EM Notes
advertisement

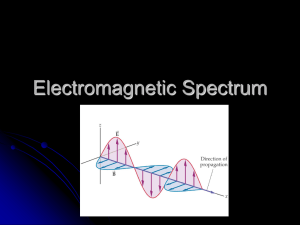
The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1 The electromagnetic spectrum is the complete spectrum (or continuum) of all forms of “light” An electromagnetic wave consists of electric and magnetic fields which vibrate - thus making waves. Vibrations 2 The electromagnetic spectrum consists of: radio waves cell phone waves microwaves radar waves infrared waves visible light waves ultraviolet waves x-ray waves gamma waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum 3 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 4 Properties of electromagnetic waves include speed, frequency and wavelength Speed (s), frequency (f) and wavelength (l) are related in the formula: s =f x l light waves travel at a speed of 3 x 108 m/s in a vacuum All The Electromagnetic Spectrum 5 All parts of the electromagnetic spectrum travel at the same speed Therefore, wavelength and frequency have an indirect relationship. This means that as one characteristic increases, the other decreases In other words, as wavelength increases, frequency decreases The Electromagnetic Spectrum 6 As wavelength decreases, frequency will? increase See the relationship The Electromagnetic Spectrum 7 Electromagnetic wave characteristics: • short wavelengths have a high frequency • long wavelengths have a low frequency Electromagnetic waves & Energy: • high frequency waves have high energy • low frequency waves have low energy The Electromagnetic Spectrum 8 Fill in the table below: wavelength frequency energy long high The Electromagnetic Spectrum 9 smaller wavelengths increasing frequency increasing energy If you haven’t already, sketch this drawing into your notes. Don’t worry so much about the actual wavelengths, just get the general shape and where the various forms of light (radio, infrared, x-ray, etc) exist. The Electromagnetic Spectrum 10 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 11 Low energy waves with longest wavelengths Includes FM, AM, radar and TV waves Wavelengths of 1 m (10 -1 m) and longer Low frequency Used in many devices such as remote control items, cell phones, wireless devices, etc. The Electromagnetic Spectrum 12 Only radio waves are longer Wavelength 1 x 10-1 m to 10 - 4 m (1 m to 0.001 m) 1x used for communication, medicine and consumer use (microwave ovens) The Electromagnetic Spectrum 13 Invisible electromagnetic waves that are detected as heat Can be detected with special devices such as night goggles Used in heat lamps Higher energy than microwaves but lower than visible light The Electromagnetic Spectrum 14 The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that human eyes can detect ROY G BIV (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet) Which color has the lowest frequency? red has the lowest frequency – violet the highest The Electromagnetic Spectrum 15 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 16 Higher Can energy than light waves cause skin cancer and blindness in humans Used in tanning beds and sterilizing equipment The Electromagnetic Spectrum 17 High energy waves Used in medicine, industry and astronomy Can cause cancer The Electromagnetic Spectrum 18 Highest energy Blocked from Earth’s surface by atmosphere The Electromagnetic Spectrum 19 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 20 ① What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength? ① What characteristic of gamma waves gives them their high energy? ① What does ROY G BIV mean? What part of the electromagnetic spectrum does it refer to? The Electromagnetic Spectrum 21 ④ Which color is more energetic, red or yellow? ⑤ Which type of wave travels faster, gamma or radio? ⑥ Why are microwaves more dangerous than radio waves? The Electromagnetic Spectrum 22 ⑦ You have just been involved in a traffic incident that leaves you stranded on the side of the road. Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum would be of the most use to you and why? The Electromagnetic Spectrum 23 ① Frequency and wavelength are properties of waves and since speed is constant for em waves, as frequency increases, wavelength decreases. In other words, they have an indirect relationship. ① Gamma waves get their high energy from their extremely short wavelengths (or extremely fast frequency) ① ROY G BIV stands for “red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. They are the colors of the visible light in order of longest wavelength to shortest wavelength. ① Yellow is more energetic than red because it has a shorter wavelength (or larger frequency) ① Gamma waves and radio waves travel at the same speed ① Microwaves are more dangerous than radio waves because they have a higher frequency and carry more energy. The Electromagnetic Spectrum 24 More Great Science from The Science Vault If you enjoyed this powerpoint, you might also enjoy these best-selling products: Chemical Bonding Go Fish – making chemical bonding less abstract and more fun; several different games differentiated for ability levels grades 8 - 12 Scientific Method / Experimental Design Unit – everything you need to teach (or review) experimental design: powerpoints, worksheets, quizzes Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Powerpoint – 50 interactive slides that introduce continental drift and plate tectonics with links to website & flash animations The Life Cycle of Stars Powerpoint – gorgeous photos and videos bring this powerpoint alive for your students THE FINE PRINT © Jan Parker, 2009 – for purchaser’s classroom use only; please do not distribute. For more great science and classroom management materials, follow me at http://www.thesciencevault.net, or on twitter @thesciencevault, or head over to my web store http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Store/The-Science-Vault If you put your classroom materials on a server for your students, please post this presentation in pdf form. Thanks! The Electromagnetic Spectrum 25