mountains & mountain forming
advertisement

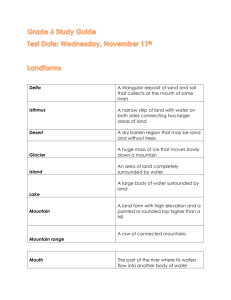
Mountains & Mountain Building Process, definition, & pictures Isostatic Rebound – crust rises as a result of __________________ removal of mass This iceberg demonstrates the process of isostatic rebound. A little bit of explanation The greater the mass above the base level (the mountain), the greater will be the mass below the base level (roots) As weathering and erosion reduces the mass above the baseline, interior uplift forces cause the mass to rise until there is balance between the mountain and its root. Continued explanation The process continues with the mass above resulting in less and less and mass, and consequently, less and less root. Eventually the mountain mass has all been reduced too the base level and the root has all but disappeared. Folded rock layers produced by compressional forces. This part of the syncline folded mountain shows a __________. Example of new crust being formed at Iceland. Sheild _____ type volcano on the mid-Atlantic ridge. Convergent-Boundary Mountains The following three slides show mountain types produced when together plates move __________. Ocean-Ocean Convergence Volcanic island arc trench Basaltic magma Examples: Aleutian Islands, Japan Phillipines,______ Ocean-Continental Convergence volcanic mountains trench metamorphic rock Examples: Cascades ________, Andes Andesitic magma, granitic intrusions Continental-Continental Convergence metamorphic and sedimentary rock folded mountains faults igneous intrusions Appalachians Examples: Himalayas,______________ Nonconvergent-Boundary Mountains The next four slides show mountains formed at divergent boundaries (plates moving _____), apart hot spots, and areas of faulting or uplift. Divergent-Boundary Mountain pillow basalts intrusive rock Example: Mid-Atlantic Ridge Volcanic Hot Spot Mountain extrusive ingneous rock Hawaii Galapagos Example: ______, Uplifted Mountains intrusive igneous rock, less structural deformation Adirondacks Example: ____________ Fault-Block Mountains mostly sedimentary rock Example:Grand __________, Tetons Basin and Range Definition There is no universally-accepted definition of mountain. Elevation, volume, relief, steepness, spacing and continuity have been used as criteria for defining a mountain. In the Oxford English Dictionary a mountain is defined as "a natural elevation of the earth surface rising more or less abruptly from the surrounding level and attaining an altitude which, relatively to the adjacent elevation, is impressive or notable." In the United States, the following points of measurement have been used and taught in geography classes: Flat to 500 feet, base to highest point Rolling Plain Highest point 501 to 999 feet above base - Hill Highest point 1000 feet or more above base - Mountain Mount Damavand, Iran Five Finger Mountain, Azerbaijan The Alps, Europe Swiss Alps The Matterhorn in the Alps, the classic pyramidal peak Mount Olympus, Greece The Himalayas Mount Everest, Himalayas Blue Ridge Mountains, Virginia Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania Great Dividing Range, Victoria, Australia Pilot Mountain, North Carolina Northern Appalachians, Quebec Yu Shan, Taiwan Tangkuban Parahu – Java, Indonesia Dinaric Alps, Montenegro Rocky Mountains, U.S. & Canada Andes Mountains, South America