premolar maxillary
advertisement

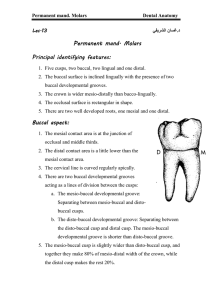
MAXILLARY FIRST PREMOLAR Dr. Saleem Shaikh INTRODUCTION Posterior teeth Present anterior to molars hence named a premolars Also known as bicuspids but some may have 3 cusps The maxillary premolars develop from 4 lobes, the middle lobe as well as the lingual lobe is well developed The lingual lobe develops to form the lingual cusp and hence no cingulum is seen. The marginal ridges are horizontal and are part of the occlusal surface and not the lingual surface. The crown of the premolars is shorter than that of the canine Maxillary first premolar usually has two roots. BUCCAL ASPECT The crown is roughly trapezoidal and resembles a canine. The mesial outline is slightly concave from the cervical line to the mesial contact area. Mesial contact area is in the middle third The mesial slope of the buccal cusp is longer and straight than the distal slope. The cusp tip is slightly distal to the line bisecting the buccal surface. The distal contact area is slightly broader than the mesial contact area and is in the middle third The distal outline below the contact area is straight. Buccal ridge is seen. LINGUAL ASPECT The lingual outline is reverse than that of the buccal cusp The crown tapers towards the lingual surface hence the lingual cusp is smaller than the buccal cusp. Parts of the buccal cusp is also seen The lingual cusp is smooth and spheroidical from the cervical line to the cusp tip. The cusp tip forms an angle of 90 degrees A well developed lingual ridge is present The lingual root is also smaller and part of the buccal root can also be seen. The lingual cusp is around 1-2 smaller than the buccal cusp MESIAL ASPECT The outline is roughly trapezoidal, the longest of uneven sides is towards the cervical portion The tips of the cusps are always within the confines of the root trunk. Most of the maxillary first premolars have a buccal and a lingual root. The buccal outline of the crown is convex and the crest of curvature lies within the cervical third From the crest of curvature the outline slopes towards the cusptip which lies below the center of the buccal root. The lingual outline is more convex, the crest of curvature is in the middle third. The lingual tip on line with lingual outline of root. A distinguishing feature seen on the mesial aspect is the presence of a depression known as “mesial developmental depression” which is present immediately below the mesial contact area and may continue onto the root. The first premolar also has a well defined developmental groove seen on the mesial marginal ridge – mesial marginal developmental groove. The root trunk is long and bifurcation of the root is seen in the apical or middle thirds. DISTAL ASPECT Looks similar to the mesial aspect but does not have the developmental depression or groove. The distal surface is more flattened than the mesial surface. OCCLUSAL ASPECT The occlusal aspect resembles a six sided hexagonal structure. The buccal sides are equal, the mesial side is shorter than the distal side and the mesiolingual side is shorter than the distolingual side. The occlusal surface is circumscribed by the cusp ridges and the marginal ridges. Both buccal and lingual cusp can be seen A well defined central groove divides the surface buccolingually The central groove extends over the mesial marginal ridge to form the mesial marginal developmental groove. Two grooves join the central groove inside the mesial and distal marginal ridges – mesiobuccal and distobuccal developmental grooves. At the junction of the grooves are the mesial and distal developmental pits. Two fossas are seen known as the mesial and distal triangular fossa Buccal and lingual triangular ridge can be seen, buccal ridge is more prominent than the lingual ridge. Maxillary nd 2 premolar 15 Buccal Aspect: The Buccal cusp appears to be slightly shorter and less pointed than the 1st premolar. The mesial cusp ridge is shorter than the distal cusp ridge (opposite in 1st premolar). The buccal ridge is not very prominent 15 Lingual Aspect: the lingual cusp is longer than in first premolar hence less of the occlusal surface is visible. Maxillary nd 2 premolar Mesial aspect: the buccal and lingual cusps of the second premolar are almost equal in height. No developmental depression or groove is seen on the 2nd premolar Distal Aspect: root depression on the distal aspect is greater than on the mesial surface. 15 15 14 14 Maxillary 2nd premolar Occlusal aspect: The crown outline is more rounded and oval rather than hexagonal. The central developmental groove is shorter and irregular. Multiple supplemental grooves are seen radiating from the central groove. This gives the occlusal surface of the 2nd premolar a wrinkled appearance. Pulp: the 2nd premolar usually has a single pulp canal whereas the 1st premolar almost always has 2 pulp canals