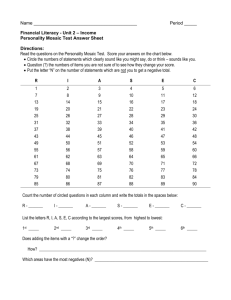
A Thematic Introduction to Cultural Geography As organized by Joe Naumann
advertisement

A Thematic Introduction to Cultural Geography As organized by Joe Naumann Adjunct Associate Professor – Geography UMSL MANY PEOPLE & MANY CULTURES The Human Mosaic CHAPTER 1 THINKING GEOGRAPHICALLY 2 INTRODUCTION Humans are by nature geographers Possess awareness of and curiosity about the distinctive character of places Can think territorially or spatially Each place on Earth is unique Places possess an emotional quality and significance that contribute to our identity as unique human beings Geographers, over the centuries, generated a number of concepts and ideas that literally changed the world 3 SEVEN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHICAL IDEAS THAT CHANGED THE WORLD The Human Mosaic Maps Human adaptation to habitat Human transformation of the earth Sense of place Spatial organization and interdependence Central place theory Megalopolis 4 The Human Mosaic GEOGRAPHY AS AN ACADEMIC DISCIPLINE Natural human geographical curiosity and need for identity First arose among the ancient Greeks, Romans, Mesopotamians, and Phoenicians Arab empire expanded geography during Europe’s Dark Ages 5 3 OF THE OLDEST MAPS The inate geographic interest inspired the first attempts at mapping the world. These were produced between the 7th and 6th centuries B.C.E. 6 The Human Mosaic LET’S CONSIDER THE TYPICAL AMERICAN LEVEL OF GEOGRAPHIC KNOWLEDGE AND CONCERN. CHECK THE FOLLOWING FEW SLIDES. 7 The Human Mosaic 8 The Human Mosaic 9 The Human Mosaic 10 The Human Mosaic 11 The Human Mosaic WHAT IS GEOGRAPHY? The study of the spatial characteristics of the interaction between humans and the physical environment through time with a particular emphasis on understanding the spatial characteristics of the present world in which we live. The processes which shape the earth both natural and human. Identify cause and effect relationships Identify and project trends 12 The Human Mosaic THE 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY Source: National Geographic Society The Five Themes LOCATION PLACE MOVEMENT HUMAN/ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION REGIONS 13 The Human Mosaic LOCATION – DETERMINING THE POSITION OF A PLACE ON THE EARTH’S SURFACE 1. Absolute location – precise positioning – latitude and longitude are the best. 2. GIS gives this new meaning Automobile systems linked to satellites Relative location – describing in relation to other, known places such as landmarks and unusual, easily recognizable features. Used by most people in giving directions 14 The Human Mosaic PLACE – THOSE FEATURES THAT GIVE CHARACTER TO A LOCATION (A DEGREE OF UNIQUENESS). 1. 2. Physical place – natural features – what nature provides – climate, landforms, vegetation, etc. Can many places no longer be called physical places – where might the human influence be absent today? This relates to the theme of human/environment interaction. Human (cultural) place – features added by humans – distinctive dress, architecture, language, religion, burial practices, agricultural practices, etc. 15 The Human Mosaic HUMAN/ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION 1. Human adaptations to natural conditions. 2. Heavy coats in winter Elevated housing in areas prone to flooding Changes (Alteration) in natural conditions made by humans. Digging canals Changing the vegetation – farming, etc. 16 The Human Mosaic MOVEMENT – THE TRANSFER OF MATERIAL AND NON MATERIAL THINGS FROM PLACE TO PLACE 1. Material things – involving tangible objects transported in a variety of ways 2. Animal and animal-powered means Land, water, and air vehicles Non-material things – information, power, culture traits Fashions, trends, fads, etc. Electronic media, etc. 17 The Human Mosaic REGIONS – MENTAL CONSTRUCTS EXPRESSING SOME COMMONALITY OR UNIFORMITY 1. Formal Regions – possesses a single common feature or a limited combination of features throughout the area 2. Political units such as states and counties Functional Regions – An operational unit based on organization, structure, and interactions – an area organized around a node. The hinterland of a major city 18 The Human Mosaic THE FIVE THEMES IN EDUCATION All elementary and secondary textbooks currently are built around the Five Themes of Geography The Five Themes are easy to remember and use 19 DESCRIBING UNIQUE LOCATIONS SITE: Physical character of a place. Important characteristics: climate, water sources, topography, soil, vegetation, latitude, and elevation SITUATION: the location of a place relative to other places. Situation helps us understand the importance of relative location. 20 The Human Mosaic INTRODUCTION CONTINUED A. The concept of region An important tool for geographic study Basis for comparing and contrasting different parts of the Earth B. Defining culture Culture is the learned, dynamic, and generally accepted way of life of a group of people which results from the accumulated and ever changing world view, attitudes, objectives, and technical skills of the group. 21 The Human Mosaic WHAT IS CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY? A. The meanings of culture 1. Learned consciously and subconsciously (unconsciously?) 2. Culture as a process 3. Human-Environment interaction B. Cultural (Human) Geography focuses on the spatial nature and expression of the items above. 22 The Human Mosaic CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Focuses on cultural phenomena that may vary or remain constant from place to place Language & religion Deep culture Surface culture Explains how humans function spatially 23 ICEBERG OF CULTURE The Human Mosaic Surface Culture DEEP CULTURE: Slow to change – often operates in the subconscious When dealing with other cultures, one may have problems because one may be aware of the surface culture traits and may not be aware of very significant elements of “deep culture.” 24 The Human Mosaic SURFACE CULTURE & HUMAN PLACE Language Religious mannerisms, rituals, celebrations Ethnic dress Architecture Cuisine Public gender roles Social manners Status symbols Technology 25 The Human Mosaic ARCHITECTURE – SOUTHEAST ASIA Distinctive religious dress 26 The Human Mosaic LATIN AMERICAN ARCHITECTURE 27 The Human Mosaic NORTH EUROPEAN ARCHITECTURE 28 The Human Mosaic DISTINCTIVE DRESS & MUSICAL INSTRTUMENT 29 The Human Mosaic DISTINCTIVE DRESS 30 The Human Mosaic CLUES TO: ECONOMIC SYSTEM & GENDER ROLES 31 The Human Mosaic DEEP CULTURE World view Foundational attitudes Ranking of life goals Foundational religious assumptions or “realities” – cosmology Foundation for social mores The “roots” that support and nourish surface culture 32 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Culture region Formal culture regions Most commonly based on more than one cultural trait Example of an Inuit culture region Similarities and differences between Greeks and Turks Cultural borders as transition zones 33 The Human Mosaic FORMAL REGIONS – ONE CRITERION OR SET OF CRITERIA 34 The Human Mosaic ONE OR MORE CRITERIA FOR A FORMAL REGION 35 The Human Mosaic TRANSITION ZONE BORDERS 36 The Human Mosaic TRANSITION FROM CBD TO RESIDENTIAL CBD Transition Zone Residential 37 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY A. Culture region Functional culture regions Organized to function politically, socially, or economically Nodes Core-periphery configuration Example of newspaper circulation area May not coincide with formal region—example of Germany 38 POSSIBLE CRITERIA FOR GERMAN CULTURE REGION The Human Mosaic 39 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Culture region culture regions: Vernacular regions are those loosely defined by people's perception (i. e., The South, The Middle East). Vernacular Perceived existence Generally lack sharp borders 40 The Human Mosaic DECREASING INCIDENCE IN TRANSTION ZONE Direction of Decrease 41 The Human Mosaic VERNACULAR REGIONS OF N. AMERICA 42 The Human Mosaic NORTHWEST, NEW ENGLAND, & THE SOUTH 43 The Human Mosaic MIDWEST & SOUTHWEST 44 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural diffusion Independent invention Types of diffusion Relocation diffusion Expansion diffusion—can be divided into three subtypes 45 The Human Mosaic 46 The Human Mosaic III. THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural diffusion Time-distance decay Absorbing and permeable barriers to diffusion 47 A SHRINKING WORLD Travel is easier, cheaper, and faster today. New York to Paris by passenger jet today takes about 6 hours 48 The Human Mosaic ACTORS PROMOTING DIFFUSION Internet Satellite Television & Radio Faster, cheeper, easier transportation Relative affluence of people in the developed countries 49 The Human Mosaic 50 The Human Mosaic III. THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY B. CULTURAL DIFFUSION 5. STAGES OF ACCEPTANCE OF INNOVATION 6. GLOBALIZATION 51 The Human Mosaic 52 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural ecology Concept of the human ecosystem Meeting ground of cultural and physical geographers Environmental determinism Humans molded by nature Had serious consequences—example of European colonization 53 The Human Mosaic 54 The Human Mosaic 55 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural ecology Possibilism Environment gives people choices Higher level of technology weakens influence of environment 56 The Human Mosaic 57 The Human Mosaic 58 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural ecology Environmental perception Choices by people made on their perception of the environment Perception of natural hazards Organic view Mechanistic view 59 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural Humans ecology as modifiers of the Earth Opposite of determinism Past effects of environmental alteration by agriculture and livestock Gender differences as Earth modifiers 60 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural interaction Cultures are complex wholes One facet of culture influences other facets Culture determinism 61 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural Spatial interaction models Model building Example of a model for Latin American cities 62 The Human Mosaic 63 The Human Mosaic III. THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural Sense interaction of place Topophilia is described in Webster's New International Dictionary of the English Language as literally love of place. It is a term used to describe the strong sense of place or identity among certain peoples. Among the geographical ideas that changed world Topophilia: 64 The Human Mosaic CULTURE & HISTORICAL GEOGRAPHY Clues to past cultural influences Architecture – house types & architectural style elements (onion domes in Slavic architecture) City or town layout – i.e. the Romans built towns with the streets laied out in a rectangular grid pattern. Toponyms – a toponym is the name given to a place on the earth. Example: many rivers and older towns in Missouri have French names (often saints), and the first European settlers in Missouri were French Christians (Catholics). 65 The Human Mosaic 66 The Human Mosaic 67 The Human Mosaic 68 ELEMENTS OF SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION Density, concentration, & pattern 69 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural Power interaction and ideology Power— what groups have it Ideology—dominant ideas and beliefs Understanding diversity within a culture 70 GLOBALIZATION A forcer or process that involves the entire world and results in making something worldwide in scope. Global economy Worldwide recession of 2008-2009 Multinational corporations – even operating in China Access to money worldwide via ATM cards Worldwide recognition of products – i.e. Coca Cola logo Entertainment 71 WORLDWIDE MARKETS 72 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural landscape Reflects the most basic strivings of humankind All bear cultural meaning Symbolic and ideological qualities 73 The Human Mosaic 74 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural landscape Settlement forms Land-division patterns Architecture and style 75 The Human Mosaic 76 The Human Mosaic 77 The Human Mosaic THE MAP IS THE MEDIUM OR LANGUAGE OF GEOGRAPHY Created by cartographers Help display information & assist location Grid essential for location Latitude & longitude grid allows absolute location Maps need to be critically “read” 78 The Human Mosaic THE MAP AS A TOOL Can convey much information quickly and effectively Can be used to establish theories Can be used to solve geographic problems May reveal possible interactions and connections Can illustrate patterns, flows, distributions, connections, sequent occupance, etc. 79 THE GEOGRAPHIC GRID (ABSOLUTE) Longitude Measures distance east to west around the globe beginning at the Prime Meridian Prime Meridian International Date Line 0-180 degrees East or West Latitude Location on the Earth’s surface between the equator and either the north or south pole Parallels 0-90 degrees North or South 80 FIVE REQUIREMENTS OF A GOOD MAP Grid – to facilitate locating places 2. Direction arrow or compass rose – to orient the map to the real world 3. Scale – to translate map distances to real-world distances 4. Key or Legend – to interpret symbols used on the map 5. Title – to alert the map reader to the topic or theme of the map Other useful information: Copyright date & Projection used 1. 81 LONGITUDE 82 LATITUDE 83 Latitude and longitude may be combined on a globe or map to create a grid. One specific parallel will only intersect a specific meridian at one place on the earth. Using the two together allows for locating places precisely. A GRID 84 The Human Mosaic ALPHA-NUMERIC GRID – COMMONLY USED IN ATLASES AND ON ROAD MAPS St. Louis is located in section D8 85 SMALLEST SCALE MAP SCALE Scales Of Area Shown – inverse relationship between scale and area shown. Large Scale Maps – show small areas in great detail Small Scale Maps – show large areas with less detail LARGEST SCALE 86 The Human Mosaic MAP PROJECTIONS Scientific (mathematical) method of transferring locations on Earth’s surface to a flat map 4 types of distortion – all maps are distorted in some way or other! Shape Distance Relative size Direction 87 The Human Mosaic TYPES OF MAP PROJECTIONS Cylindrical Conic Planar Equal Area Equidistant Conformal Special cases 88 The Human Mosaic MERCATOR PROJECTION: CONFORMAL – USEFUL FOR NAVIGATION Proportional areas! Distorted areas Equal-area Projection: good for spatial comparisons. 89 90 The Human Mosaic 91 The Human Mosaic 92 The Human Mosaic REMOTE SENSING Acquisition of data about Earth’s surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or from highflying aircraft Remote sensing data plus GIS software = great, accurate maps. 93 The Human Mosaic REMOTE SENSING (GPS) 94 The Human Mosaic GIS 95 The Human Mosaic THEMES IN CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY Conclusion Close relationship of themes Geography bridges social and earth sciences 96