Medical Mycology Exam: Fungi, Mycoses, and Dermatophytes
advertisement

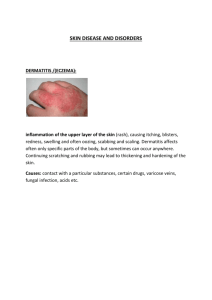
وزارة التعليم العالي جامعة المجمعة كلية العلوم الطبية التطبيقية قسم علوم المختبرات الطبية Ministry of Higher Education Majmaah University College of Applied Medical Sciences Department of Medical Laboratory Name of Instructor: Dr. Omar Amer Location: Majmaah male campus MCQ: Please find the proper answer of the following: 1- Mycologists are a) Scientists who study fungi b) Scientists who study bacteria c) Scientists who study viruses d) Scientists who study algae 2- A fungus does not have a) Chlorophyll b) Cell wall c) Multiple cells d) Nucleus 3- Cell wall of true fungi is composed of a) Chitin b) Cellulose c) Ergosterol d) Cholesterol 4- The yeast like fungi is grouped together in the genus……. a. Cryptococcus neoformans b. Candida c. Fungi d. Moulds 5- Vegetative reproduction in Fungi is achieved through…….. a. Fragmentation of mycelium b. Fission of yeast cells c. Budding of yeast cells d. All of them 1 4- A multinucleate mass of protoplasm, without a cell wall is called a) Hyphae b) Plasmodium c) Anthridium d) Oogonium 5- Fungi that produce sexual resting spores by the union of two gametes a) Ascomycota b) Deutromycota d) Zycomycota c) Basidiomycota 6- Fungi are classified according to a) b) c) d) Their method of reproduction Their mode of living Their economic importance Their occurrences 7- Basidiomycetes are characterized by a) a septate mycelium b) Non septate mycelium c) Production of zygospores d) Production of ascospores 8- Sexual reproduction of Ascomycetes results in a) Formation of basidium b) Formation of sporangium c) Formation of ascus d) Formation of conidia 9- Deutromycetes are characterized by a) Reproduction asexually b) Reproduction sexually c) Production of zoospores d) Production of basidiospores 10- The superficial mycoses are usually confined to a) Dermis b) Hypodermis c) Stratum corneum d) Tissues 11- The organism that is said to be responsible for Tinea versicolor is a) Aspergillus sp. b) Melassezia furfur c) Trichophyton sp. d) Epidermophyton 12- The clinical findings of Tinea nigra a) Brownish maculae on palms b) Depigmented maculae on arms c) Black nodules on the hair d) White nodules on the hair 2 13- Which of the following is causing keratomycosis a) Exophiala werneckii b) Piedraia hortae c) Trichosporon d) Histoplasma capsulatum 14- The treatment that can be used for keratomycosis is a) Surgery b) Shaving c) Topical salicylic acid d) Tincture of iodine 15- Cutaneous mycoses are usually extended to a) Dermis b) Hypodermis c) Epidermis d) Tissues 16- Etiological agents for cutaneous mycoses are called a) Dermatophytes b) Tinea c) Saprophytic fungi d) Candida species 17- Generally the dermatophytes are unable to grow in living tissue but multiply in structure which contain a) Pectin b) Collagen c) Keratin d) Fibrin 18- Which of the following is not a cause of ringworm? a) Microsporum b) Trichophyton c) Candida albicans d) Epidermophyton 19- Anthropophilic species are keratin utilizing on a) Human b) Animal c) Soil d) Plant 20- The ringworm infection of the nails is called a) Tinea capitis b) Tinea corporis c) Tinea unguium d) Tinea pedis 21- Tinea barbae is a ringworm infection of a) The foot b) The scalp c) The groin d) The beard 22- Which of the following cannot be caused by Epidermophyton a) Tinea capitis b) Tinea corporis c) Tinea unguium d) Tinea pedis 23- The major sources of ringworm infection are 3 a) Animals b) Military camps c) Schools d) All of them 24- Balanitis is a) Candidiasis of the eye c) Oral candidiasis b) Candidiasis of the penis d) Vaginal candidiasis 25- Esophagitis is a type of a) Cutaneous infections b) Mucous membrane infections c) Systemic infections d) none of them 26- The color of Candida albicans on chromagar medium is a) White creamy b) Green c) Blue d) Red 27- A 35-year-old female has a red, raised rash on the inside of her thighs. Gramstained skin scrapings show large budding cells with pseudohyphae. The infection is caused by a) Candida albicans b) Histoplasma capsulatum. c) Aspergillus sp. d) Piedraia hortae 28- The general characteristics of microconidia of Trichophyton are a) Absent b) Abundant c) Rare d) Moderate 29- The causative agent of Onychomycosis is a) Penicillium sp. c) Candida albicans b) Alternaria sp. d) Trichophyton 30- Frequently Sporotrichosis is caused when the infectious agent is introduced into wounds by a) Lotions b) Rusty nails c) Food preparation d) Thorns 31 - A substance known to be a source of Rhinosporidium seeberii is a) Cow manure b) Plant c) Soil d) Ponds 32- Which of the following can be treated with topical chemotherapeutic agents? a) Eumycetoma b) Sporotrichosis c) Lobomycosis d) Chromoplastomycosis 4 33- Another name for Mycetoma is a) Madura hand c) Lobomycosis b) Blastomycosis d) Maduromycosis 34- The causative agent of Lobomycosis is the dimorphic fungus a) Acremonium b) Pseudallescheria boydii c) Phialophora d) Lacazia loboi 35- The common etiological agent of Mycetoma in Saudi Arabia is a) Madurella mycetomatis b) Pseudoallescheria boydii c) Phialophora d) Lacazia loboi 36- A causative agent of subcutaneous mycosis cannot be cultured in the lab is a) Actinomyces b) Alternaria c) Phialophora d) Lacazia loboi 37- A 75-year-old male has intramuscular lesions with abscess filled with pus and surrounded by a fibrous wall. The examination of aspirates from cysts showed a pigmented hyphae. The disease is called a) Phaeohyphomycosis c) Lobomycosis b) Blastomycosis d) Maduromycosis 38- Clinical features of Chromoblastomycosis appeared as a) Friable polyps in eye b) Warty cutaneous nodules c) Abscess formation d) Lesions with slight pruritis 39- The site of infection in Rhinosporidiosis a) Eyes b) Hands c) Feet d) Legs 40- Sclerotic bodies is one of the key for identifications the causative agent of a) Rhinosporidiosis c) Lobomycosis b) Chromoblastomycosis d) Sporotrichosis 1. Cell walls of eukaryotes contain ……………that provides rigidity & support, mannan & other polysaccharides a. Lipids b. Chitin c. Sugars d. Ergosterol 5 2. Fungi are considered heterotrophic organism, that means: a. They prepare their food by themselves via photosynthesis. b. They depend on O2 for respiration. c. They parasite living bodies to absorb nutritive materials. d. Both (a) & (c). 3. The term "Mycosis" is referring to: a) b) c) d) The poisoning caused by fungal cells. The infection caused by fungal cells. The infection caused by fungal toxins. The allergy caused by fungal cells. 4. The only pathogenic molds in medical mycology is: a) b) c) d) Cryptococcus neoformans. Candida albicans. Rhodotorula rubra. Histoplasma capsulatum. 5. Sexual reproduction in Basidiomycetes is by the formation of exogenous a. Buds b. Basidiospores c. Hypha d. Basidium 6. Glomus, Gigaspora (mycorrhyzal fungi) have a symbiotic relation with…… a. Plants. b. Human. c. Bacteria. d. All of them. 7. Pityriasis versicolor (tinea versicolor) is caused by: a) Aspergillus niger b) Malassezia furfur. c) Histoplasma capsulatum. d) Exophiala werneckii 8. Spaghetti and meatballs morphology is the characteristic microscopic appearance for diagnosing of: a) Black Piedra 6 b) Tinea Nigra c) Pityriasis versicolor d) White Piedra 9. Mycotic keratitis refers to: a) Fungal infection of scalp. b) Bacterial infection of scalp. c) Mycotic infection of scalp and hair. d) Fungal infection of cornea 10. The most potent treatment of keratomycosis may include: a) Nystatin. b) Erythromycin antibiotic. c) Amphotericin B d) Both a) and c). 11. Trichosporon species, that prefer temperate zone for its growth, causes: a) Black Piedra b) Tinea Nigra c) keratomycosis d) White Piedra 12. In the opposite figure of Rhizopus species, a species of zygomycetes, The arrow is pointed towards: a) b) c) d) Ascus. Columela/ Kolumela. Sporangium. sporangiophore 13. The superficial mycoses are those fungal infectious diseases usually confined to: a) Skin and mucous membrane. b) The outermost layer of skin, hair only. c) The hair roots. 7 d) The outermost layer of skin, tendons and bone. 14. The name of Tinea Nigra is refers to: a) b) c) d) The first reported case with this infection was in Niger. The dark pigmentation of both its hyphae and lesions. The etiology of the disease which is Aspergillus niger. The restricted infection of black – colored people. 15. Dermatophytes or called (skin plant) are keratinophilic, this is refers to: a) b) c) d) The Dermatophytes are unable to invade keratin layer. The Dermatophytes love keratin. Dermatophytes are filled with keratin. Dermatomycosis can be treated with topical keratin. 16. According to the source and mode of infection with ringworm (tinea), Dermatophytes species are classified into three classes, among them, geophilic species, this group is called with this name due to: a) This group of dermatophytes is restricted to certain geographical areas, the name refers to geography. b) The lesions are characterized with geometric appearance, refers to geometry. c) The source of transmission of fungus and infection is the soil, refers to geology. d) None of the above. 17. Tinea capitis is the ringworm infection of: a) b) c) d) Scalp hair. Scalp, head, eyebrows, eyelashes. Soft skin (abdomen, back and legs). Axillary hair and eyelashes. 18. Tinea capitis NEVER been caused by: a) b) c) d) Epidermophyton. Trichophyton. Aspergillus flavus. Both a) and c). 8 19. The absence of microconidia is very characteristic microscopic feature of: a) b) c) d) 20. Microsporum canis Microsporum gypseum. Epidermophyton fluccosum Trichophyton species. Lesions of …………………………… develop at the site of implantation of the etiological agent in the subcutaneous tissue. a) b) c) d) Black Piedra. White Piedra. Tinea favosa. Lobomycosis. 21. Madura foot is caused by: a) Malassezia furfur. b) Pseudoallescheria boydii c) Trichosporon species d) Histoplasma capsulatum. 22. All of the following are related to "Madura foot" except one choice which is not related to this disease: (either we have to take this Q or Q 14 of short answer) a) b) c) d) The city where the first case of the infection appeared in. The site of infection. It is an infection of subcutaneous layer of foot, legs, arms and hand. It is called also "Tinea pedis" because it is localized in foot and legs. 23. The lesions of Madura foot are very characteristic, the most clear one is: a) The small particles or grains leak out of the lesions. b) Nodules on the skin, subcutaneous tissue and in the LNs which later soften & ulcerate. c) Pus and exudate leak out of the lesions. d) Black pigmentation of the affected lesions. 24. The most common etiological agent of Madura foot in Saudi Arabia and neighboring area is: 9 a) b) c) e) Actinomycetes Madurella mycetomatis Madurella grisea Malassezia furfur. 25. Sporotrichiosis may be called "The Flower Disease), this is because: a) b) c) d) 26. It is endemic in USA, the country of flowers. Lesions appear on the top of the skin as flowers. Due to the arrangement of conidia as flower on thin hyphae. All of the above. Rhinosporidiosis is a chronic disease caused by: a) b) c) d) Trichosporon species Rhinosporidium seeberi Trichophyton species. Aspergillus flavus. 27. All of the following describe "Chromobalstomycosis" except one which is: a) b) c) d) It is caused by demateceious fungi. It is called "Verrucous dermatitis" Relapse (recurrence) is very common. Can be treated with chromium element. 28. Lacazia loboi, the hydrophilic fungi may cause: a) b) c) d) Keratomycosis. Lobomycosis. Phaeohyphomycosis Sporotrichiosis. 29. The most characteristic laboratory test for diagnosing C. albicans is: a) b) c) d) Histopathology for detecting the hyphae. Germ tube test. Polysaccharide capsule. Pigmentation on specific media. 30. Chromo agar is a differential medium used to diagnose: 10 a) b) c) d) Chromobalstomycosis. Candidiasis. Cryptococcosis. Chromium deficiency. 31. Compact mass of fungal mycelia located in lung surrounded by dense fibrous walls and called "FUNGUS BALL" is the clinical form of: a) b) c) d) Aspergilloma. Cryptococcoma. Mycotoxicosis. Candidiasis. 32. …………………………… occurs and even pyelonephritis is described but the urinary tract site is less common than one would expect with severely disseminated disease and may simply reflect the length of routine culture methods. a) b) c) d) Cryptococcoma. Cryptococcuria. Cryptococcal peritonitis. Ocular Cryptococcosis. 11 Short Answers Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Compare between fungi and bacteria (only two items). Compare between mycosis and allergy caused by fungi? Define mycotoxicosis? Mention some of medically important fungal genera (only two items). According to the type of reproduction spores type or morphology, fungal kingdom can be classified into five (5) divisions, please mention them? 6. Compare between white and black Piedra infections? 7. Mention some of superficial Mycotic diseases and explain why do they prefer this tissue to infect? 8. Mention some of the causative agents of Mycotic keratitis and the predisposing factors stimulate (initiate) this infection? 9. Mention the factors affecting the severity of infection with ringworm (tinea)? 10. Explain the term "Anthropophilic species of dermatophytes" 11. Compare between Trichophyton and Trichosporon? 12. Count the three genera of dermatophytes? 13. Compare between the three genera of dermatophytes? 14. Mention the reason of naming the fungal infection of foot with the name "Madura foot"? 15. Give reason for incubating Sporothrix schenckii at two different incubators, one of them adjusted on 250 C and the other on 370 C? 16. Sporothrix schenckii may be diagnosed through clinical findings, detection of the organism in tissue and/ or in the lesion. Mention the name of the most useful test used to diagnose Sporotrichiosis in the lesion? 17. Count the three forms of clinical forms of "Phaeohyphomycosis"? 18. Count some of clinical forms of Aspergillosis as an opportunistic fungal infection? 19. Define "Mycotoxicosis" and give an example? 20. Compare between antifungal antibiotics and synthetic antifungal? 21. Compare between opportunistic fungi and systemic mycosis? 22. Compare between coccidioides and paracoccidioides? 23. Sensitivity test has absolute importance for all the clinical isolated microorganisms these days, but for Candida spp. show great importance, give reason for that? 24. Count some of Cryptococcus neoformans virulence factors? 1. 12



![Occupational Health - Zoonotic Disease Fact Sheets #15 DERMATOMYCOSES Foot)]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/013216770_1-db2cdf56a16f26d122fecafe6758caad-300x300.png)


