younger Hmmm….learning experiences…… older
advertisement

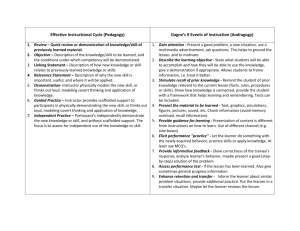
‘Education is not preparation for life; education is life itself.’ home (John Dewey) younger Hmmm….learning experiences…… older passive vs. active learning *pedagogy the art, science or profession of teaching; especially education *andragogy the art and science of teaching adults *Source: http://www.merriam-webster.com In 1926, the American Association for Adult Education began and quickly started researching better ways to educate adults. Influenced by Dewey, Eduard C. Lindeman wrote in The Meaning of Adult Education: Our academic system has grown in reverse order. Subjects and teachers constitute the starting point, [learners] are secondary. In conventional education the [learner] is required to adjust himself to an established curriculum....Too much of learning consists of vicarious substitution of someone else's experience and knowledge. Psychology teaches us that we learn what we do....Experience is the adult learner's living textbook. four assumptions about adults as learners Adults tend to be more self-directed as a result of their maturity. Adults possess personal histories which defines their identities and serve as a resource of experiential learning upon which new learning can be applied. Malcolm Knowles 1913 - 1997 Motivation in adults is directed to more socially relevant learning. Adult learners have interest in immediate application for problem-solving. Pedagogy Andragogy ‘play’ vs. ‘work’ The Learner The learner is dependent upon the instructor for all learning The teacher/instructor assumes full responsibility for what is taught and how it is learned The teacher/instructor evaluates learning self-directed responsible for his/her own learning Self-evaluation is characteristic of this approach Role of the Learner’s Experience The learner comes to the activity with little experience that could be tapped as a resource for learning The experience of the instructor is most influential The learner brings a greater volume and quality of experience Adults are a rich resource for one another Different experiences assure diversity in groups of adults Experience becomes the source of self-identify active vs. passive learning Readiness to Learn Pedagogy Andragogy Students are told what they have to learn in order to advance to the next level of mastery Any change is likely to trigger a readiness to learn The need to know in order to perform more effectively in some aspect of one’s life is important Ability to assess gaps between where one is now and where one wants and needs to be Orientation to Learning Learning is a process of acquiring prescribed subject matter Content units are sequenced according to the logic of the subject matter Learners want to perform a task, solve a problem, live in a more satisfying way Learning must have relevance to real-life tasks Learning is organized around life/work situations rather than subject matter units Pedagogy Andragogy Motivation for Learning Primarily motivated by external pressures, competition for grades, and the consequences of failure Internal motivators: self-esteem, recognition, better quality of life, self-confidence, self-actualization Adults are internally motivated* Adults have specific reasons for engaging* Adults bring life experience to their learning activities well designed LMS (Learning Management System) Three basic components to any course site INFORMAT ION Make information (content) available to students COMMUNICATION Provide communication channels for students and instructors to share information and provide feedback ASSESSMENT Provide assessment tool(s) for evaluation How can we accommodate the demands, limitations and requirements of adults and their multiple personal/social/professional commitments? How can we leverage the unique skills, talents and experiences adults bring to the classroom? How does an andragogical perspective change the traditional role of ‘teacher’? “youth is wasted on the young” G.B. Shaw How can we accommodate the demands, limitations and requirements of adults and their multiple personal/social/professional commitments? Full-time job Responsibility for family/children Synchronous or asynchronous? Course materials available from multiple channels? (streaming, RSS, wiki/blog sites) Flexibility when setting deadlines for assignments (what are deadlines for?) Alternatives for project completion Learning contracts Online assessments (realistic tests: identify explicit knowledge requirements— practice tests—lists-recorded test reviews) How can we leverage the unique skills, talents and experiences adults bring to the classroom? student-led discussions group projects learning contracts How does an andragogical perspective change the traditional role of ‘teacher’? Instructor functions as guide and active participant in learning process Don’t teach students content ; teach students how to find and use content to achieve their learning goals Information is no longer difficult to access; the challenge now is to help students develop independent learning skills Learning Contracts learning goal(s) learning resources and strategies target date for completion evidence of accomplishment of objective(s) criteria and means for validating evidence Three basic components to any course site INFORMAT ION Make information (content) available to students 27/7; multiple sources; mobile apps COMMUNICATION Provide communication channels for students and instructors to share information and provide feedback Collaboration: student-student; student-teacher; studentother resources. Make sure communication functions to achieve student learning goals ASSESSMENT Provide assessment tool(s) for evaluation Online testing; portfolios, projects authentic assessment; assessments that measure student-identified learning objectives So, how do we design courses that maximize these concepts? Access to course content synchronous or asynchronous ? Documents, media, presentations available online ? RSS? Choosing content-allow students the freedom to pursue information that is of interest to them Interaction /collaboration with instructors and peers Have students define areas of interest Have students lead discussions assessment Self/peer evaluation Learning Contracts Learning is enhanced when it is immediately applicable to real-life contexts