Mexico
advertisement

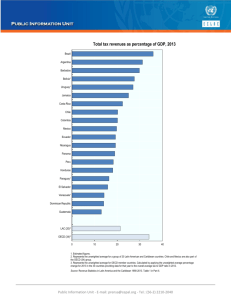
National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Informatics of Mexico Information Exchange Between OECD and Mexico using SDMX Geneva, April 2006 Agenda The new role of INEGI The National System of Statistical and Geographical Information The National Net of Information (RNI) International information exchange Diagnosing the exchange of information between OECD and Mexico Improvements Working plan Conclusions The New Role of INEGI Mexico is a federal country with a division of powers: Executive, Legislative and Judicial INEGI was a federal government office that belonged to the Executive power Now INEGI is in transit to be an autonomous institution, it means that it does not depend of the Federal Government In its new role, INEGI has to coordinate the production, standardization and disemination of all statistical information of national interest The National System of Statistical and Geographical Information (SNIEG) Production of statistical and geographical information of national interest Dissemination of information Promotion of knowledge and use of information Preservation of information The National System of Statistical and Geographical Information (SNIEG) UPI UPI UPI INEGI (UPI) Access to Information User UPI UPI UPI * UPI: Information Producer Unit The National Net of Information (RNI) A set of processes for the support of: Information exchange Information safeguard Coordination of the SNIEG and its subsystems Dissemination of information through the Public Information System Information System for the National System of Statistical and Geographical Information (SISNIEG) Set of technological elements that supports the Statistical and Geographical Information Infraestructure Logical Nets of the SISNIEG Net for the Colaboration and Exchange of Information with International Organisms National Offices of International National Offices of Geographical Organisms Statistics Information Collaboration and Information Exchange Systems Collaboration and Information Exchange Systems Collaboration and Information Exchange Systems Net for the collaboration and information exchange with the Information Producer Units System for the access of information of/to international organisms User Access system for public dissemination of information INEGI (UPI) UPI UPI Collaboration and Information Exchange Systems Collaboration and Information Exchange Systems Collaboration and Information Exchange Systems Systems for dissemination of Information Systems for dissemination of information Systems for dissemination of information Net for the dissemination of information International information exchange Mexico is collaborating with the Secretary of Foreign Affairs (SRE) in a program to establish a unique point for the dissemination of statistical information at international level It implies that all Federal Agencies will have a new mechanism for the interchange of statistical and geographical information Diagnosing the exchange of information between OECD and Mexico Mexico has to report statistical information to OECD Information is being sent by several Federal Agencies to offices of the OECD Only part of the information exchange is correctly identified We need to develop new ways of coordination Background Works made in Paris Building of an information flow matrix 10 working days 34 interviews Data in the matrix: OECD area Information source in Mexico Communication media OECD and Mexico relationship Information flow matrix Information flow matrix of Mexico - OECD Aspect Periodicity Source Media Mexico Contact Economic Outlook Half-yearly DatabaseEconomic Department (ECO) BANXICO INEGI Internet pages of Mexico Central Bank and INEGI MEI Real Indicators Annual INEGI email Annual Annual BANXICO Internet page of INEGI Internet page of Mexico Central Bank Prices Annual BANXICO Internet page of BANK OF MEXICO Labor Statistics Annual INEGI-STPS Questionnaire Ricardo Rodarte Roberto López Esquinca Annual National Accounts Annual INEGI Questionnaire Oscar Abaonza Jorge Daude Jaime de la Llata MEI Financial Indicators Fatima Pérez, Coordinador de Análisis Estadístico de Series Económicas Information flow Tax México SEP Prices OECD DSTI MEI PPP’s INEGI Economic Ooutlook SHCP STPS Balance of Payments IMSS Bank Profitability CONACYT National Accounts SAGARPA Consultor Education Database BANXICO International Migration CNBV Institutional Investors SSA Territorial Agricultural ECMT ELSA OECD statistics program Nombre Año Publicaciones Agriculture and Fisheries Statistics Agri-Environmental 1999 Enviromental Indicators for Indicators Agriculture Agricultural 2004 OECD Agricultural Outlook Commodities Anual Agricultural Market Access Agricultural Policies in Anual Agricultural Policies in Emerging Emerging and 2002 and Transition Economies Transition Economies Economic Accounts for Agriculture Producer and Consumer Support Estimates Review of Fisheries in OECD Countries Economic Accounts for Agriculture Agricultural Policies in OECD Countries - Monitoring and Evaluation Review of Fisheries Statistics in OECD Countries: Country Statistics 2001 to 2003--2005 Bianual Volumen 1: Policies and Summary Anual Volumen 2: Fisheries country 2005 statistics Base de datos Nitrogen Balance Database The Agricultural Commodities Database Agricultural Market Access Database (AMAD) Agricultural Policies in Emerging and Transition Economies M Administrador del a programa i R Kevin Parris e vGarry Smith (Jesús Antón, Senior Analysis, Agricultural Peter Liapis On-going Wayne Jones Variables Economic Accounts for Agriculture (EAA) Producer and Consumer Support Darryl Jones Estimate Luis Portugal Statistics on Fisheries (available for free on the OECD Public Website) Recolección de datos Carl-Christian Schmidt On-going Variables Datos Improvements Creation of a portal for infomation exchange Implementation of international standards Integration of the statistical information of mexican government agencies Use of SDMX Automation of information exchange Application of web services Information exhange channel INEGI OECD BANXICO SHCP SEP SAGARPA SEMARNAT parameters SDMX transformation components DataSet SDMX Update Web Service Client parameters Supporting architecture Concepts, codes and data SDMX schemas Base de Datos Clientdel database cliente Database of the provider (Data and metadata) Early experiences Access to indicators of INEGI’s echonomical database Objective: Information reports of economical and financial indicators from INEGI directly to the database of the Treasure Deparment (SHCP) Strategy: Implementation of a mechanism to access the INEGI database and transform the results using web services technology Applied architecture INEGI SHCP Web Services server .NET Client Internet Java Client Different platforms support Database server Firewall Economic Information Database Web service instrumentation Client example Web service functionality: Last actualization of an indicator in an especific time interval All the indicators by actualization date Last actualization for an especific indicator Last actualization of all indicators 238 XML output Implementation of SDMX Client Example SDMX component functionality WSDL Querying of current catalogues (measurement unit, periodicity, etc.) Transformation of time series to SDMX format 238 WSDL List of Available Services Service Contract Sample of the SDMX client SDMX output for one indicator SDMX output for a time series SDMX code lists (Catalogs) Collaboration efforts with OECD 1. 2. 3. Portal to integrate the statistical information exchanged with OECD Participation in the SDMX implementation pilot project (with other countries) Transformation of the information in the portal to SDMX format and incorporation of web services technology International information exchange portal International coordination through the portal International data collection International data collection Working plan Integration of information from mexican agencies that has to be sent to the OECD Gradual transformation of data files to SDMX format In the near future we are planning to establish web services to automate information exchange with those agencies Tasks that remain to be done with international partners and colleagues Strong and efficient communication ties Collaboration groups for the exchange of experiences Joint review of processes to speed up the whole project Joint work to get the goals done Conclusions Mexico is in the way of implementing SDMX as a tool to improve the internal information interchange The international exchange will be strongly supported by the application of standards like SDMX Our efforts are not limited to technological issues, we need agreements with agencies, working frameworks, standardized catalogs, common definitions among other things We need to create international team to achieve more challenging goals in a relative short time and with few resources Conclusions SDMX will allow us to fulfill compromises with international agencies But, above all, we pretend to have an effective way to collect, to process and to interchange statistical and geographical information among all the levels of government: federal, state and municipal Thank you…