Upper Limb structures and assessment
advertisement
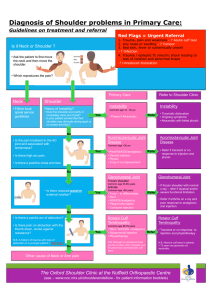
Upper Limb structures and assessment Learning Objectives • Recognize different shoulder pathology • Perform special test to identify different shoulder pathology • Justify PT treatment procedures for different shoulder pathology • Analyze the factors related to thoracic out let syndrome • Write treatment plan for 2 types of shoulder pathology 4 The shoulder Injuries and pathology The Commonest cause of shoulder pain is from the cervical in origin and mostly due cervical spondylosis There are many pathology affecting the shoulder itself, some are needed to be treated by Physical therapy. • The rotator cuff and the sub deltoid bursa and capsule may be compressed during sudden, forceful glenohumeral abduction. • The commonest site is subacromial bursa. Causing a painful arc of movement between 70 and 120 degree of abduction 4 • Symptoms may occur acutely, or chronic, particularly in the older patient. In this latter group there are usually 1. degenerative changes in the acromiclavicular joint. which leads to a reduction in size of the supraspinatus tunnel, 2. Thickening of the subdeltoid bursa of the rotator cuff tendons Treatment • Ice followed by US to the area • AROM • Trigger release with Shoulder PNF a 1. Occurs in young athletes as a result of violent traumatic incidents 2. Most commonly the supraspinatus region is involved and the patient has difficulty in initiating abduction of the arm 3. Other cases of torn cuff may cause impingement on the acromion during abduction giving rise to a painful arc of movement 4. It may require surgical intervention 1. Gross restriction of shoulder movements which is associated with contraction and thickening of the joint capsule (Inferior anterior part) 2. It is a condition that affects the middle-aged in whose shoulder cuffs degenerative changes are occurring. 3. Restriction of movement is often sever especially rotation with abduction 4. Pain is often sever and may disturb sleep. 4 5. In some cases the condition is initiated by a period of immobilization of the shoulder by using a sling after elbow or wrist fracture 6. Radiographs of the shoulder appears normal. 7. Pain may subside after a while, but restriction of movement may be permanent unless treated Treatment • Ultrasound to the spot of restriction (the lower part of the capsule) • Stretching and mobilization exercise (inferior glide, and anterior- posterior glide) • Shoulder wheel • AROM 1. Degenerative changes in the shoulder cuff may be accompanied by the local deposition of calcium salts. 2. Calcified material may give rise to inflammatory changes in the subdeltoid bursa, sudden sever incapacitating pain results. The shoulder become tender and is often swollen and warm to the touch 3. It may mix with Gout and infections symptoms, 4. Symptoms relieved by removing the calcified material from the site of deposition 4 Dr. salameh al dajah 2014 Treatment • Ice for 5 minutes followed by US on the muscle insertion • AROM • Active exercise like pendulum exercise • Acromioclavicular joint is exposed to a high level of stress • Results of fall or sport hitting • Classified into 6 types Dr. salameh al dajah 2014 • • Shoulder may be affected by anterior, posterior, or inferior instability. Anterior stability is the commonest, and in many cases. It occurs most frequently in the 20-40 years age group. • • • The dislocation may occur by trauma for the first time and then reoccur due laxity of ligaments and shoulder tendons. 4. Depending on the mechanism of the trauma, the anterior or posterior dislocation is occurring. 5. Shoulder recurrent dislocation is different from habitual dislocation which occur as a results from ligaments laxity, or psychological factors Treatment • • • • Stabilize for 6-8 weeks Mobility exercise (AROM and Active mobility) Modalities to relieve pain Strengthening exercise for deltoids, pectoralis, scapular muscles, rotator cuff muscles 2 • Moderate swelling, painful, and decreased mobility • Affect the capsule and other inter articular soft tissue • Most of the pyogenic causes are • Tuberculosis of the shoulder • Gonococcal arthritis 2 Dr. salameh al dajah 2014 • Upper trunk region as a functional unit is affected by common factors • The first and second rib are attached to the cervical spine and the clavicle by a group of muscles (Scalene muscles) and group of ligaments • The subclavian artery bends over and passes through a sulcus in the first rib. • Brachial plexus lies stretched and lies tautly without bony protection in this region. • Anterior scalene syndrome and the costoclavicular syndrome (cervical rib) compression are two conditions recognized as thoracic outlet syndrome. • X -ray is essential to determine the presence of the cervical rib, but it is not a prove that it is the cause of the symptoms. h • Adison’s test: Neurovascular compression of the subclavian artery and brachial plexus (cervical rib) • Allen test: maneuver Thoracic outlet syndrome • Roos’ test: Thoracic outlet syndrome 4 • • • • • • • Procedure The examiner locates the radial pulse of the involved extremity The patient’s head is rotated to the involved extremity The patient extends the neck as the examiner externally rotates and extends the shoulder The patient takes a deep breath and holds it Loss of the pulse is a positive test If the test is negative, it is repeated having the patient rotate the head to the uninvolved extremity Dr. salameh al dajah 2014 Procedure The patient’s elbow is flexed to 90 degree The shoulder is abducted and externally rotated As the examiner palpate the radial pulse, the patient rotate the head away from the involved extremity If the pulse disappears when the head is rotated, it is a positive test result for thoracic outlet syndrome Dr. salameh al dajah 2014 • • Procedure While in the seated position, the patient positions both arms at 90 degrees and abducts and externally rotates them • The patient repeatedly opens and closes the fists for up to 3 minutes If this maneuver reproduces the usual symptoms of discomfort, the patient probably has thoracic outlet syndrome Treatment • Modalities to relieve muscle spasm around the shoulder • Stretching and mobilization of the first rib to relieve pressure on the artery • Active shoulder ROM