucho
Now Venezuela, Colombia,
Panama, + Ecuador were united into a country called Gran
Colombia
Bolivar envisioned this as a
United States of South
America
Mexico
Indians + Mestizos lead indep. movement
1810, a priest named Miguel Hidalgo spoke to the peasants gathered in his church + issued a call for rebellion against the Spanish
“The Cry of Dolores”
The next day an army marched towards Mexico City
Soon numbered 80,000 men
Army defeated by Spanish + Creoles
Rebels then unite under a priest named Jose Maria Morelos who leads for 4 yrs before being defeated in
1815 by Creole Agustin de Iturbide
But in 1820, a revolution in
Spain puts a more liberal gov.’t in power. Creoles in
Mexico get worried about a possible loss of privileges, so they unite against Spain.
Led by the same Agustin de
Iturbide who years earlier, crushed a rebellion for indep.
He declares himself
Mexico’s emperor in
1821 (lasts for 2 yrs)
Countries in Central America declare their indep. from
Mexico
Brazil
1807, Napoleon’s army invaded
Portugal
Portuguese Prince John + royal family flee to Brazil (Portugal’s largest colony) + rule from there for
14yrs
When Napoleon is defeated King
John returns to Portugal but son
Dom Pedro stays in Brazil
Brazil was supposed to return to colony status, but Brazilians sign a petition asking Dom Pedro to rule + he agreed.
1822, he officially declared indep. after considerably less fighting than what occurred in the Spanish colonies
End Section 1
24.2
Meanwhile, in Europe…
3 Schools of Political
Thought
1. Conservatives:
Usually wealthy property owners + nobility
Favored traditional monarchies
2. Liberals:
Mostly middle-class business leaders + merchants
Wanted more power for elected parliaments, but only the educated + the landowners could vote
3. Radicals:
Favored drastic change to extend democracy to all people
Nationalism
Emerges
Nationalism: belief that people’s loyalty should not be to a king or empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture + history
Rise of nationalism is linked w/ spread of democratic ideas + growth of educated middle class
They want to decide how they are governed
Rise of nation-states - country w/ independent gov.’t + common culture + identity
(fancy way of saying country)
Results of Nationalism
Positive
Overthrow of Colonial rule
Many democratic gov.’ts form
People w/in a nation overcoming their differences for the common good
Competition among nations scientific + technological advances
Negative
Forced assimilation of minority cultures into the nation’s majority culture
Ethnic cleansings
Extreme nationalist movements
(ex. Nazis)
Competition between nations leading to war
Nationalist
Movements in Europe
Greeks 1 st
Controlled by Ottoman Empire
Kept alive memory of their ancient history + culture
Rebelled against Ottomans in 1821
Supported around the world despite
European gov.’ts opposition to rebellions
Christian Orthodox connection to Russians
Educated Europeans +
Americans respected ancient
Greek culture
Gain indep. in 1830
Supported by British, French, +
Russian militaries
Many failed nationalist rebellions throughout Europe (Italians, Poles,
Czechs, etc…)
France goes back + forth between a strong monarchy + republic
1848, Louis-Napoleon
(Napoleon’s nephew) wins presidential election. 4 yrs later took title of Emperor
Napoleon III. France prospers
+ modernizes due to his good policies.
Russian Czar Alexander II frees serfs in 1861. Later assassinated.
End Section 2
24.3
Type
Nationalism: 3 types
Characteristics Examples
Unification
State-
Building
Mergers of politically divided but culturally similar lands
Separation Culturally distinct group resists being added to a state or tries to break away
Culturally distinct groups form into a new state by accepting a single culture
-
19 th Century
Germany
-
19 th Century
Italy
-Greeks in the
Ottoman Empire
- Frenchspeaking
Canadians
-The United
States
-Turkey
Break-ups
Nationalism – breaks apart
Austrian, Russian, + Ottoman
Empires
Italy
Forms from crumbling empires
Sardinia is the largest + most powerful Italian state
Has a liberal constitution
Unites other Italian states through wars (1858-1870)
Germany
Starting in 1815, part of
Confederation of 39 German states dominated by Austria
(established at Congress of
Vienna)
Prussia, led by King Wilhelm I appoints Otto von Bismarck prime minister
Bismarck was a master at realpolitik
– “the politics of reality” power politics w/ no idealism
He declares (w/ king’s approval) that he would rule w/o consent of parliament + w/o a legal budget
Violates their constitution
Prussia would unite various German states through wars stirred up by
Bismarck to gain territory
During Franco-Prussian War (1867)
Prussia fights w/ France
Capture Napoleon III
Final stage of German unification
King Wilhelm I of Prussia crowned Kaiser (German emperor)
“2 nd Reich” (Holy Roman
Empire was 1 st + Nazis would proclaim theirs the 3 rd )
End Section 3
24.4
Revolutions in the Arts
Romanticism
(End of the
1700s)
Movement reflecting deep interest in nature and the thoughts + feelings of individuals
Reaction against Enlightenment
(going away from reason to focus on emotion)
Romantics rejected the rigidly ordered world of the middle class
Inspired by nationalism
Poetry was the highest form of expression
Ex: Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein
Victor Hugo’s Les Miserables
Grimm Brothers’ fairy tales
Ideas of
Romanticism
1. Emphasized feelings + imagination
2. Focused on the mysterious, supernatural, exotic, grotesque
3. Loved beauty of untamed nature
4. Idealized the past as a simpler + nobler time
5. Glorified heroes
6. Valued common people + the individual
7. Promoted radical change + democracy
Realism
(1850s)
Charles
Dickens
Movement in which artists + writers tried to show life as it was, not as they thought it should be
Started due to rapid industrialization
– made dreams of romantics seem pointless
Reflected the political importance of the working class
1 st camera invented – showed grim reality
Ex. Works of Charles Dickens +
French author Honore de Balzac wrote a series of almost 100 novels describing in detail the brutal struggle for wealth + power, exposed miseries of workers, + led to reforms in labor laws
Impressionism
(1860s)
Movement in painting + music in which artists tried to convey their impressions of subjects or moments in time
Reaction against realism
Showed a more positive view of the new urban society in western Europe
Ex. Instead of showing abused workers, they’d show workers enjoying themselves in cafes or dancing
Ex. Claude Monet
End Section 4