maxillary molars
advertisement

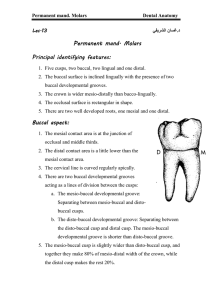
MORPHOLOGY OF MAXILLARY MOLARS Dr. Saleem Shaikh INTRODUCTION They are the largest and the strongest maxillary teeth. Although the crowns are slightly shorter than the premolars, they are greater in all other dimensions. The first molar usually appear in the oral cavity when the child is 6 yrs of age. They erupt posterior to the second deciduous molar, hence it is not a succedaneous tooth. The maxillary molar has four well developed cusps and a Supplementary cusp. It has three roots BUCCAL ASPECT The crown is roughly trapezoidal. When the tooth is viewed from the buccal aspect with the buccal groove at right angles to the line of vision, the distal surface can be seen because the distobuccal line angle is obtuse. The mesiobuccal and distobuccal cusps are seen. The mesiobuccal cusp is broader. And the distobuccal cusp is more sharper, as its mesial and distal slope meet each other at right angles. A buccal groove separates the two cusps. The mesial outline of the crown is straight and it curves occlusally as it reaches the crest of contour of the mesial surface, which is its contact area. This is seen at the junction of occlusal and middle thirds BUCCAL ASPECT The distal outline is more convex and spheroidal, the distal contact area is in the middle of middle third. All three roots are seen from this aspect Lingual root is the longest. The point of bifurcation of the two roots is around 4 mm from the cervical line (root trunk). LINGUAL ASPECT From this aspect only the lingual cusps are seen. The mesiolingual cusp is the largest and the longest cusp of the tooth. 60 % of the lingual surface is made up of the mesiolingual cusp. The mesiolingual cusp is more sharp than the distolingual cusp. The mesial outline makes an angle of around 90o with the Mesial surface. The distolingual cusp is very smooth and spheroidal, and merges with the distal outline. The fifth cusp is seen on the lingual surface of the mesiolingual cusp, it may or may not be prominent. known as CUSP OF CARABELLI A lingual developmental groove is seen between the two cusps. MESIAL ASPECT MESIAL ASPECT From this aspect, mesiobuccal, mesiolingual & cusp of carabelli is seen. starting from the cervical line buccally the crest of curvature is seen in the cervical third. The buccal outline then may be a little concave followed by convexity until the tip of the mesiobuccal cusp. On the lingual outline the crest of curvature is seen in the middle third. The lingual outline is smooth if the fifth cusp is not well developed or if the fifth cusp is developed, the outline may have a depression of the lingual cusp. Two roots are seen from this aspect, the mesio buccal root is broad and flattened The level of bifurcation of the root is a little closer to the cervical line than on the buccal surface. DISTAL ASPECT As the crown tapers distally and is more narrower on this surface, most of the buccal surface can be seen. It is very similar to the mesial aspect. The distal marginal ridge is slightly lower hence triangular ridges can be seen. the distobuccal root is narrower than the mesiobuccal hence all three roots are visible from this aspect. The lingual root is banana shaped. OCCLUSAL ASPECT The outline of the molar from occlusal aspect is rhomboidal. The crown is wider mesially than distally and wider lingually than buccally. All five cusps are seen, mesiolingual cusp is the largest cusp, followed by the mesiobuccal,distolingual and distobuccal. The two buccal cusps and the mesiolingual cusp are the primary cusps. The distolingual cusp is the secondary cusp. Primary cusps form the primary cusp triangle OCCLUSAL ASPECT Two major and two minor fossa are seen. Major – central fossa and distal fossa Minor – mesial and distal triangular ridge Most characteristic feature of the maxillary molar is its oblique ridge, which runs from the mesiolingual cusp to the distobuccal cusp. This ridge is slightly reduced in height in the center of the occlusal surface. The mesial and distal marginal ridges are seen on sides. OCCLUSAL ASPECT The central fossa has a central pit, central and buccal developmental groove are seen in this pit. Sometimes another groove from the central fossa may cross the oblique ridge, this is known as the transverse groove of the oblique ridge. The distal fossa has a distal obligue groove and the lingual developmental groove. PULP CHAMBER Pulp chamber is wide and has pulp horns corresponding to the cusps. The pulp chamber is rectangular in shape. It usually has three roots and three canals, the palatal canal is the largest. The mesiobuccal root often has two canals.