TRANSMISSION MEDIAS
advertisement

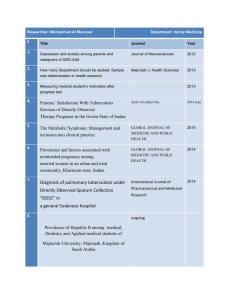
CEN-444 Networks Structure And Protocols Transmission Medium Mohammed Saleem Bhat m.bhat@mu.edu.sa Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University PHYSICAL MEDIA Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Physical Media Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Physical Media Copper Coaxial Cable - Thick or Thin Unshielded Twisted Pair - CAT 3,4,5,5e&6 Optical Fiber Multimode Singlemode Wireless Short Range Medium Range (Line of Sight) Satellite Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Copper Media: Coaxial Cable Coaxial cable is a coppercored cable surrounded by a heavy shielding and is used to connect computers in a network. Outer conductor shields the inner conductor from picking up stray signal from the air. High bandwidth but lossy channel. Repeater regenerate signals. is used to the weakened Category Impedance Use RG-59 75 W Cable TV RG-58 50 W Thin Ethernet RG-11 50 W Thick Ethernet Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Copper Media: Twisted Pair Twisted-pair is a type of cabling that is used for telephone communications and most modern Ethernet networks. A pair of wires forms a circuit that can transmit data. The pairs are twisted to provide protection against crosstalk, the noise generated by adjacent pairs. There are two basic types, shielded twisted-pair (STP) and unshielded twisted-pair (UTP). Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Consists of 4 pairs (8 wires) of insulated copper wires typically about 1 mm thick. The wires are twisted together in a helical form. Twisting reduces the between pairs of wires. interference High bandwidth and High attenuation channel. Flexible and cheap cable. Category rating based on number of twists per inch and the material used CAT 3, CAT 4, CAT 5, Enhanced CAT 5 and now CAT 6. Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Categories of UTP UTP comes in several categories that are based on the number of twists in the wires, the diameter of the wires and the material used in the wires. Category 3 is the wiring used primarily for telephone connections. Category 5e and Category 6 are currently the most common Ethernet cables used. Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Categories of UTP: CAT 3 Bandwidth 16 Mhz 11.5 dB Attenuation 100 ohms Impedance Used in voice applications and 10baseT (10Mbps) Ethernet Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Categories of UTP: CAT 4 20 MHz Bandwidth 7.5 dB Attenuation 100 ohms Impedance Used in 10baseT (10Mbps) Ethernet Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Categories of UTP: CAT 5 100 MHz Bandwidth 24.0 dB Attenuation 100 ohms Impedance Used for high-speed data transmission Used in 10BaseT (10 Mbps) Ethernet & Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Categories of UTP: CAT 5e 150 MHz Bandwidth 24.0 dB Attenuation 100 ohms Impedance Transmits high-speed data Used in Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps), Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) & 155 Mbps ATM Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Categories of UTP: CAT 6 250 MHz Bandwidth 19.8 dB Attenuation 100 ohms Impedance Transmits high-speed data Used in Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) & 10 Gig Ethernet (10000 Mbps) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Media Optical fibers use light to send information through the optical medium. It uses the principal of total internal reflection. Modulated light transmissions are used to transmit the signal. Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Total Internal Reflection Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Media Light travels through the optical media by the way of total internal reflection. Modulation scheme used is intensity modulation. Two types of Fiber media : Multimode Singlemode Multimode Fiber can support less bandwidth than Singlemode Fiber. Singlemode Fiber has a very small core and carry only one beam of light. It can support Gbps data rates over > 100 Km without using repeaters. Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Single and Multimode Fiber Single-mode fiber Carries light pulses along single path Uses Laser Light Source Multimode fiber Many pulses of light generated by LED travel at different angles Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Media The bandwidth of the fiber is limited due to the dispersion effect. Distance Bandwidth product of a fiber is almost a constant. Fiber optic cables consist of multiple fibers packed inside protective covering. 62.5/125 µm (850/1310 nm) multimode fiber 50/125 µm (850/1310 nm) multimode fiber 10 µm (1310 nm) single-mode fiber Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber-Optic Cable Contains one or several glass fibers at its core Surrounding the fibers is a layer called cladding Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Optic Cable FO Cable may have 1 to over 1000 fibers Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Wireless Media Very useful in difficult terrain where cable laying is not possible. Provides mobility to communication nodes. Right of way and cable laying costs can be reduced. Susceptible to rain, atmospheric variations and Objects in transmission path. Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Wireless Media Indoor : 10 – 50m : BlueTooth, WLAN Short range Outdoor : 50 – 200m: WLAN Mid Range Outdoor : 200m – 5 Km : GSM, CDMA, WLAN Point-to-Point, Wi-Max Long Range Outdoor : 5 Km – 100 Km : Microwave Point-to-Point Long Distance Communication : Across Continents : Satellite Communication Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Frequency Bands Band Range Propagatio n Application VLF 3–30 KHz Ground Long-range radio navigation LF 30–300 KHz Ground Radio beacons and navigational locators MF 300 KHz–3 MHz Sky AM radio HF 3–30 MHz Sky Citizens band (CB), ship/aircraft communication VHF 30–300 MHz Sky and line-of-sight VHF TV, FM radio UHF 300 MHz–3 GHz Line-ofsight UHF TV, cellular phones, paging, satellite SHF 3–30 GHz Line-ofsight Satellite communication Line-ofEHF 30–300 GHz Long-range radio navigation Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University sight Wireless LAN PC Access Point Internet Router Switch PC Access Point Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Terrestrial Microwave Microwaves do not follow the curvature of earth Line-of-Sight transmission Height allows the signal to travel farther Two frequencies for two way communication Repeater is used to increase the distance Hopby-Hop Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Satellite Communication Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University UTP AND FIBER CABLING Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Structured Cabling Infrastructure Mounted and permanent Allows patching Comfort that infrastructure is OK Components: Information Outlet with Face Plate Patch Panel UTP Cable Patch Cord Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University I/O & Faceplates Faceplate mounts on or in wall or in raceway Single or Dual Information Outlet (I/O) Provide network connectivity to the Hosts through a Patch Cord Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Patch Panel Termination punchdown in back Patch cord plugin in front Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Patch Cord & UTP Connectors Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Color Codes Data Tx: 1 & 2 Data Rx: 3 & 6 Crossover 13 26 PoE +VDC: 4 & 5 PoE -VDC: 7 & 8 Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Cutting, Striping & Crimping Tools Make your own patch cords Cuts and strips pairs RJ45 end crimped onto ends of wire Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Punching Tool Terminates wires to back of patch panels and in Information Outlets Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Making Cables Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Wire Testing Equipment Test wire for correct termination of 8 wires Test for speed capabilities Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Cabling Rules Try to avoid running cables parallel to power cables. Do not bend cables to less than four times the diameter of the cable. If you bundle a group of cables together with cable ties (zip ties), do not over-cinch them. You should be able to turn the tie with fingers. Keep cables away from devices which can introduce noise into them. Here's a short list: copy machines, electric heaters, speakers, printers, TV sets, fluorescent lights, copiers, welding machines, microwave ovens, telephones, fans, elevators, motors, electric ovens, dryers, washing machines, and shop equipment. Avoid stretching UTP cables (tension when pulling cables should not exceed 25 LBS). Do not run UTP cable outside of a building. It presents a very dangerous lightning hazard! Do not use a stapler to secure UTP cables. Use telephone wire/RJ6 coaxial wire hangers which are available at most hardware stores. Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Optic Cabling Infrastructure Components: Fiber Cable Fiber Pigtail Fiber Connectors LIU Coupler Fiber Patch Cord Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Optic Connectors Terminates the fibers Connects to other fibers or transmission equipment Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Patch Cords & Pigtails Ends are typically either SC or ST Pigtails have connectors on only one side and Patch Cords have it on both sides. Pigtails are spliced to the fiber to terminate the fiber Patch Cord connects switches to the Fiber cable Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University LIU & Couplers Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Optic Installation – Outside Plant Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fiber Optic Installation – Outside Plant Fiber is blown in HDPE Pipes, 1 m deep. The HDPE pipes is covered with sand and brick lining Fiber Roles are typically 2 Km. Fiber cables are spliced using Jointers Faults like fiber cut are located using OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University LAN TECHNOLOGIES Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Technology Options Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet 10 Gig Ethernet WLAN Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Media Access Ethernet and Wi-Fi are both “multi-access” technologies Broadcast medium, shared by many hosts Simultaneous transmissions will result in collisions Media Access Control (MAC) protocol required Rules on how to share medium The Data Link Layer is divided into two Part MAC Media Access Control) Sublayer and LLC (Logic Link Control) Sublayer Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University 802.3 Ethernet Carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD). CS = carrier sense MA = multiple access CD = collision detection Base Ethernet standard is 10 Mbps. 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps standards came later Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Ethernet CSMA/CD CSMA/CD (carrier sense multiple access with collision detection) media access protocol is used. Data is transmitted in the form of packets. Sense channel prior to actual packet transmission. Transmit packet only if channel is sensed idle; else, defer the transmission until channel becomes idle. After packet transmission is started, the node monitors its own transmission to see if the packet has experienced a collision. If the packet is observed to be undergoing a collision, the transmission is aborted and the packet is retransmitted after a random interval of time using Binary Exponential Backoff algorithm. Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Ethernet Address End nodes are identified by their Ethernet Addresses (MAC Address or Hardware Address) which is a unique 6 Byte address. MAC Address is represented in Hexa Decimal format e.g 00:05:5D:FE:10:0A The first 3 bytes identify a vendor (also called prefix) and the last 3 bytes are unique for every host or device Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Ethernet Frame Structure Preamble: 7 bytes with pattern 10101010 followed by one byte with pattern 10101011 Used to synchronize receiver, sender clock rates Addresses: 6 bytes, frame is received by all adapters on a LAN and dropped if address does not match Length: 2 bytes, length of Data field CRC: 4 bytes generated using CR-32, checked at receiver, if error is detected, the frame is simply dropped Data Payload: Maximum 1500 bytes, minimum 46 bytes If data is less than 46 bytes, pad with zeros to 46 bytes Computer Engineering and Networks, College Length of Engineering , Majmaah University Ethernet 10 Base 5 (Thicknet) (Bus Topology) 10 Base 2 (Thinnet) (Bus Topology) 10 Base T (UTP) (Star/Tree Topology) 10 Base FL (Fiber) (Star/Tree Topology) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Ethernet BUS Topology Repeater Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Ethernet STAR Topology Hub Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Ethernet Physical Media :10 Base5 10 Base2 10 BaseT 10 BaseFL - Thick Co-axial Cable with Bus Topology Thin Co-axial Cable with Bus Topology UTP Cat 3/5 with Tree Topology Multimode/Singlemode Fiber with Tree Topology Maximum Segment Length 10 Base5 - 500 m with at most 4 repeaters (Use Bridge to extend the network) 10 Base2 - 185 m with at most 4 repeaters (Use Bridge to extend the network) 10 BaseT - 100 m with at most 4 hubs (Use Switch to extend the network) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fast Ethernet 100 Mbps bandwidth Uses same CSMA/CD media access protocol and packet format as in Ethernet. 100BaseTX (UTP) and 100BaseFX (Fiber) standards Physical media :100 BaseTX - UTP Cat 5e 100 BaseFX - Multimode / Singlemode Fiber Full Duplex/Half Duplex operations. Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Fast Ethernet Provision for Auto-Negotiation of media speed: 10 Mbps or 100Mbps (popularly available for copper media only). Maximum Segment Length 100 Base TX - 100 m 100 Base FX - 2 Km (Multimode Fiber) 100 Base FX - 20 km (Singlemode Fiber) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University Gigabit Ethernet 1 Gbps bandwidth. Uses same CSMA/CD media access protocol as in Ethernet and is backward compatible (10/100/100 modules are available). 1000BaseT (UTP), 1000BaseSX (Multimode Fiber) and 1000BaseLX (Multimode/Singlemode Fiber) standards. Maximum Segment Length 1000 Base T - 100m (Cat 5e/6) 1000 Base SX - 275 m (Multimode Fiber) 1000 Base LX - 512 m (Multimode Fiber) 1000 Base LX - 20 Km (Singlemode Fiber) 1000 Base LH - 80 Km (Singlemode Fiber) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University 10 Gig Ethernet 10 Gbps bandwidth. Uses same CSMA/CD media access protocol as in Ethernet. Propositioned for Metro-Ethernet Maximum Segment Length 1000 Base-T - Not available 10GBase-LR - 10 Km (Singlemode Fiber) 10GBase-ER - 40 Km (Singlemode Fiber) Computer Engineering and Networks, College of Engineering , Majmaah University