Cardiovascular system
advertisement

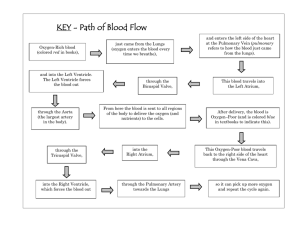
Unit 4: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions of the Heart • Generating blood pressure • Routing blood – Heart separates pulmonary and systemic circulations • Ensuring one-way blood flow – Heart valves ensure one-way flow • Regulating blood supply The double pump The double pump Lungs the right side of the the left side of the system system deals with deals with deoxygenated blood. oxygenated blood. Body cells Location and Orientation within the Thorax • Heart – typically weighs 250–350 grams (healthy heart) • Largest organ of the mediastinum – Located between the lungs – Apex lies to the left of the midline – Base is the broad posterior surface Location and Orientation within the Thorax Located in thoracic cavity in mediastinum The membrane around the heart is PERICARDIUM Pericardium Heart Walls: 3 Distinct Layers 1. Endocardium: the innermost layer of the heart (endothelial cells) 2. Myocardium: the thickest main layer, consists of cardiac muscle. 3. Epicardium: the thin, outer covering around the heart Heart Walls : 3 Distinct Layers Anatomy of the Heart ♥ Heart is enclosed in a membranous sac called pericardium. ♥ Consists of 2 separate pumps that maintain unidirectional flow of blood; the Left & Right heart. ♥ Left heart pumps oxygenated blood Systemic circulation. ♥ Right heart pumps deoxygenated blood Pulmonary circulation. ♥ Each pump contains 2 chambers: an atrium & a ventricle. Heart Chambers Chambers Atria- (2) upper chambers Thin walled Receive blood from veins Send blood to ventricles Ventricles- (2) lower chambers Thick walled Receive blood from artery Pump blood out through arteries Pulmonary valve Left atrium Aortic valve Right atrium Mitral valve Left ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Right ventricle Inferior View of the Heart The coronary circulation consists of the blood vessels that supply blood to (coronary artery), and remove blood from the heart muscle (coronary sinus) itself. ♥ 2 Atria: ■ ■ Chambers of the Heart ♥ 2 Ventricles: Thin-walled chambers. Receive blood returning to heart. Thicker, muscular walls. ■ Pump blood from heart. ■ Each has same capacity & pumps same volume of blood in a given period of time. ■ Ventricles • Both ventricles (Right & left) – thick walled • Left ventricle – three times thicker than right – Left ventricle has to push the blood to all the body parts while RV has to push the blood to closely lying lungs only Valves of the Heart ♥ 2 Atrioventricular (AV) ♥ 2 Semilunar valves : ■ One way valves. ■ At origin of pulmonary artery ■ One way valves. & aorta. ■ Allow blood to flow from ■ Pulmonary (Right) & Aortic atria into ventricles. (Left). ■ Tricuspid (Right) & Mitral (Left). ■ Open during ventricular contraction. valves: Pathway of Blood Through the Heart • Oxygen-poor blood draining from the body through veins into the superior and inferior vena cava flows to the right atrium, through the tricuspid valve, and into the right ventricle. • As the right ventricle contracts, oxygen-poor blood passes through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary arteries and on to the lungs to receive oxygen. Pathway of Blood Through the Heart • Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs enters the heart through the pulmonary veins, passing into the left atrium. • Then through the mitral valve to the left ventricle. Contraction of the left ventricle forces blood through the aortic valve into the aorta. • Various arteries branch off from the aorta to supply blood to all parts of the body. Blood Flow Through the Heart Pulmonary and Systemic Circulations • Pulmonary circulation: – Path of blood from right ventricle through the lungs and back to the heart. • Systemic circulation: – Oxygen-rich blood pumped to all organ systems to supply nutrients. • Rate of blood flow through systemic circulation = flow rate through pulmonary circulation. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits ()الدائرة Systemic circuit • Longer than pulmonary circuit • Offers greater resistance to blood flow Conducting System ()إجراء النظام • Cardiac muscle tissue has intrinsic ability to – Generate and conduct impulses ()نبضات – Signal these cells to contract rhythmically • Conducting system – A series of specialized cardiac muscle cells – Sinoatrial (SA) node sets the inherent rate of contraction Physiology of Cardiac Muscle The heart is composed of 2 major types of cardiac Cells: 1: Contractile cells. 2: Autorhythmic (or automatic) cells. Contractile cells: Contract when stimulated, in same way as skeletal muscle except for longer duration. Heart : Conducting Tissues • • • • Sinoatrial Node (SA node) Located high on the right atrium. Pacemaker of the heart. Causes the wave of contractions in the atria. – Sending blood into the ventricles Cardiac Cycle • Heart is two pumps that work together, right and left half • Repetitive contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of heart chambers • Blood moves through circulatory system from areas of higher to lower pressure. – Contraction of heart produces the pressure Heartbeat • 70 – 80 beats per minute at rest – Systole – contraction of a heart chamber – Diastole – expansion/relaxation of a heart chamber Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) • Electrocardiogram: – Measure of the electrical activity of the heart per unit time. • Potential differences generated by heart are conducted to body surface where they can be recorded on electrodes on the skin. • Does NOT measure the flow of blood through the heart. Cardiac Output (CO) • Is volume of blood pumped/min by each ventricle • Heart Rate (HR) = 70 beats/min • Stroke volume (SV) = blood pumped/beat by each ventricle – Average is 70-80 ml/beat • CO = SV x HR • Total blood volume is about 5.5L