week 2 early development
advertisement

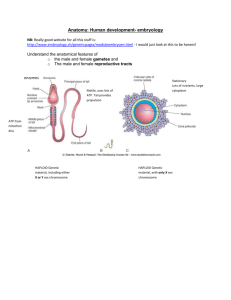
EARLY DEVELOPMENT & GERM LAYERS Dr. Saleem Shaikh Introduction Development starts once the ovum and sperm fuse to each other to form Zygote It goes into multiple rounds of cell division (cleavage) 2,4,6, and 16 cell stage where its called as morula. takes about 4 days for the zygote to reach the uterus and till then this division continues. As the cleavage proceeds to 16 cell stage it is known as morula. If we cut a section through the morula – it shows an inner cell mass which is surrounded by an outer layer of cells. The outer layer of cells give rise to trophblast Inner cell mass gives rise to embryo proper hence called as embryoblast Some fluid enters into the morula and seperates the cells of the inner cell mass from the trophoblast. Throphoblast cells flattened and inner cell mass gets attached to one end of trophoblast The MORULA becomes a BLASTOCYST The cavity seen inside is called as blastocoele Formation of Germ layers The blastocyst gives rise to all the tissues and organs of the body, it also forms many structures which support the embryo and help it to acquire nutrition. This blastocyst converts to a three layered disc…known as the embryonic disc. The three layers are Endoderm Ectoderm Mesoderm All the tissues of the body are derived from these three layers Some cells of the inner cell mass become flattened and line the lower surface this is known as HYPOBLAST The remaining cells become columnar and called as EPIBLAST A space is seen between the epiblast and the trophoblast – this is known as amniotic cavity, filled with amniotic fluid The hypoblast cells spread and line inside the blastocystic cavity to form the primary yolk sac. The cells of the trophoblast proliferate to give rise to a mass of cells known as extra embryonic mesoderm. Chorion, amnion and extra embryonic coelom are formed. The primary yolk sac becomes smaller and is known as secondary yolk sac, and the cells become cubical The cubical cells of the hypoblast become tall (columnar) near the margin of the disc. This area is called as the prochordal plate. This helps to identify the head end of the embryo Next some of the epiblast cells near the tail end proliferate and bulge into the amniotic cavity. This elevation is called as PRIMITIVE STREAK The cells of the primitive streak proliferate and push themselves between the epiblast and hypoblast. These cells form the intra embryonic mesoderm. Some of these proliferating cells displace the hypoblast and form the endoderm. The remaining cells of the epiblast form the ectoderm This process of formation of the primitive streak, intraembryonic mesoderm and endoderm is called as Gastrulation. The cells of the primitive streak do not spread to the area of the prochordal plate. Hence no mesoderm is seen in this region and forms the bucco-pharyngeal membrane Thank you!!!