Lecture no 18
advertisement

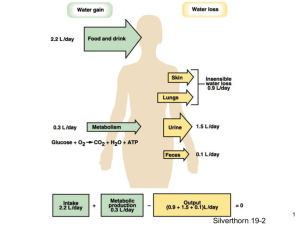
THIRST DR. Shaheenkousar Haroon Rashid Learning Objectives At the end of the session you should be able to Describe the basic physiological mechanism of thirst Discuss body’s response to thirst THIRST A need to drink is perceived as thirst, which causes an individual to seek thirst quenching beverages. The sensation is mediated by higher cortical areas- anterior singulate gyrus and insular cortex. Thirst is sated well before osmolality changes probably because of sensory input from oropharyngeal and GI osmoreceptors Sodium balance Most NaCl intake added during food preparation Sweat output depends on body temperature Urine output of NaCl is regulated by blood pressure Water balance Metabolically produced by oxidation of H-containing nutrients Insensible loss: expiration of 37 saturated air, evaporation through skin (different from sweat) Urine output regulated by vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone ADH) Regulation of ECF • Sympathetic nervous system: decreased MAP in afferent arteriole trigger sympathetic activity • Renin-angitensin-aldosterone system • Antidirutic hormone • Atrial Natriuretic peptide Vasopressin (ADH) release & actions Vasopressin release stimulated by: 1. slight (1%) increase in plasma osmolality 2. large (~10-15%) reduction in plasma volume Vasopressin action: increases permeability of collecting duct to water Renal medulla ADH levels collecting duct permeability water reabsorption urine volume with osmolality ADH Mechanism of Action Receptor binds, causes vesicles to fuse and insert aquaporins (water channels) into the membrane. Juxtaglomerular apparatus Macula densa: specialized cells in wall of distal tubule Juxtaglomerular cells (Granular cells): contain renin, sympathetic nerves Water Loading 4. Drink Water Plasma Osmolality Activation of osmoreceptors in anterior hypothalamus ADH secretion from Post. Pituitary Water permeability in late DT and CT Water Reabsorption Urine Osmolality Urine Volume Water Deprivation 4. Drink Water Plasma Osmolality Activation of osmoreceptors in anterior hypothalamus ADH secretion from Post. Pituitary Water permeability in late DT and CT Water Reabsorption Urine Osmolality Urine Volume Water transport & vasopressin actions Juxtaglomerular apparatus Macula densa: specialized cells in wall of distal tubule Juxtaglomerular cells (Granular cells): contain renin, sympathetic nerves Mesangial cells. 1. Sympathetic NS 3. Pressure (less stretch) RENIN 2. Decreased NaCl sensing Renin angiotensin aldosterone system Actions of aldosterone Aldosterone actions: is a steroid hormone (mineralocorticoid family) produced by the outer section (zona glomerulosa) of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland It plays a central role in the regulation of blood pressure mainly by acting on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron, increasing reabsorption of ions and water in the kidney, to cause the conservation of sodium, secretion of potassium, increase in water retention, and increase in blood pressure and blood volume. Regulation of thirst Sensation of thirst stimulated by: 1. 1% osmolality 2. >10-15% blood volume 3. angiotensin II Diabetes Insipidus Loss of ADH secretion or insensitivity of kidneys to ADH Large severely dilute amounts of urine Increased intake of water Danger lies in hyponatremia and ultimate central nervous system edema and death. Isotonic saline Extracellular volume Blood pressure - Renin, angiotensin aldosterone Atrial Natriuretic peptide Sympathetic NS Sodium excretion ADH secretion Plasma osmolality Water excretion SIADH (hypotonic expansion) vs. Diabetes Insipidus (hypertonic contraction) ↑ Anti-diuretic hormone ↓ ↑ water excretion ↑ water reabsorption at principal cells ↑ thirst – activation of hypothalamic osmoreceptors ↓ vascular volume ↑ vascular volume ↓ MAP ↑ MAP ↑ ANP ↑ renin-angiotensin aldosterone ↓ renin-angiotensinaldosterone ↓ Na reabsorption ↓ K excretion hyponatremia hypernatremia ↑ Na reabsorption ↑ K excretion Water retention + Na excretion explains low plasma osmolality and relatively increased urine osmolality (SIADH) Take Home message Always, through my whole life, I've had a thirst for knowledge. Emith Smith Practice Questions Define Thirst Discuss the mechanism of Regulation of Thirst Role of Kidneys in regulation of ECF osmolality THANK YOU