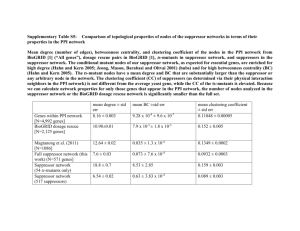
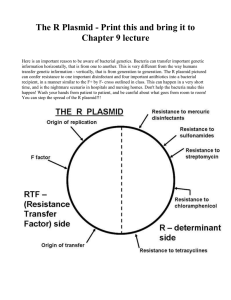
PDF of research poster (9.895Mb)
advertisement
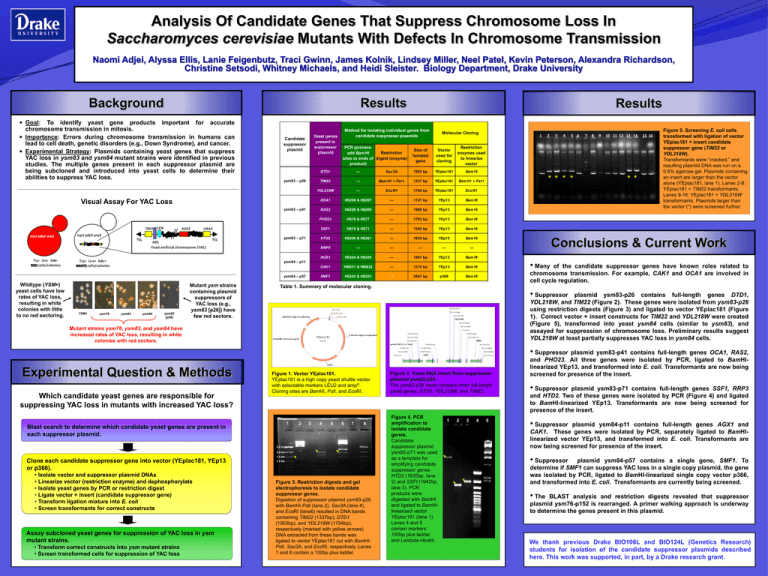
Analysis Of Candidate Genes That Suppress Chromosome Loss In Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mutants With Defects In Chromosome Transmission Naomi Adjei, Alyssa Ellis, Lanie Feigenbutz, Traci Gwinn, James Kolnik, Lindsey Miller, Neel Patel, Kevin Peterson, Alexandra Richardson, Christine Setsodi, Whitney Michaels, and Heidi Sleister. Biology Department, Drake University Background Results Results Goal: To identify yeast gene products important for accurate chromosome transmission in mitosis. Importance: Errors during chromosome transmission in humans can lead to cell death, genetic disorders (e.g., Down Syndrome), and cancer. Experimental Strategy: Plasmids containing yeast genes that suppress YAC loss in ysm83 and ysm84 mutant strains were identified in previous studies. The multiple genes present in each suppressor plasmid are being subcloned and introduced into yeast cells to determine their abilities to suppress YAC loss. Method for isolating individual genes from candidate suppressor plasmids Yeast genes present in suppressor plasmid Candidate suppressor plasmid ysm83 – p26 Visual Assay For YAC Loss ysm83 – p41 ysm83 – p71 PCR (primersRestriction add Bam HI sites to ends of digest (enzyme) product) Molecular Cloning Size of isolated gene Vector used for cloning Restriction enzymes used to linearize vector DTD1 --- Sau 3A 1903 bp YEplac181 Bam HI TIM22 --- Bam H1 + Pst 1 1337 bp YEplac181 Bam H1 + Pst 1 YDL218W --- Eco R1 1794 bp YEplac181 Eco R1 OCA1 HS206 & HS207 --- 1127 bp YEp13 Bam HI RAS2 HS208 & HS209 --- 1980 bp YEp13 Bam HI PHO23 HS76 & HS77 --- 1703 bp YEp13 Bam HI SSF1 HS70 & HS71 --- 1942 bp YEp13 Bam HI HTD2 HS200 & HS201 --- 1635 bp YEp13 Bam HI RRP3 --- --- --- --- --- AGX1 HS204 & HS205 --- 1967 bp YEp13 Bam HI CAK1 HMS31 & HMS32 --- 1374 bp YEp13 Bam HI SMF1 HS202 & HS203 --- 2647 bp p366 Bam HI ** * * Conclusions & Current Work ysm84 – p11 ysm84 – p57 Wildtype (YSM+) yeast cells have low rates of YAC loss, resulting in white colonies with little to no red sectoring. YSM+ ysm76 ysm83 ysm84 ysm83 [p26] Mutant ysm strains containing plasmid suppressors of YAC loss (e.g., ysm83 [p26]) have few red sectors. • Many of the candidate suppressor genes have known roles related to chromosome transmission. For example, CAK1 and OCA1 are involved in cell cycle regulation. Table 1. Summary of molecular cloning. • Suppressor plasmid ysm83-p26 contains full-length genes DTD1, YDL218W, and TIM22 (Figure 2). These genes were isolated from ysm83-p26 using restriction digests (Figure 3) and ligated to vector YEplac181 (Figure 1). Correct vector + insert constructs for TIM22 and YDL218W were created (Figure 5), transformed into yeast ysm84 cells (similar to ysm83), and assayed for suppression of chromosome loss. Preliminary results suggest YDL218W at least partially suppresses YAC loss in ysm84 cells. Sau 3A (2911 ) PstI ( 250) Sau 3A (2944) BamHI ( 264) Sau 3A (31 42) EcoRI ( 285) pB R 3 22 origin of re plic a t ion Y DL218W Sau 3A (3485) Mutant strains ysm76, ysm83, and ysm84 have increased rates of YAC loss, resulting in white colonies with red sectors. Sau 3A (3560 ) P s tI (3626) Sau 3A (1 0 41 ) 2 mic ron origin of re plic a t ion Y Eplac181 A mpic illin re s is t a nc e ge ne EcoRI (3948) Sau 3A (1 0 26) 5741 bp Sau 3A (40 16) Sau 3A (970) partial CDC13 (~5' half) EcoRI (473) Sau 3A (38 7) Sau 3A (1 ) TIM22 EcoRI (21 54) Sau 3A (4714) EcoRI (1 904) Sau 3A (48 52) EcoRI (1 8 50 ) Sau 3A (4963) DTD1 Bam HI (4963) LEU 2 Experimental Question & Methods Which candidate yeast genes are responsible for suppressing YAC loss in mutants with increased YAC loss? ysm83-p19 Figure 1. Vector YEplac181. YEplac181 is a high copy yeast shuttle vector with selectable markers LEU2 and ampR. Cloning sites are BamHI, PstI, and EcoRI. 1 Blast search to determine which candidate yeast genes are present in each suppressor plasmid. 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 3.0 kb 2.0 kb 1.5 kb Clone each candidate suppressor gene into vector (YEplac181, YEp13 or p366). • Isolate vector and suppressor plasmid DNAs • Linearize vector (restriction enzyme) and dephosphorylate • Isolate yeast genes by PCR or restriction digest • Ligate vector + insert (candidate suppressor gene) • Transform ligation mixture into E. coli • Screen transformants for correct constructs Assay subcloned yeast genes for suppression of YAC loss in ysm mutant strains. • Transform correct constructs into ysm mutant strains • Screen transformed cells for suppression of YAC loss 1.0 kb Figure 3. Restriction digests and gel electrophoresis to isolate candidate suppressor genes. Digestion of suppressor plasmid ysm83-p26 with BamHI-PstI (lane 2), Sau3A (lane 4), and EcoRI (lane6) resulted in DNA bands containing TIM22 (1337bp), DTD1 (1903bp), and YDL218W (1794bp), respectively (marked with yellow arrows). DNA extracted from these bands was ligated to vector YEplac181 cut with BamHIPstI, Sau3A, and EcoRI, respectively. Lanes 1 and 8 contain a 100bp plus ladder. ** Figure 5. Screening E. coli cells transformed with ligation of vector YEplac181 + insert candidate suppressor gene (TIM22 or YDL218W). Transformants were “cracked,” and resulting plasmid DNA was run on a 0.6% agarose gel. Plasmids containing an insert are larger than the vector alone (YEplac181, lane 1). Lanes 2-8: YEplac181 + TIM22 transformants; Lanes 9-16: YEplac181 + YDL218W transformants. Plasmids larger than the vector (*) were screened further. Figure 2. Yeast DNA insert from suppressor plasmid ysm83-p26. The ysm83-p26 insert contains three full-length yeast genes: DTD1, YDL218W, and TIM22. 4967 bp Figure 4. PCR amplification to isolate candidate genes. Candidate suppressor plasmid ysm83-p71 was used as a template for amplifying candidate suppressor genes HTD2 (1635bp, lane 2) and SSFI (1942bp, lane 3). PCR products were digested with BamHI and ligated to BamHIlinearized vector YEplac181 (lane 1). Lanes 4 and 5 contain markers: 100bp plus ladder and Lambda-HindIII. 1 2 3 4 5 • Suppressor plasmid ysm83-p41 contains full-length genes OCA1, RAS2, and PHO23. All three genes were isolated by PCR, ligated to BamHIlinearized YEp13, and transformed into E. coli. Transformants are now being screened for presence of the insert. • Suppressor plasmid ysm83-p71 contains full-length genes SSF1, RRP3 and HTD2. Two of these genes were isolated by PCR (Figure 4) and ligated to BamHI-linearized YEp13. Transformants are now being screened for presence of the insert. • Suppressor plasmid ysm84-p11 contains full-length genes AGX1 and CAK1. These genes were isolated by PCR, separately ligated to BamHIlinearized vector YEp13, and transformed into E. coli. Transformants are now being screened for presence of the insert. • Suppressor plasmid ysm84-p57 contains a single gene, SMF1. To determine if SMF1 can suppress YAC loss in a single copy plasmid, the gene was isolated by PCR, ligated to BamHI-linearized single copy vector p366, and transformed into E. coli. Transformants are currently being screened. • The BLAST analysis and restriction digests revealed that suppressor plasmid ysm76-p152 is rearranged. A primer walking approach is underway to determine the genes present in this plasmid. We thank previous Drake BIO106L and BIO124L (Genetics Research) students for isolation of the candidate suppressor plasmids described here. This work was supported, in part, by a Drake research grant.