Document 15349438
advertisement

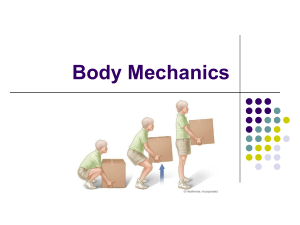
The dynamic process by which the body’s position is maintained in equilibrium. Equilibrium means that the body is either at rest (static equilibrium) or in steady-state motion (dynamic equilibrium). The body’s center of mass (COM) or center of gravity (COG) is maintained over its base of support (BOS). COG, LOG, BOS Balance control (varying conditions) COP& GRF Contents Types of Balance Effect of Gravity on body segments (LOG) Balance control Effect of Gravity on body segments *Center of Gravity (COG) or Center of mass (COM) It is an imaginary balancing point where the body weight can be assumed to be concentrated and equally distributed. Anterior 2nd sacral vertebra (adult) Line of Gravity (LOG) • The vertical line passing through the COG called Line of Gravity (LOG). Base of Support (BOS) The boundaries of the contact area between the body & its support surface. Relationship between LOG & BOS The less height of LOG, the more stability. The nearest the LOG to the center of base of support, the more stabilty. Height COG LOG Stability Center BOS Newton’s law & Center Of Pressure The location of the vertical projection of the ground reaction force (GRF) Effect of Gravity on body joints LOG Trunk Hip Knee Ankle Ant., Pos., or through Joint Musculo skeletal Nervous Contextual effects Balance control Contextual effects that interact with the two systems are the environment whether it is closed (predictable with no distractions) or open (unpredictable and with distractions), the support surface (i.e., firm versus slippery, stable versus unstable, Types of balance control Static dynamic Automatic Static balance control ◦ Maintaining sitting. ◦ Half-kneeling, ◦ Tall kneeling, ◦ Standing postures on a firm surface, ◦ Tandem, Single-leg stance. ◦ Working on soft surfaces (e.g., foam, sand, grass), ◦ Narrowing the BOS, moving the arms, or closing the eyes. 1. 1. Dynamic Balance Exercises Using Movable Surfaces: Swiss Ball Tilt Boards