EBM
advertisement

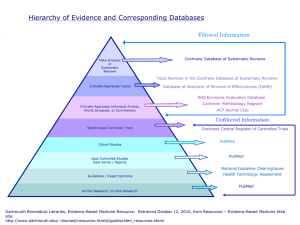
Evidence Based Medicine Dr. Mansour AlZahrani SB-FM,ABFM,MRCGP[INT] Consultant and Assistant professor of Family Medicine Objectives • Know the definition of evidence based medicine. • Discuss steps of evidence-based medicine. • Discuss types of the studies. • Define Randomized control, diagnostic, meta-analysis & systematic review, cohort and case control studies. Definition Evidence-based medicine requires the integration of the best research evidence with our clinical expertise and our patient’s unique values and circumstances. Patient Values Straus SE, Richardson WS, Glasziou P, Haynes RB. Evidence-based medicine: how to practice and teach EBM 3d ed. London: Churchill Livingstone, 2005 EBM Best research evidence Clinical Expertise Why is EBM important? • Physician is taking a decision all the time. • Physicians asked 2 questions for every 3 patients. • Only 30% of physicians' information needs were met during the patient visit, usually by a colleague. • EBM can confirm your plan but it can change it totally. • Is EBM a "cook book medicine“ ?!! STEPS IN EVIDENCE BASED RESEARCH 1. 2. Asking answerable questions Finding the best evidence 3. 4. 5. Critically appraising the evidence Applying a decision Evaluation Heneghan C, Badenoch D. Evidence-based medicine toolkit. 2d ed. Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2007 The Answerable Question STEP 1 • Asking answerable questions – focused, searchable, clinical • PICO • Patient, Problem, Population (subjects) • Intervention or therapy • Comparison, Control • Outcome (results) Can You Identify PICO? • In children under 6 months, how does sleeping on back compared to sleeping on the stomach in terms of risk of SIDS? • In children under 6 months (P), how does sleeping on back (I) compared to sleeping on the stomach (C) in terms of risk of SIDS (O)? STEP 2 • Finding the best evidence with which to answer the question through structured searches and understanding the literature Just do it!! • Um Ahmed is a new patient in your clinic. She is 70 year old and has a history of congestive heart failure brought on by several myocardial infarctions. • She has been hospitalized twice within the last 6 months for worsening of heart failure. Her medications (enalapril, aspirin and simvastatin). • You think she should also be taking digoxin but you are not certain if this will help keep her out of the hospitalization. You decide to research this question before her next visit. Step 1 • PICO designed question. • In elderly patients with congestive heart failure, is digoxin effective in reducing the need for hospitalization? Types of studies Medline • The world’s largest biomedical database • Over 5,000 journals indexed, with worldwide coverage • Covers all aspects of biosciences and healthcare • Database of 19+ million journal citations, 1950 to the present • 90% are in English ; 79% have abstracts • The primary component of PubMed So What Is PubMed? • PubMed is a tool to search: • MEDLINE (1950 to present) • Produced by NCBI • National Center for Biotechnology Information, part of NLM • Accessible worldwide on the Web at no charge Accessing PubMed • Directly at: http://pubmed.gov • Or, National Library of Medicine’s homepage: http://www.nlm.nih.gov Definitions • Case-control study: A study which involves identifying patients who have the outcome of interest (cases) and patients without the same outcome (controls), and looking back to see if they had the exposure of interest. • Case series A report on a series of patients with an outcome of interest. No control group is involved. • Cohort Study Involves identification of two groups (cohorts) of patients, one which received the exposure of interest, and one which did not, and following these cohorts forward for the outcome of interest. • Randomized control clinical trial (RCT) Participants are randomly allocated into an experimental group or a control group and followed over time for the variables/outcomes of interest. • Systematic review A summary of the medical literature that uses explicit methods to perform a comprehensive literature search and critical appraisal of individual studies and that uses appropriate statistical techniques to combine these valid studies. • Meta-analysis A systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.