Navigation: More than Common Sense Valerie Gomez de la Torre
advertisement

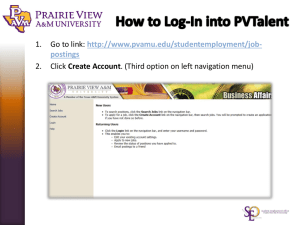
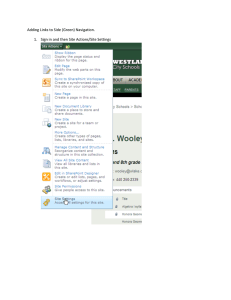
Navigation: More than Common Sense Valerie Gomez de la Torre Information Architecture & Design I INF 384C October 26, 2004 Overview of presentation • IA’s , “Common Sense” & Velma • Users have questions • Types of navigation systems & menus IAs ,“Common Sense” & Velma • Role of IAs – User advocate • Focus on users’ needs, goals and behaviors when designing a navigation system • Focus on the differences between users – seeking behaviors – experience levels • “Design is not decoration, it is communication” Wodtke, 2003, p.204 Users want to know: • Where am I? • Where are the things I am looking for? • How do I get to what I am looking for? Wodtke, 2003, p.34 1. Where am I? • Well placed logos and upfront value propositions • Obvious placement of navigation systems 2. Where are the things I am looking for? • Global navigation systems • Local navigation systems • Contextual navigation systems • Supplemental navigation systems Global navigation systems • Most commonly located on the top of all pages of a web site – links to important content, major categories, and search tools. • Also can be located on the bottom of page – less commonly accessed areas linking to privacy policy, contact information, etc. Global navigation systems Tab Menu Horizontal Menu Bottom Menu Local navigation systems • Local navigation systems complement the global system by allowing users to explore the immediate area and its list of available categories • User behaviors – Pogosticking – Crabwalking Local navigation systems Cascading Menu Sidebar Fly-out Menu Drop-down Menu Contextual navigation systems • Embedded or ‘in line’ hypertext links • Associative links Supplemental navigation systems • Search • Sitemaps • Indexes • Guides • Breadcrumbs • Pagination Supplemental navigation examples Search Site Map Pagination Site Index Supplemental system examples • Breadcrumbs – Location – Path – Attribute 3. How do I get to what I am looking for? • Links should look ‘clickable’ – Transference -“expectations about an interface’s behavior based on their previous experience with other interfaces” (Withrow) • Labeled with clear expectations of what lies beneath • Visual perception – group links to gain meaning through context • ‘The Gestalt rule of proximity indicates that items closet together are perceived as being Advanced navigation • Personalization – website remember user’s name, credit card info, address, etc. – attempt to guess as to what users want • Customization – the user tells the site what she wants • local weather, scores for favorite teams, etc. Rosenfeld & Morville, 2002, p. 127 Conclusion • When planning and designing a navigation system, we can’t always anticipate all the paths users will take. learn more Conclusion • When planning and designing a navigation system we can’t always anticipate all the paths users will take. • But with user testing, we can come close! – testing is essential both before designing a navigation system and Resources • Bernard, Michael, and Chris Hamblin. Software Usablity Reseach Lab. 1 May 2003. 20 Oct. 2004 http://psychology.wichita.edu/surl/Default.htm • Garrett, Jesse James. Digital Web Magazine. 17 Dec. 2002. Adaptive Path. 18 Oct. 2004 http://www.digital-web.com • Instone, Keith E. "Location, path and attribute breadcrumbs." (n.d.). 16 Oct. 2004 http://www.user-experience.org • Krug, Steve. (2000). Don't make me think. 1st ed. Indianapolis, IN: New Riders • Merholz, Peter. Peterme.com. 12 May 2003. 05 Oct. 2004 <http://www.peterme.com>. • Nielsen, Jakob. (2000). Designing Web Usability: The Practice of Simplicity. 1st ed. Indianapolis, IN: New Riders • Rosenfeld, L., & Morville, P. (2002). Information architecture for the World Wide Web. 2nd ed. Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly • van Duyne, D. K., Landay, J. A., & Hong, J. I. (2003). The design of sites: Patterns, principles, and processes for crafting a customer-centered Web experience. Boston, MA: AddisonWesley. • Withrow, Jason. Boxes and Arrows . 11 Aug. 2003. 17 Oct. 2004 http://www.boxesandarrows.com • Wodtke, Christina. (2003). Information Architecture: Blueprints for the Web. ed. Indianapolis,