The Project Planning Phase – Project Initiation and Project Management Lecture 2
advertisement

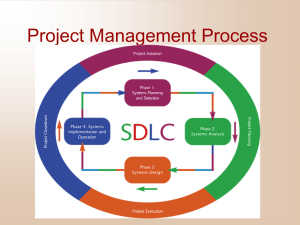
The Project Planning Phase – Project Initiation and Project Management Lecture 2 Courtesy to Dr. Dasgupta 1 Objectives The Systems Development Lifecycle (SDLC) SDLC Phases The Project Management Phase Project schedule Project Feasibility 2 IS Development Phases 3 Project Management People Organizing Directing Planned result Scheduling Budgeting 4 Participants in Development Project 5 Project Management Body of Knowledge Scope management Human resource management Time management Cost management Communications management Risk management Procurement management Quality management 6 Project Initiation Driving forces Respond to opportunity Resolve problem Conform to directive 7 Project Initiation Long-term IS strategic plan (top-down) Weighted Scoring Department managers or process managers (bottom-up) Response to outside forces 8 Activities of the Project Planning Phase 9 Producing Project Schedule Develop work breakdown schedule List of tasks required for project Like an outline Build a PERT/CPM chart Assists in assigning tasks Critical path method Tracking GANTT chart 10 Figure Graphical diagrams that depict project plans (a) A Gantt Chart (b) A PERT chart 11 Comparison of Gantt and PERT Charts Gantt Visually shows duration of tasks Visually shows time overlap between tasks Visually shows slack time PERT Visually shows dependencies between tasks Visually shows which tasks can be done in parallel Shows slack time by data in rectangles 12 PERT - Project Representation Basics AoA = Activity on Arc AoN = Activity on Node Event - An event marks the start or completion of a particular task or activity. Activity - An activity is a task or a subproject that occurs between two events. Two methods: Critical Path Method (CPM), PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique 13 Critical Path Method Step 1 - Draw the network of activities Step 2 - List all possible paths from start to end Step 3 - Calculate the total time for each path in Step 2 Step 4 - The path with the highest duration is the critical path and its duration is the project completion time. Step 5 - Calculate slack times if needed 14 Calculation of Slack Times Step 5 Earliest Start ( Forward Pass ) ES activity = max( ES predecessor + duration predecessor ) LS activity = min ( LS successor - duration activity ) 15 Project Management Example Activity Predecessor Duration ( Weeks ) A - 3 B A 2 C A 4 D B, C 5 E B, C 2 F E 5 16 PERT - Program Evaluation and Review Technique A PERT chart is a graphical representation of project task activities and their interrelationships. Allows stochastic activity completion times. More realistic than Critical Path Method in which all durations are deterministic. 17 PERT steps Identify each activity to be completed in the project Determine time estimates and calculate the expected completion time for each activity. Determine the sequence of activities and precedence relationships among all activities by constructing a Gantt and PERT chart. Determine the critical path. 18 Calculation of Time Estimates and Completion Times Three time estimates for each activity o = optimistic duration (reflects the minimum amount of time needed for an activity to be completed) p = pessimistic completion time for an activity r = realistic completion time for an activity ET = estimated time for the completion of an activity ET = (o+4r+p)/6 19 Confirming Project Feasibility Economic Cost/benefit analysis Cash flow analysis Organizational and cultural Technological Schedule Resource 20 Economic Feasibility Economic feasibility for tangible costs and benefits uses the “Time Value of Money” Time value of money refers to the concept of comparing present cash outlays to future expected returns. Useful method to comparing competing projects with different useful life expectancy 21 Commonly Used Techniques Net Present Value (NPV): uses a discount rate determined from the company’s cost of capital to establish the present value of a project. The discount rate is used to determine the present value of both cash receipts and outlays. 22 Present Value If i = discount rate or the company’s cost of capital Y = amount of money “n” years from now PVn= present value of Y dollars “n” years from now then PVn=Y [1/(1+i)n] 23 Example If we calculate the present value of $1000 received two years from now with a discount rate of 10%. Then the present value would be: PV2 = 1000 [1/(1+0.10)2] = 1000 x 0.8264 = 826.40 24 Net Present Value The Net Present Value is calculated as the sum of all present values. Example: if we have to calculate NPV of 3 payments received in the next three years then, NPV = PV1+PV2+PV3 25 Return on Investment (ROI) ROI is the ratio of the net cash receipts of the project divided by the cash outlays of the project. Selection of projects can be made by comparing their representative ROI ratios. ROI = (Overall NPV / NPV of all costs) 26 Break-even analysis Break-even analysis finds the amount of time required for the cumulative cash flow from a project to equal its initial and ongoing investment. For the first year the overall NPV cash flow is non-negative, Break-even ratio = (Yearly NPV Cash Flow - Overall NPV Cash Flow) / Yearly NPV Cash Flow 27 Intangibles in Economic Feasibility Costs and benefits cannot always be measured Intangible Benefits Increased levels of service Customer satisfaction Survival Need to develop in-house expertise Intangible Costs Reduced employee moral Lost productivity Lost customers or sales 28 Organizational and Cultural Feasibility Each company has own culture New system must fit into culture Evaluate related issues for potential risks Computer competency Computer phobia Perceived loss of control Shift in power Fear of job changes Fear of employment loss Reversal of longstanding procedures 29 Technological Feasibility Does system stretch state-of-the-art? Does expertise exist in-house for development? Does a third party need to be involved? 30 Schedule Feasibility Interim evaluations to reassess completion dates Realistic assumptions and estimates Completion date flexibility Involvement of experienced personnel Proper allocation of resources 31 Resource Feasibility Team member availability Team skill levels Equipment and supplies Support staff Physical facilities 32 Project Staffing Develop resource plan for the project Identify and request specific technical staff Identify and request specific user staff Organize the project team into work groups Conduct preliminary training and team building exercises 33 Launching Project Oversight committee is finalized and meets to give go-ahead Formal announcement made 34