Embryology lecture. HUMN110. Morphological changes during maturation of gametes
advertisement

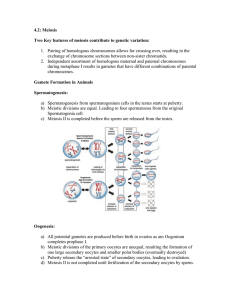
Morphological Changes During Maturation of the gametes • At the end of this session, the student should be able to: • a) Define and classify gametogenesis. • b) Describe morphological changes during maturation of oocytes. • c) Describe morphological changes during maturation of sperms . • d) Describe abnormal gametes . • Ref: Langman’s Medical Embryology, 11th edition, chapter 2, pages 21-26 Gametogenesis • The process of formation and development of specialized generative cells, gametes. This process, involving the chromosomes and cytoplasm of the gametes, prepares these sex cells for fertilization. The chromosome number is reduced by half and the shape of the cells is altered. – Spermatogenesis – Oogenesis • Spermatogenesis is the sequence of events by which spermatogonia are transformed into mature sperms. • Oogenesis is the sequence of events by which oogonia are transformed into mature oocytes. Primordial germ cells(PGC) • Gametes are derived from PGCs that are formed in the epiblast during 2nd week and that move to wall of the yolk sac. • During 4th week these cells begin to migrate from yolk sac towards developing gonads where they arrive at the end of 5th week. Oogenesis Maturation of oocytes begins before birth • PGCs (in gonads)→Oogonia → undergo mitotic divisions • ↓5th month= 7 million germ cells (in ovary) • Oogonia start degenerating and by 7 month most have degenerated. • All surviving germ cells (as primary oocyte) have entered prophase of meiosis 1. Maturation of Oocytes continue at puberty • At the time of birth= All oocytes in prophase of meiosis 1 (arrested in its diplotene stage). • Primary oocytes remain arrested in prophase and do not finish meiosis 1 before puberty is reached (OMI). • Number of primary oocytes at birth= 6-8 lacs. • Number at beginning of puberty= 40,000. • Number being used during life= ˃ 500. Maturation continues • Primordial follicle: A primary oocyte surrounded by flat epithelial cells. • Pool of growing follicles. • Every month 15-20 of growing follicle start maturating → primary follicles → secondary→ Preovulatory. • Meiosis 1 is completed (surge in LH stimulates preovulatory growrh)→ enters meiosis 2 but arrests in metaphase about 3 hours before ovulation. M 2 is completed only if oocyte is fertilized. Spermatogenesis It begins at puberty • At birth, germ cells in male infant are recognized in the testes sex cords as large, pale cells surrounded by supporting(sertoli) cells. • Before puberty, the sex cords acquire a lumen and become seminiferous tubules. PGCs give rise to spermatogonial cells →type A →type B → primary spermatocytes (enters the meiosis and form secondary spermatocyte and finally spermatids. Spermiogenesis • It is the series of changes resulting in the transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa. • Time required: 74 days. • Changes include: – Formation of acrosome. – Condensation of the nucleus. – Formation of neck, middle piece and tail. – Shedding of the most of the cytoplasm. Clinical Correlates • Abnormal gametes