The periodic table - MCQ topic quiz - Lesson element (DOC, 279KB) Updated 29/03/2016
advertisement

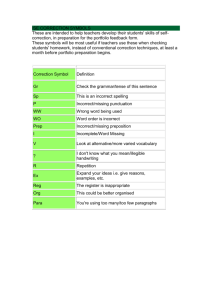
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz 3.1 The Periodic Table Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions cover the learner activity section which can be found on page 7. This Lesson Element supports OCR AS and A Level Chemistry A. When distributing the activity section to the learners either as a printed copy or as a Word file you will need to remove the teacher instructions section. The Activity This Lesson Element is a teaching and learning resource containing 10 multiple choice questions (MCQs) on the theme of the periodic table. Some questions might require synoptic thinking, using knowledge and ideas from various topics across the full A Level content. This resource can be used to test and consolidate understanding at the end of a topic or to revisit and refresh knowledge at a later point in the course. Learning Outcomes This lesson element relates to the specification learning outcomes 3.1.1(a), 3.1.1(b), 3.1.1(c), 3.1.1(g), 3.1.2(a), 3.1.2(b), 3.1.2(d), 3.1.3(c), 3.1.4(a). Introduction Multiple choice questions allow rapid coverage of a wide range of sub-topics. Contrary to a widespread belief among students, multiple choice questions are not necessarily easy – they can be easy, moderate or difficult. The questions are written so that the incorrect answers are plausible distractors based on common errors or misconceptions. The questions in this quiz cover topics mainly from specification sections: 3.1 The Periodic Table. Version 1 1 © OCR 2016 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz - answers 1. Which of the statement(s) below is/are true? 1) Elements in the same group have the same number of electrons. 2) Elements in the same group have similar chemical reactions. 3) Elements in the same group have different mass and proton numbers. A 1, 2 and 3 Incorrect, it is the OUTER electrons which are the same. B only 1 and 2 Incorrect, it is the OUTER electrons which are the same. C only 2 and 3 Correct answer. Reactions are similar within a group and proton number is different for all elements. D only 1 Incorrect, it is the OUTER electrons which are the same. Your answer 2. What causes the trend in first ionisation energy from left to right across the periodic table? A greater number of electrons Incorrect, number of electrons simply increases with number of protons. B greater shielding Incorrect, number of electron shells is constant across a period. C increased nuclear charge Correct answer. More protons means greater attraction to the nucleus. D larger atomic radii Incorrect, radii decrease as nuclear charge has greater effect on outer electrons. Your answer Version 1 C 2 C © OCR 2016 3. What causes the largest changes in melting point across period 2 elements? A change in bonding structure Correct answer. The jump in melting point between giant and simple covalent compounds is huge. B greater electronegativity Incorrect, electronegativity does not have an effect on the melting point of elements. C greater number of electrons Incorrect, this will affect the melting point down a group (e.g. group 17) when there are no other factors. D increase in nuclear charge Incorrect, this has little effect on intermolecular forces and melting points. Your answer 4. When group 2 ions form, the outer electrons are found in: A s orbitals Incorrect, group 2 atoms have their electrons in s orbitals. B p orbitals Correct answer, once the outer 2 electrons are removed, the outer electrons are in p orbitals. C d orbitals Incorrect. D f orbitals Incorrect. Your answer 5. B Which reaction does not involve the oxidation of magnesium? A magnesium reacting with hydrochloric acid Incorrect, it changes from elemental magnesium to ionic, Mg Mg2+ B MgCO3 + HNO3 Correct answer, the magnesium is a 2+ ion as a reactant and product. C Mg + O2 Incorrect, it changes from elemental magnesium to ionic, Mg Mg2+ D magnesium reacting with water (steam) Incorrect, it changes from elemental magnesium to ionic, Mg Mg2+ Your answer Version 1 A 3 B © OCR 2016 6. Which is the most soluble in water? A Mg(OH)2 Incorrect, they have remembered the trend upside down. B Ca(OH)2 Incorrect, probably a guess. C Sr(OH)2 Incorrect, probably a guess. D Ba(OH)2 Correct answer, solubility increases down the group, an explanation is not needed. Your answer 7. D Which will not result in a reaction? A potassium bromide with aqueous iodine Correct answer. Iodine is less reactive than bromine and cannot displace it. B potassium bromide with silver nitrate Incorrect, all halides react with silver nitrates making coloured precipitates. C potassium iodide with chlorine water Incorrect, chlorine is more reactive and displaces the iodide. D potassium iodide with silver nitrate Incorrect, all halides react with silver nitrates making coloured precipitates. Your answer 8. A What colour change will be seen in the following reaction? 2NaI(aq) + Cl2(aq) I2(aq) + NaCl (aq) A brown clear Incorrect, they may be mixing up whether the ionic or elemental iodine causes the colour. B clear brown Correct answer, the iodine formed in the reaction is brown in aqueous solution. C clear purple Incorrect, they may be thinking of the purple colour iodine gives in organic solvents. D orange clear Incorrect, they are mixing up whether the ionic or elemental iodine cases the colour, and have misremembered the colour. Your answer Version 1 4 B © OCR 2016 9. Which test will identify Na2SO4? A Reaction with acid causing effervescence. Incorrect, this tests for carbonates. B Reaction with BaCl2 forming a white precipitate. Correct answer, this is the test for sulfates. C Reaction with silver nitrate forming a precipitate. Incorrect, this is the test for halides. D Reaction with sodium hydroxide forming a characteristic gas which turns blue litmus red. Incorrect, this is the test for ammonium cations. Your answer 10. Which test will identify NH4NO3? A Reaction with acid causing effervescence. Incorrect, this tests for carbonates. B Reaction with BaCl2 forming a white precipitate. Incorrect, this is the test for sulfates. C Reaction with silver nitrate forming a precipitate. Incorrect, this is the test for halides. D Reaction with sodium hydroxide forming a characteristic gas which turns blue litmus red. Correct answer, this is the test for ammonium cations, forming ammonium gas. Your answer Version 1 B 5 D © OCR 2016 This resource has been produced as part of our free Chemistry teaching and learning support package. All the Chemistry teaching and learning resources, including delivery guides, topic exploration packs, lesson elements and more are available on the qualification webpages. If you are looking for examination practice materials, you can find Sample Assessment Materials (SAMs) and a link to the Practice Papers on the qualification webpages: Chemistry A, Chemistry B. We’d like to know your view on the resources we produce. By clicking on ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ you can help us to ensure that our resources work for you. When the email template pops up please add additional comments if you wish and then just click ‘Send’. Thank you. If you do not currently offer this OCR qualification but would like to do so, please complete the Expression of Interest Form which can be found here: www.ocr.org.uk/expression-of-interest OCR Resources: the small print OCR’s resources are provided to support the teaching of OCR specifications, but in no way constitute an endorsed teaching method that is required by the Board, and the decision to use them lies with the individual teacher. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content, OCR cannot be held responsible for any errors or omissions within these resources. © OCR 2016 - This resource may be freely copied and distributed, as long as the OCR logo and this message remain intact and OCR is acknowledged as the originator of this work. OCR acknowledges the use of the following content: n/a Please get in touch if you want to discuss the accessibility of resources we offer to support delivery of our qualifications: resources.feedback@ocr.org.uk Version 1 6 © OCR 2016 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz 3.1 The Periodic Table Learner Activity 1. Which of the statement(s) below is/are true? 1) Elements in the same group have the same number of electrons. 2) Elements in the same group have similar chemical reactions. 3) Elements in the same group have different mass and proton numbers. A 1, 2 and 3 B only 1 and 2 C only 2 and 3 D only 1 Your answer 2. What causes the trend in first ionisation energy from left to right across the periodic table? A greater number of electrons B greater shielding C increased nuclear charge D larger atomic radii Your answer Version 1 7 © OCR 2016 3. What causes the largest changes in melting point across period 2 elements? A change in bonding structure B greater electronegativity C greater number of electrons D increase in nuclear charge Your answer 4. When group 2 ions form, the outer electrons are found in: A s orbitals B p orbitals C d orbitals D f orbitals Your answer 5. Which reaction does not involve the oxidation of magnesium? A magnesium reacting with hydrochloric acid B MgCO3 + HNO3 C Mg + O2 D magnesium reacting with water (steam) Your answer 6. Which is the most soluble in water? A Mg(OH)2 B Ca(OH)2 C Sr(OH)2 D Ba(OH)2 Your answer Version 1 8 © OCR 2016 7. Which will not result in a reaction? A potassium bromide with aqueous iodine B potassium bromide with silver nitrate C potassium iodide with chlorine water D potassium iodide with silver nitrate Your answer 8. What colour change will be seen in the following reaction? 2NaI(aq) + Cl2(aq) I2(aq) + NaCl (aq) A brown clear B clear brown C clear purple D orange clear Your answer 9. Which test will identify Na2SO4? A Reaction with acid causing effervescence. B Reaction with BaCl2 forming a white precipitate. C Reaction with silver nitrate forming a precipitate. D Reaction with sodium hydroxide forming a characteristic gas which turns blue litmus red. Your answer 10. Which test will identify NH4NO3? A Reaction with acid causing effervescence. B Reaction with BaCl2 forming a white precipitate. C Reaction with silver nitrate forming a precipitate. D Reaction with sodium hydroxide forming a characteristic gas which turns blue litmus red. Your answer Version 1 9 © OCR 2016