2 lecture Presented by Dr. Sarah Mustafa Eljack nd
advertisement

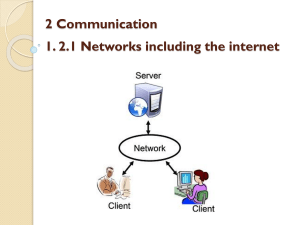
2nd lecture Presented by Dr. Sarah Mustafa Eljack Based on their scale, networks can be classified as : Local Area Network (LAN) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Wide Area Network (WAN) Personal Area Network (PAN) 2 Local Area Network (LAN) A computer network covering a small physical area, like a home, office, or small group of buildings, such as a school, or an airport. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) A network that connects two or more local area networks or campus area networks together but does not extend beyond the boundaries of the immediate town/city. 3 Wide Area Network (WAN) A computer network that covers a broad area The biggest one Personal Area Network (PAN) A computer network used for communication among computer devices close to one person. The smallest one 4 WAN MAN AN AN MAN AN AN … WLAN AN AN … WLAN WLAN WLAN 5 According to Network Structure networks can be classified as : Peer–to–Peer Network.. Server Based Network. Q: Define the client-server model, then classify networks according to structure? Sol: in Client-Server model: • Resources (H/W and S/W) are stored at the server. • Users use simple machines (clients). • Clients and servers are connected through a network. • Clients can request any server resources then the server replies clients requests. Peer-to-Peer Network: All network computers are identical, known as peers. No servers. No administrator for the network, each user controls his computer. Peer-to-Peer Network: It is simple, smaller in size (10 or fewer machines), less expensive than server based networks. Each computer functions as client and server. Server Based Network: • it is the standard model (Opened in size). • The network has servers • Resources are centralized at the server, hence it can be easily controlled. • More expensive than peer-to-peer because Powerful servers are required. Q: what are the different server types? Sol: File server : Stores the shared files and backups. Mail server : Stores and forward e-mail messages between clients. Web server : Stores shared web pages. o Printer server : Allows different clients to use the same printer. Shared Printer Print Server Print Queue Print Job Database server : stores Databases files used by network clients. Proxy server : exists between your network and other networks to protect your network from the external attacks (acts as a firewall). LAN switch Proxy server External Hosts (other networks) Peer-to-Peer networks Server Based network • all computers are identical. No servers. • Use powerful computers as Servers, while the others are clients. has servers.• Distributed resources Centralized resources Definition Peer-to-Peer Network Administration Shared between network users. Server based Network Centralized. Peer-to-Peer networks Shared resources. Distributed. Difficult to be controlled. Server Based network Centralized. Easily controlled. Size Has small size (usually 10 or fewer computers). Has opened size. Cost Less expensive More expensive According to connectivity, there are two main types: Wired Networks. Wireless Networks. Q: Classify computer networks according to connectivity? Wired Networks: Use wires to connect network computers. Wireless Networks: No wiring, connection is done using radio signals. There are three different types: Bluetooth network. Wireless LAN. Wireless WAN. Wireless LAN: A LAN connected through a radio signals. Each computer has a radio modem connecting using base station. Base Station Antenna Radio Modem • Wireless WAN: – A wireless network covers a large geographical area. Thanks for your attention Any questions