physiology lecture cvs ECG, BLOOD PRESSURE for 1st year

•
ECG
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
•
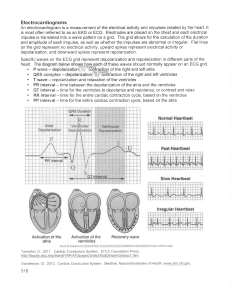
The ECG records the electrical activity of the heart.
•
If an electrode is placed so that wave of depolarization spreads toward the recording electrode, the ECG records a positive (upward) deflection.
•
If wave of depolarization spreads away from recording electrode, a negative (downward) deflection occurs.
• Sinoatrial (SA) node [the pacemaker of heart] is located in right atrium.
• Depolarization spreads from SA node across atria and results in the P wave.
• Three tracts (Internodal fibers) within atria conduct depolarization to Atrioventricular (AV) node.
•
Conduction slows in AV node to allow atria to empty blood into ventricles before ventricular systole.
•
Bundle of His connects AV to bundle branches.
• Purkinje fibers are terminal bundle branches.
•
P wave
•
QRS complex
ECG Complexes
•
T wave
•
P-Q interval
•
Q-T interval
•
S-T segment
• Conducting system
• Pacemaker
- S.A node
- Internodal fibers
- A.V node
- Bundle of his
- Bundle branch
- Purkinje fibers
Electrocardiogram
• P wave
– Depolarization of atria
– Followed by contraction
• QRS complex
– 3 waves (Q, R, & S)
– Depolarization of ventricles
– Followed by contraction
• T wave
– Repolarization of ventricles
• P-Q interval
• Q-T interval
Electrocardiogram
• P-Q interval (or P-R)
• Time atria depolarize
& remain depolarized
• Q-T interval
• Time ventricles depolarize & remain depolarized
• P wave represents depolarization of atria which causes atrial contraction.
• Repolarization of atria not normally detectable on an ECG
• Excitation of bundle of His and bundle branches occur in middle of PR interval
• QRS complex reflects depolarization of ventricles
• T wave reflects repolarization of muscle fibers in ventricles
BLOOD PRESSURE
•
Arterial Blood Pressure (BP)
The lateral pressure / force generated by the pumping action of the heart on the walls of major vessels like aorta during cardiac cycle.
BP is the pressure on arterial blood vessels per unit area.
Pressure inside big arteries (aorta & big vessels).
Measured in (mmHg)
By a device called Sphygmomanometer
Blood pressure has 2 components:
–
Systolic = 110-130 mmHg.
–
Diastolic = 70-90 mmHg.
–
Normal Range considered is 120/80 mmHg.
• KOROTKOFF’S SOUND
While checking the blood pressure, after the placement of diaphragm of stethoscope in the antecubital fossa over the brachial artery, as the pressure is slowly released from the inflated cuff, sounds are heard, that is called korotkoffs sounds. When sounds are heard, that is systolic blood pressure and when sounds disappear that is diastolic blood pressure.
Diastolic pressure is more important, because diastolic period is longer than the systolic period in the cardiac cycle.
FACTORS DETERMINING BLOOD PRESSURE
Blood Pressure = Cardiac Output X Peripheral Resistance
(BP) (CO)
Flow
■ BP depends on:
1. Cardiac output
CO = SV X HR.
2. Peripheral resistance.
3. Blood volume.
(PR)
Diameter of arterioles
FACTORS AFFECTING BLOOD PRESSURE
Sex
… M > F …due to hormones.
Age
… Elderly > children …due to atherosclerosis.
Emotions
… due to secretion of adrenaline/noradrenaline
Exercise … due to
venous return.
Hormones
…
(e.g.Adrenaline,noradrenaline,thyroid)
Gravity …
Lower limbs > upper limbs.
Sleep
… due to
venous return.
Pregnancy
… due to
metabolism.