اسئلة و اجوبة على الباب الاول و الثانى
advertisement

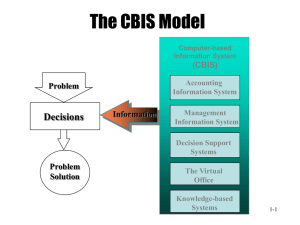
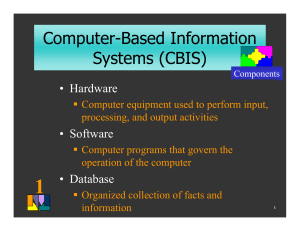
Chapter 1 - Introduction Information system = a set of components that collect (input), manipulate (process) and share (output) information and provide feedback. Information concepts Data versus information Data = raw facts with little value on their own. Information = facts that have been organised (processed) into something meaningful. The type of information created depends on the relationships defined among the data. Process = tasks performed to achieve an outcome. (Turning data into information). Knowledge = awareness & understanding of how to make information useful. Information += data made useful through the application of knowledge. Characteristics of valuable information: Relevant - Info must be applicable. Economical - Balance info value with production costs. Accurate - Info without errors. Complete - Contains all the important facts. Timely - Info is delivered when needed. Simple - Information that is concise and not overloaded. Flexible - Info can be used for many purposes (by managers, sales people, etc…) Reliable - Info can be depended on. Reliability depends on the source of information. Verifiable - Info can be checked. Accessible - Info should be obtained in the right format at the right time. Secure - Info should be secure from unauthorized users. The value of information Measuring value: Additional profit minus the cost of the information. System and modeling concepts System = a set of components that interact to accomplish goals. System components = inputs, processing mechanisms, outputs and feedback. Knowledge is needed to define relationships among inputs and to organize elements. System components and concepts System boundary = the limits of the system. The system boundary defines the system and distinguishes it from everything else, whereas the system configuration refers to the organization of system elements. System types: Temporary - Exists for a short time. Permanent - Exists for a long time. Open - Interacts with environment. Closed - No interaction with environment. Adaptive - Can change in response to changes in the environment. Nonadaptive - Can’t change in response to changes in the environment. Dynamic - Undergoes rapid and constant change. Stable - Undergoes little change. Simple - Few components, with straightforward interaction. Complex - Many elements, highly interconnected. System performance and standards 1. Efficiency = doing things right (with minimum waste / effort). = A measure of what is produced divided by what is consumed. (0-100%) 2. Effectiveness = doing the right thing (getting the desired result). = A measure of the extent to which a system achieves its goals. Divide goals actually achieved by stated goals. System performance standard = a specific objective of the system. E.g. The objective of baking no more than 100 loaves of bread a day. Once standards are established, performance is measured and compared with the standard. System variables and parameters System variable = something that can be controlled by the decision maker (like product price) System parameter = something that can’t be controlled (like the cost of raw materials). Modeling a system Model = an abstraction used to represent reality to help you understand real-world situations. Many contain assumptions (e.g. length of working time), which should be realistic, and users must be aware of them. Types of system models 1. Narrative: Verbal and written descriptions (reports, documents, conversations). 2. Physical: Tangible representation of reality (scale models, E.g. prototype of a new cinema). 3. Schematic: Graphic representation of reality (graphs, charts, diagrams, pictures). 4. Mathematical: Arithmetic representation of reality (logical models used in business). Information systems Input, processing, output, and feedback 1 Input = capturing raw data, manually or automatically. 2 Processing = converting data into useful outputs, manually or with computers. 3 Output = producing useful information in the form of documents or reports. Computer output: printers and display screens. Manual output: handwritten documents and reports. 4 Feedback = output that is used to make changes to input or processing. Errors might make it necessary to correct input or change a process. If output indicates low inventory levels, this feedback can be used to order more. Reactive approach - The feedback system alerts the manager of the problem. Proactive approach - The system predicts future events to avoid problems (= forecasting). Manual & computerised information systems Computerising a manual information system doesn’t guarantee improved performance, because if it is flawed, computerising it might magnify the impact of the flaws. Computer-Based Information Systems (CBIS) Technology infrastructure (hardware, software, databases, telecommunications, people, procedures) forms the foundation of each CBIS. 1 Hardware = computer equipment used to perform input, processing and output activities. 2 Software = programs that operate the computer. 3 Databases = organised collection of facts and information. (= Very valuable to a CBIS) 4 Telecommunications Telecommunications enables organisations to carry out tasks through computer networks. Extranet = a network that allows selected outsiders to access authorised intranet resources. (You’re using an extranet when you track a parcel). 5 People IS personnel = people who manage, run, program, and maintain the system Users can also be IS personnel. People are the most important element in most CBISs. 6 Procedures = Strategies, policies, methods and rules for using the CBIS. A disaster recovery plan is a procedure because it outlines what course of action to take.