Technical Challenges for the Next Generation of Large Telescopes
Technical Challenges for the Next
Generation of Large Telescopes
David R. Smith
September 25, 2000
Edinburgh, Scotland
New Initiatives Office
Goals
Enable the science:
Investigate known ‘tall pole’ engineering challenges
Determine the scale of problems
Develop potential solutions
Uncover unexpected ‘tall poles’ before major design effort
Approach
Develop strawman ‘Point Design’ to
Focus technical studies
Test implications of design approaches
Reveal critical interfaces
Provide ‘real’ constraints for potential solutions
Determine which specifications are easy/hard to meet
Simultaneously conduct studies on known challenges
Wind buffeting of M1 and M2
Effects of enclosures
Control system interactions
MCAO (Rigaut; this meeting)
Current Status
Point Design
Optical and Structural layout generated
Interfaces developing
Optics/structure (central hole, segment size)
MCAO/structure (DM stroke, space requirements)
Instruments/structure (size, location)
Instruments/optics (location, scale)
Controls/structure (heirarchy and interaction)
Wind buffeting studies
First round tests performed
Initial results available
Further data reduction underway
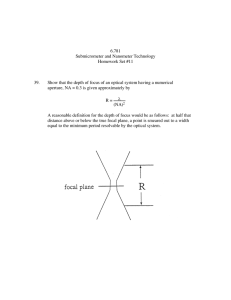
Point Design: Optical Layout
Cassegrain layout
30m f/1 primary
2m secondary
Final focal ratio of f/15
Seeing-limited FoV of 15' at Cassegrain focus
Considering prime focus camera
MCAO FoV of ~2'
What it provides
Basic interface dimensions for structure
Geometry for discussions of optical fabrication issues
Reference point for MCAO or instrument ideas
Point Design: Structure and Controls
Cable-braced tripod
Primary reflector truss
Elevation axis
Raft and Segment Layout
Point Design: Controls
Active optics (quasi-static)
Hierarchical control
Rafts controlled on structure
Segments controlled on rafts
Edge sensing (high spatial frequency)
Wavefront sensing (low spatial frequency)
Adaptive optics
Removes residual structural errors
Controls Issues
Correction and stabilization of the primary
High bandwidth, large displacement, large moving mass
Potential control-structure interaction
Single (or small count) point correction spillover
Highly distributed correction expensive
Optical correction via AO
Stabilization of the secondary
Disturbance suggests high bandwidth
Potential control-structure interaction
Model-based controllers
Wind Studies
Results from NRO 45m (SPIE 2000)
Scale and structural frequencies well matched
Deflection scale
Experiment at Gemini North/South 8-m
Target of opportunity
Well characterized telescope (good benchmark)
Wide range of enclosure configurations
Simultaneous structural and wind measurements
Gemini South Test
Modal Testing
Controlled, calibrated input
Allows validation of FEA
Operating Data Testing
Total (uncontrolled) response
75 channels of accelerometers
24 channels of wind pressures
15 channels of wind speed
Factors varied
Azimuth angle (w.r.t. wind): 0, 45, 90, 135, 180
Elevation angle: 30, 45, 60, 75
Upwind vent gate: open, half, closed
Downwind vent gate: open, half, closed
Experimental Approach
Full factorial test impractical (5*4*3*3 = 180 tests)
Wind not constant
Time (equipment availability and cost)
Other activities at site
Statistical coverage in 34 tests using orthogonal arrays
Two ‘L8’ (Four factors, two levels each)
Combined into an optimal L16 (full-factorial)
Some interaction information
Two ‘L9’ (Four factors, three levels each)
No interaction information
Additional 20 tests (impact, checkout, elevation sweep)
Results: Wind Pressure
Vent Gates Closed Vent Gates Open
Results: Structural
Next Steps
Develop Point Design and interfaces
System Engineering
Structure performance estimates
Controls
Identify and support studies
Generate SOW’s, schedules, costs
Seek funding to support community studies
Optical fabrication, wind studies, structural trades, etc.