Unit 07 - MOSFETs Lesson Element - Learner Task (DOC, 1MB)

Unit 7: Electrical devices
LO1: Understand semiconductor and programmable devices
MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors)
Learner activity sheet
Activity 1
MOSFETs (metal –oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) are semiconductor devices that are often used as switches. They are voltage controlled – meaning that they will conduct current from the drain to source terminals when a voltage is applied to the gate terminal.
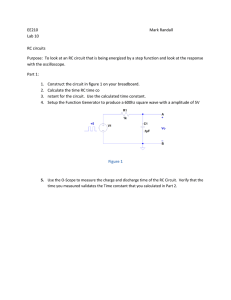
This Activity requires that you build and test the operation of the circuit. Circuit 1 shows a switch circuit using a MOSFET.
Follow the circuit diagram to build the circuit. You could use breadboard, solder the components to veroboard or even manufacture a printed circuit board.
Version 1
If you have access to circuit simulation software then you could simulate circuit operation before building a physical circuit.
A suitable MOSFET is the BS107 N-channel MOSFET (although you could use an alternative).
The datasheet for the BS107 can be found at the following website: http://www.rapidonline.com/design-technology/bs170-n-channel-mosfet-fch-47-0142#techSpecs
+ 5V
SW1 d
R2 = 1K
D1 = LED
R1 = 100M g s
MOSFET
Circuit 1
The MOSFET has three terminals
– the gate, drain and source. Be careful to connect the MOSFET correctly in circuit. Typical pin-out
(looking from the pin side) is shown here – but you may wish to check the datasheet.
GND s g s d d view from pin side g
Version 1
3.
4.
2.
Answer the following questions:
1. What happens when SW1 is pressed and held?
What happens when SW1 is released?
Remove R1 from the circuit – what happens when SW1 is pressed and held?
With R1 removed, what happens when SW1 is released
– and why does this happen?
Version 1
Activity 2
Circuit 2 is similar to circuit 1 except that a capacitor (C1) has now been connected from the gate terminal to ground. A resistor (R3) has also been included through which the capacitor (C1) charges.
Follow the circuit diagram and build the circuit. You may be able to simulate the circuit if you have access to circuit simulation software.
As before, take care to make sure the MOSFET is connected correctly. You must also take care to connect the capacitor the correct way round if you use a polarised type as shown.
+5V
SW1
R2 = 1K
C1 = 100
F
R3 = 100R g
R1 = 100M d s
D1 = LED
MOSFET
GND
Version 1
Answer the following questions:
1. What happens when SW1 is pressed and held?
2. What happens when SW1 is released?
4.
3. Remove R1 from the circuit – what happens when SW1 is pressed and held?
With R1 still removed, what happens when SW1 is released, and why?
Version 1
Activity 3
Investigate the MOSFET further – what makes it different from a normal bipolar transistor?
Version 1