introduction to prostho
advertisement

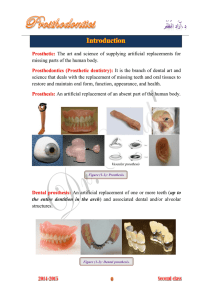
WEL-COME DR. TAJammul AHMED /[dr. taj] Department of Prosthodontics a.tajammul@gmail.com UNIVERSITY OF MAJMAAH, COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY, AZ-ZULFI, KSA. INTRODUCTION TO PROSTHODONTICS Course code;212 sds Objective of learning prosthodontics??? To treat this patient Objectives of today’s class; To get familiarized with the contents, guidelines, assessment tools, do’s and don'ts in this semester. To define the term prosthodontics. To enumerate the branches in prosthodontics. To enumerate the scope of removable prosthodontics, & in brief about complete dentures. This is the first course in prosthodontics. It consists of didactic and practical components. It has two parts: • The first part is introductory to prosthodontics in the form of lectures. • The second is the practical components covering some of the basic technical aspects in removable prosthodontics. The laboratory phase of this course is a coordinated effort in building and improving the basic technical skills in prosthodontics and occlusion. Course laboratory contents 1. Anatomical landmarks of the maxilla and mandible. 2. Primary impression and pouring of the primary cast. 3. Special tray. 4. Final impression, Boxing & pouring (demonstration). 5. Relief and Post dam. 6. Construction of record rims and acrylic bases. 7. Articulators, face bow and mounting (demonstration). All the students shall be evaluated in each laboratory session according to the recommended laboratory step by the course director and instructor. Assessment tools The following percentages (%) of the total grade will be assigned: In-course assessments 60% • • • • • o Quizzes and assessments10% o Weekly practical quizzes 10% o Midterm written examination15% o Midterm practical examination 15% o Oral exam10% Final examination 40% • o Final written examination30% • o Final practical examination10% Important instructions; It is preferable to protect your eyes with protective glasses while you are trimming the special trays or trial denture bases. It is preferable to put on your face masks. Never throw hard plaster mix, alginate or remnants of self cured acrylic resin in water sinks. Be sure that you closed the gas valves after finishing your work, if you suspect any gas leakage; report it directly to your supervisor. Any questions should be referred to the instructors or course director. Keep the lab clean whenever you finish your work. Introduction: Prosthodontics (Prosthetic Dentistry); It is the dental specialty pertaining to the diagnosis, treatment planning, rehabilitation and maintenance of the oral function, comfort, appearance and health of the patients with clinical conditions associated with missing or deficient teeth and / or maxillofacial tissues using biocompatible substitute. Prosthodontist A specialist in prosthodontics Branches in prosthodontics A condition in which natural teeth are present in the mouth. A condition in which the mouth is without teeth. A condition in which some of the natural teeth are present and some are lost. Complete denture prosthodontics: • Involves an artificial replacement of the lost natural dentition and associated structures of the maxilla and mandible for patient who has lost all their remaining natural teeth. Complete denture • A removable dental prosthesis that replaces the entire dentition and associated structures of the maxilla or mandible. Function of complete denture: 1- Mastication: • chew food for swallowing and digestion. 2- Speech (phonetics): • the teeth either natural or artificial assist the tongue and lips to form some of the sounds of speech. 3- Appearance (aesthetic): • is influence by the shape of jaws together with the position and occlusal relation ship of the teeth. 4- Health of the alveolar bone and the tempro-mandibular joints (T.M.J). Types of dental removable prosthesis 1. Conventional Complete dentures 2. Partial dentures Acrylic base metallic base 3. Overdentures A complete denture supported both by mucosa and by a few remaining natural teeth that have been altered, as by insertion of a long or short coping, to permit the denture to fit over them. 4. Immediate dentures A removable artificial denture that is placed in the mouth immediately after the surgical removal of all remaining teeth at the same appointment as the tooth extractions to maintain normal appearance and the ability to chew food. It may be complete or partial. Clinical and laboratory steps of complete denture construction Clinical laboratory 1. Examination of the mouth. 2. Preliminary impression making. Pouring of impression to obtain the Construction of special (custom) trays 3. Final impression. Boxing and pouring of the final Construction of recording bases Mounting of the models with occlusal rims on articulator. setting-up of teeth and waxing-up. Processing of the dentures (flasking, wax elimination, packing, curing, deflasking & polishing 4. Recording jaw relationships and selection of artificial teeth. 5. Try-in of the waxed-up denture. 6. Insertion of the finished denture. 7. Post-insertion care. Thank You