ld patheungcentral eng feb09
advertisement

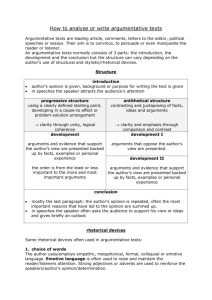
Catering for learner diversity – using variation theory to enhance students’ understanding of argumentative writing Pat Heung Central Primary School – To Kwok Kuen 2009.2.19 Background and Aim • New English Language Curriculum Guide (different text types - 6 categories*) • Individual differences (reading comprehension) • Students learning problems (lack the experience) • *Narrative texts, Information texts, Exchanges, Procedural texts, Explanatory texts, Persuasive texts, (CDC, 2004 - p.17) Background and Aim Aim: To use variation theory to improve students’ understanding of argumentative writing Flowchart Students’ problem Teachers’ meeting (critical aspects) Reflection Assessment Intervention About the lesson preparation…… • Students had problems in understanding the structure of argumentative writing • Students had great individual differences • A pre-test was conducted in order to better understand their ways of understanding or seeing argumentative writing Students’ different ways of seeing (Pre-test) Case 1 Teacher : What is argumentative writing? Student A: Oh, argumentative writing is to argue about … write something to tell someone that this is good and this is bad and argue about it. Case 2 Teacher : What is argumentative writing? Student B: There is no who, where, what and when and no background information in argumentative writing. Students’ different ways of seeing (Pre-test) Case 3 Teacher : What is argumentative writing? Student C: Oh, argumentative writing is to argue about … write something to tell someone that this is good and this is bad and argue about it. Case 4 Teacher : What is argumentative writing? Student D: Argumentative writing has many paragraphs but fewer words. Students’ different ways of seeing (Pre-test) Case 5 Teacher : What is argumentative writing? Student E: Argumentative writing is something about gossip. Case 6 Teacher : What is argumentative writing? Student F: I don’t know. About the lesson preparation…… • Dr Pang’s suggestions • 3 experienced English teachers prepared and designed the lessons together - We focused on: • Students’ learning problems • Students’ learning diversity About the lesson preparation…… The 2 critical aspects identified are: • 1. different ways of reading texts resulting in different understandings • 2. different genres having different structures Lesson plan (1) Pattern of variation/ invariance Text Act Learner i v i Text Meaning Learner i v v Text Act Learner v i i Text Meaning Genre v i v Text Type Characteristics v i v Outcome Makes act visible Makes meaning visible Generalizes act across texts Brings out genre related differences between texts Brings out differences between texts within same genre Lesson plan (1) Stage 1 Teacher uses the variation theory to make the act visible (Same text A but different in act) Students should discern that there are different ways of reading Stage 2 Teacher uses the variation theory to make the meaning visible (Same text A but different in meaning from their summaries) Up to here, students should discern if they use different ways of reading to read a text, they may have different understandings on the same text. Lesson plan (1) Stage 3 Teacher generalizes act across texts (Read text A and B and generalize the way of understanding and reading the texts)* Students should discern the relationship between the way of reading and the understanding of the text *-Text A and B are narrative texts Lesson plan (1) Stage 4 Teacher points out genre-related differences between texts (narrative and argumentative) Read text C (similar topic/meaning to text B but different in genre, that is argumentative) Lesson plan (1) Stage 5 Teacher guides students to discuss the differences between text C and text D (both of them are argumentative texts but they have different themes) Teacher brings out differences between texts within same genre Reflection The 3 teachers discussed the performance of students in the 4 lessons after the instruction. The teachers reviewed the students’ work and interviewed some students. They found that after the two critical aspects of the object of learning were introduced, students had no significant improvement after the instruction. Reflection The teachers decided to start another cycle to deal with the students’ problem. After discussion, it was concluded that some critical aspects of the object of learning might be missed and the texts that students have read might be too difficult for them at this level. Reflection The three additional critical aspects: 3. the difference between the meaning of descriptive sentence and writer’s opinion 4. the words used in argumentative and narrative writing (support, agree, should….) 5. the structures of argumentative and narrative writing. Reflection Two extra lessons were spent on helping students achieve the object of learning. At the same time, all the texts used in the lessons were tailored and shortened. Lesson plan (2) Example 1: Ask students to read the 5 sentences on the lefthanded column (writer’s opinion) Guide them to find out the similarities of the 5 sentences Variant: wordings Invariant: function of the sentences Separation and generalization Example 2: Lesson plan (2) Let students read text C (Theme - Lies and Honesty, argumentative) Text C has a similar topic to text B (Theme - An Honest Boy, narrative) Variant: structure of the text (genre) Invariant: theme Students may discern the differences of the text structure. Contrast Results • Introducing variations in the second instructional design did help improve students’ understanding of the features of argumentative writing. • Students made significant improvement in discerning the features of argumentative writing. • More than half of them were able to either state the features of argumentative writing or categorize the given texts correctly. Suggestions • Appropriate and sufficient variations be introduced in teaching to enhance students’ learning. • Teacher’s reflection is important to the use of variation theory in teaching and learning. Thank you !